


The program can be used to control the quality of the data obtained, sequencing environmental samples by means of a technique known as metagenomics, which shows how complete the sequences mapped are, and whether they are contaminated by genetic material from other microorganisms.
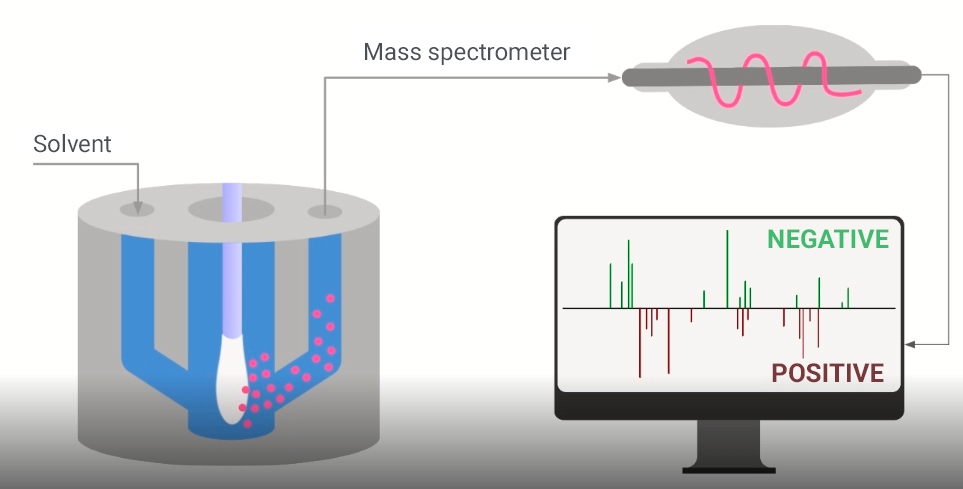
A system developed by Brazilian researchers detects the presence of the virus in a nasopharyngeal swab in less than a minute.
Scientists affiliated with institutions in Brazil and elsewhere presented research findings that highlighted the importance of data sharing in the fight against COVID-19.
Brazilian researchers followed 38 COVID-19 patients and found that it took a month on average for the diagnostic test to become negative. In three patients, the virus remained detectable for more than 70 days.

The study involving 376 patients was conducted in São Paulo and could contribute to the formulation of public policy to improve accident prevention.
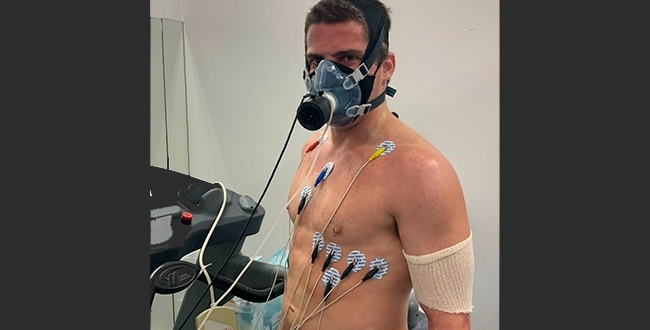
The results of a study by researchers at the University of São Paulo could serve as a basis for new recommendations on health and fitness during the COVID-19 pandemic.

Test developed by startup BiDiagnostics with FAPESP’s support promises faster and more accurate diagnosis of deep mycosis that causes sores and potentially fatal organ damage in domestic cats.
Using two low-cost techniques, researchers in Brazil differentiate patients with the disease from healthy subjects. Next steps include refining the approach to diagnose the disease in its early stages.

Experiments conducted at Butantan Institute (Brazil) show how the primate’s immune system prevents multiplication of the parasite in the organism. The discovery will facilitate the identification of targets for novel therapies and vaccines.
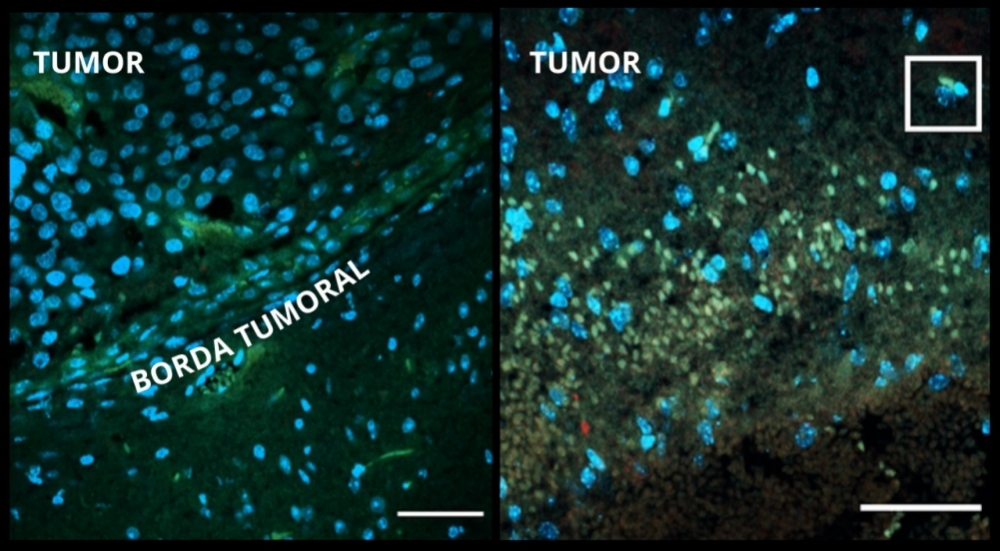
Experiments conducted at a FAPESP-supported research center showed that besides directly combating tumor cells, zika alerted the immune system to the presence of cancer. The study opens up prospects for the use of virotherapy for central nervous system tumors.
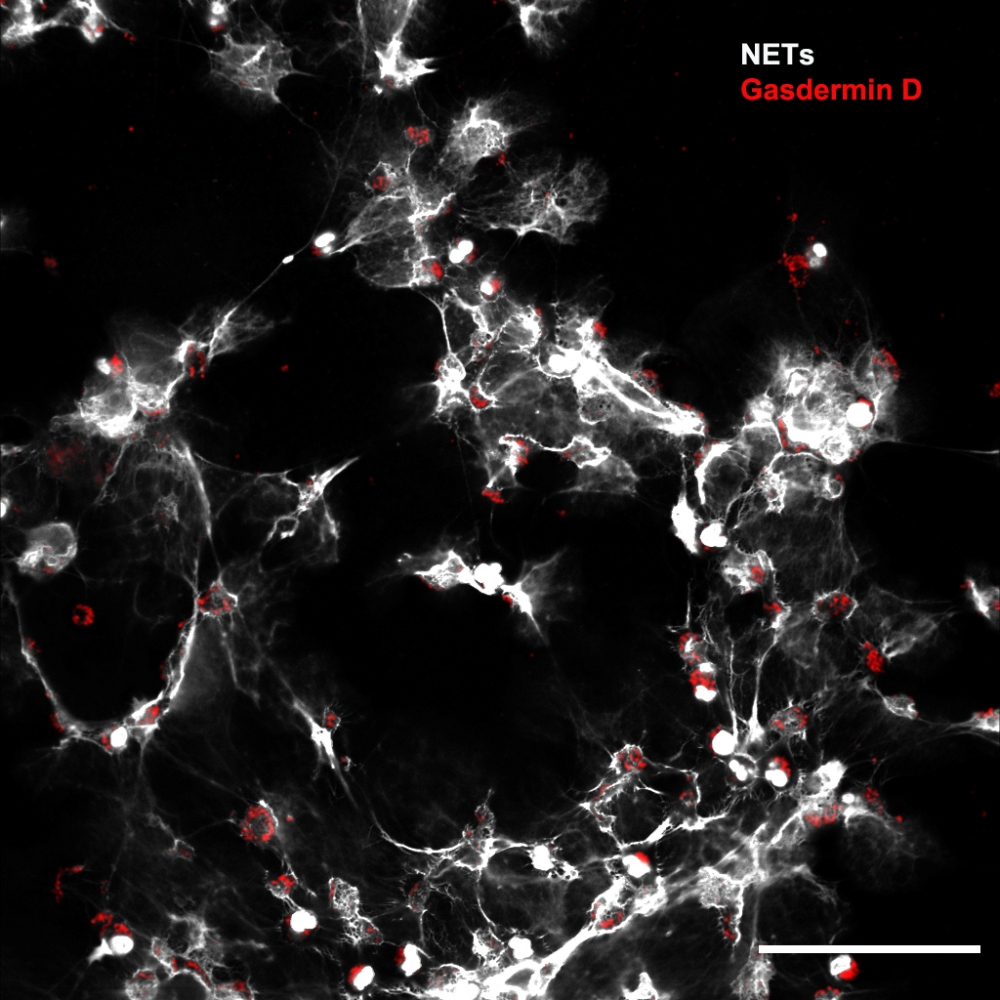
Researchers affiliated with a FAPESP-funded research center showed that a protein called gasdermin D is involved in septic patients’ organ lesions. The study also proved that a drug originally indicated to treat alcohol dependence can inhibit the molecule’s action and prevent complications.

FAPESP has funded development of the solution, which can in future be used to bioprint human organs using cells from the recipient.

Participants in an online seminar presented the results of research projects approved under a fast-track call issued by FAPESP at the start of the pandemic. The projects led to important discoveries on the mechanisms of the disease, development of vaccine and diagnostic technologies, and a deeper understanding of the role of governments in public health emergencies.
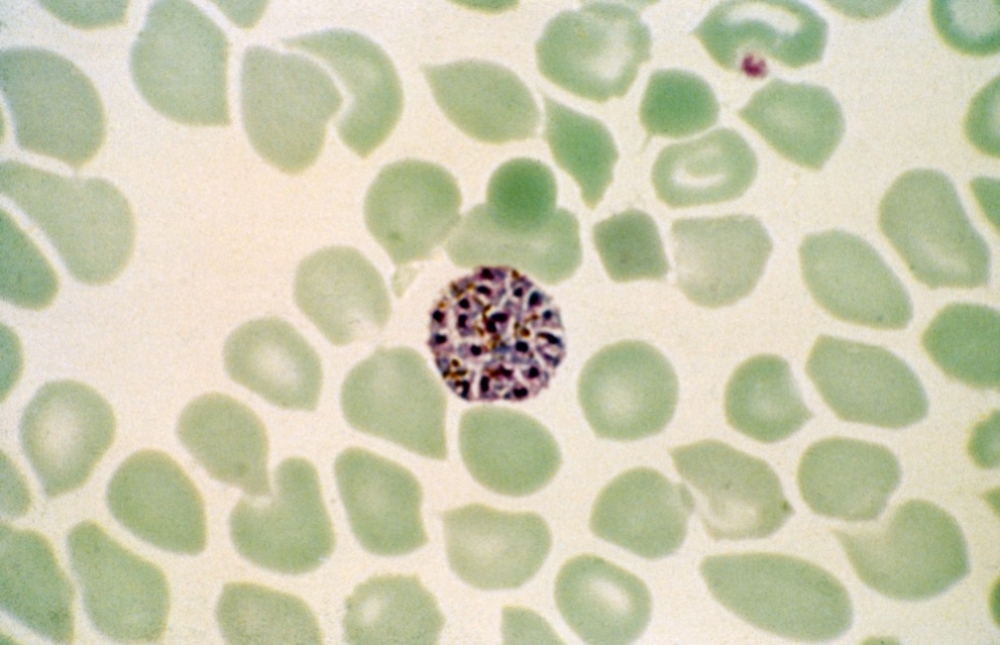
A research group led by scientists at the University of Campinas in Brazil found total parasite biomass to be a better predictor of complications from malaria than parasite burden in the bloodstream. The discovery can help develop treatment and a Plasmodium vivax vaccine.
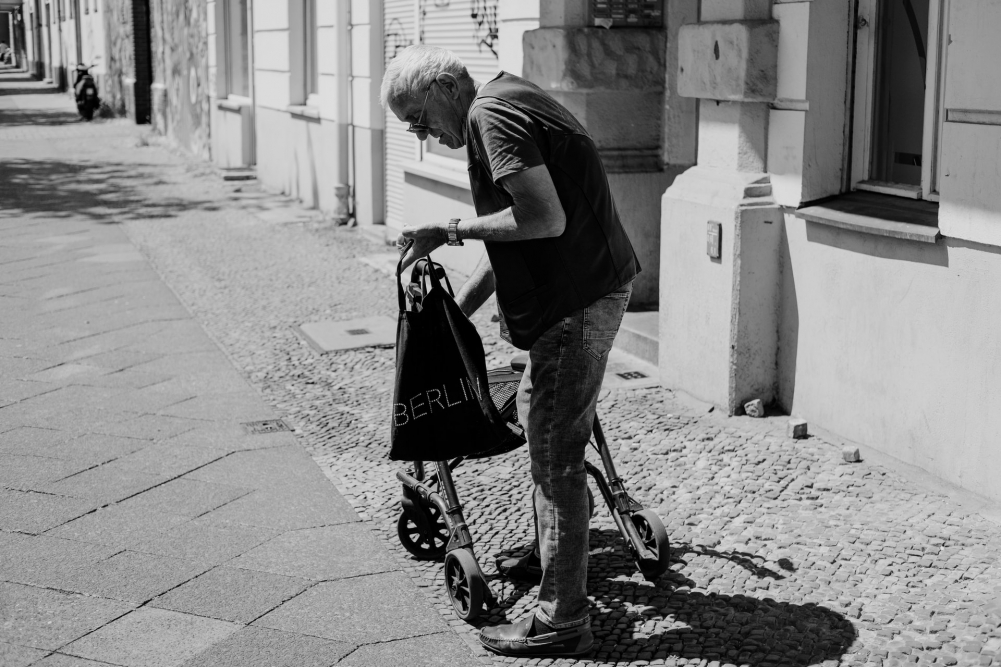

The finding is reported in an article in the Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle by researchers in Brazil and the UK, who analyzed data for more than 3,000 people aged 60 and over.
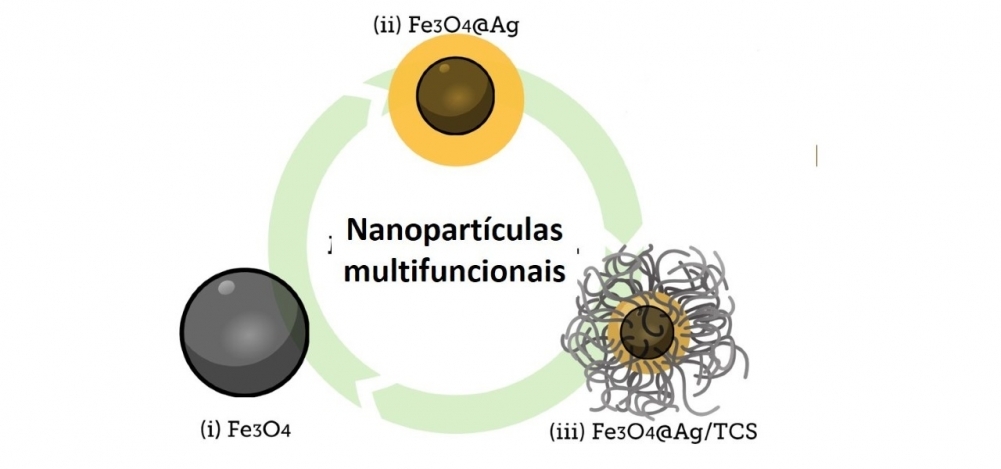
The proposition is to use nanoparticles that can be guided by applying an external magnetic field to attack solid tumors resistant to conventional treatment.
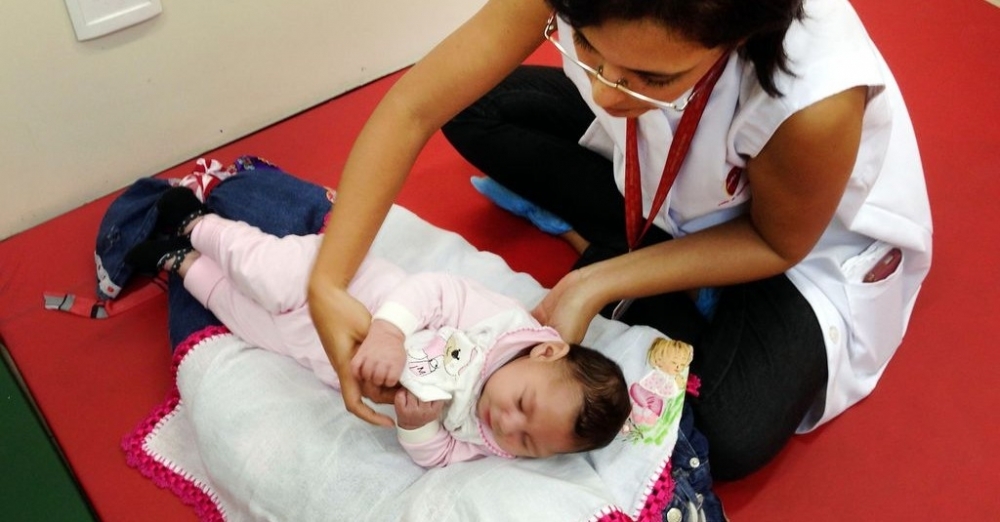
Assessment of two- and three-year-olds can help health professionals design personalized treatment. The study involved scientists in Brazil and the United States, and is published in PLOS ONE.
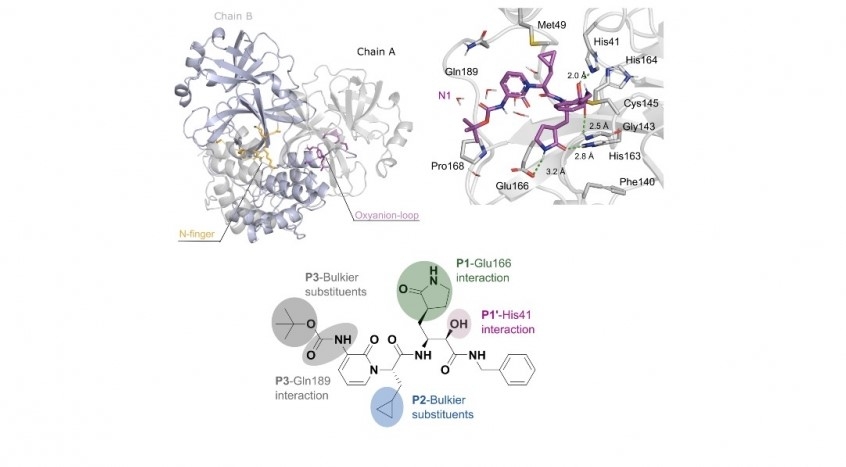
The technique was used by researchers affiliated with institutions in Brazil, Germany and Finland to study the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), a key driver of the virus’s reproductive cycle.
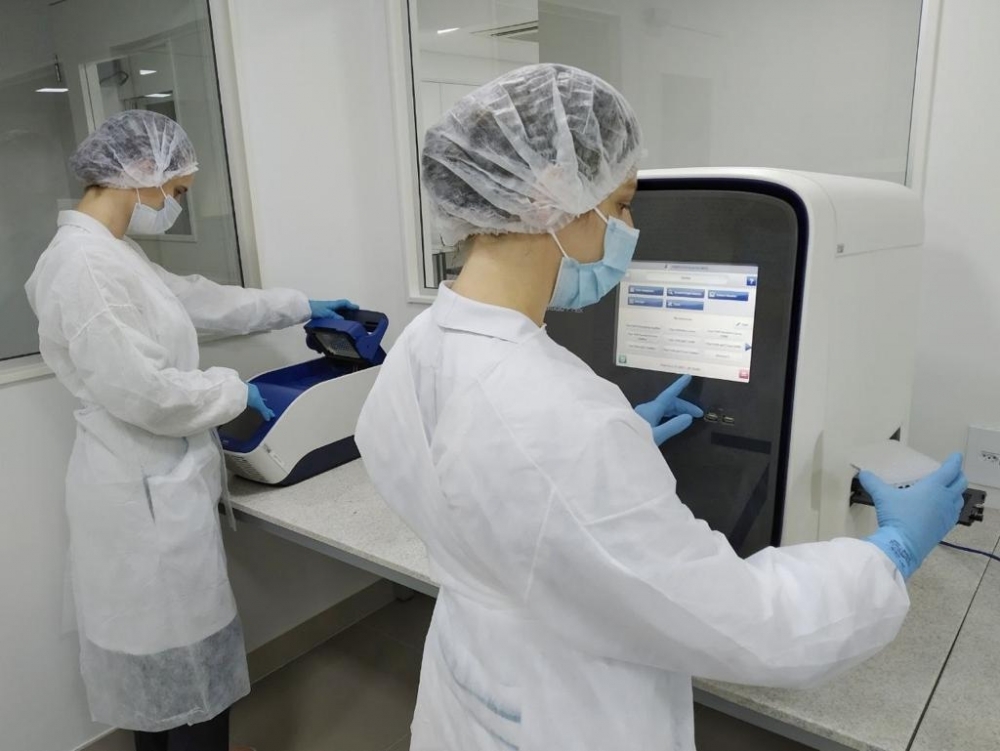

The molecular test mir-THYpe uses biomarkers to detect whether a thyroid nodule classified as indeterminate is cancerous.
In a study conducted at a FAPESP-funded research center, a bile acid derivative known by the acronym TUDCA reduced food intake and increased energy expenditure in mice, improving quality of life. The results are promising for humans.
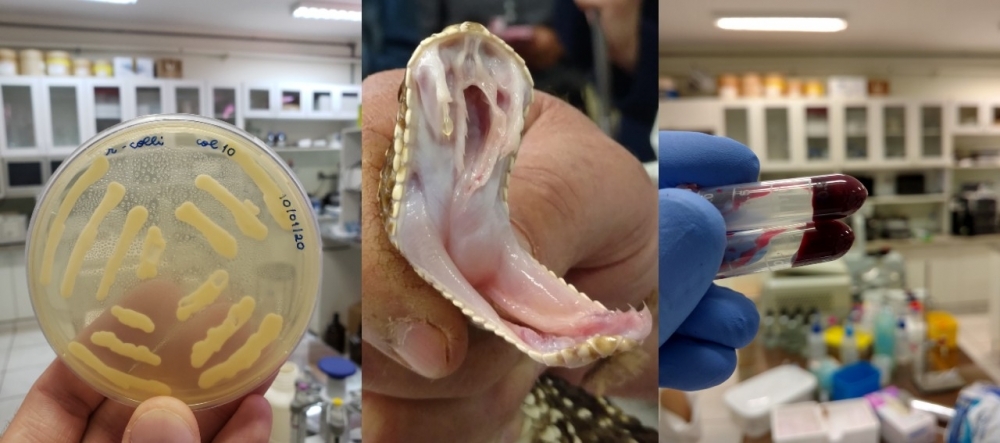
Procedure tested by researchers in Brazil and Belgium made the molecule more stable in the organism. Potential applications include anti-coagulants and wound dressings.
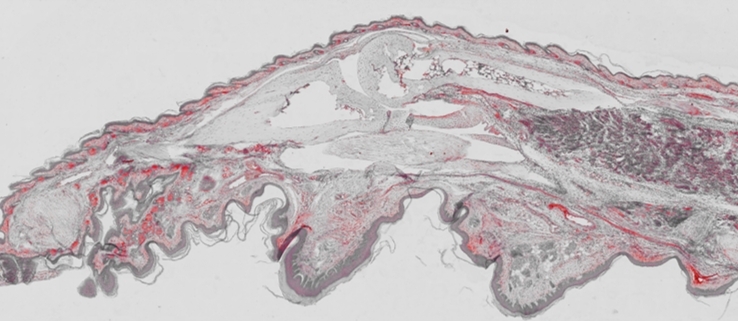
Scientists at the University of São Paulo confirmed the finding in experiments with mice and blood serum from patients.

The point was stressed by participants in the 6th FAPESP 60 Years Conference, featuring experts from Brazil, the UK and the US who discussed the search for drugs to treat diseases that affect some 2 billion people worldwide.
Speakers of an online seminar organized by FAPESP detailed methods used to identify and remove barriers that delay or interrupt effective interventions.
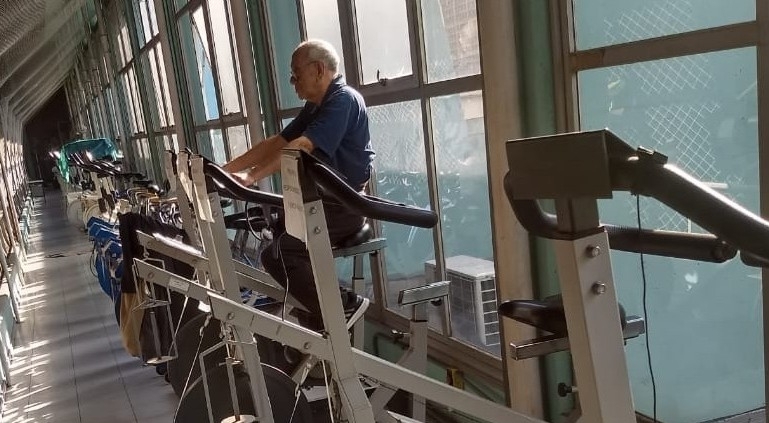

Scientists at the University of São Paulo compared the effects of morning and evening aerobic exercise on middle-aged men. The results suggest that training between 6 p.m. and 9 p.m. stimulates mechanisms that keep blood pressure fine-tuned.