

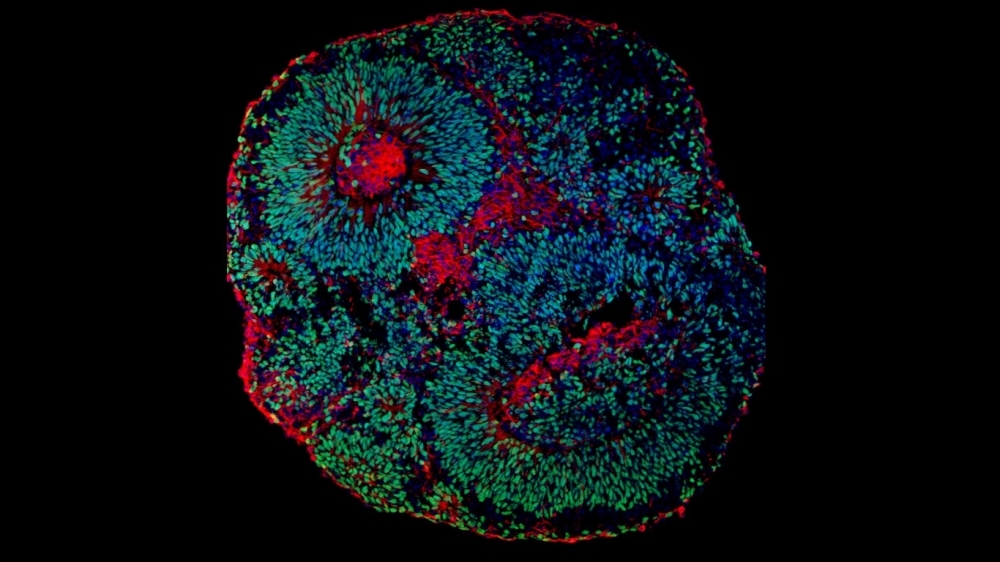
Researchers at the State University of Campinas and the University of California San Diego have discovered the mechanism that causes this rare but severe autism spectrum disorder. They reversed progression of the syndrome in laboratory models, opening up new possibilities for treatment using drugs and gene therapy.
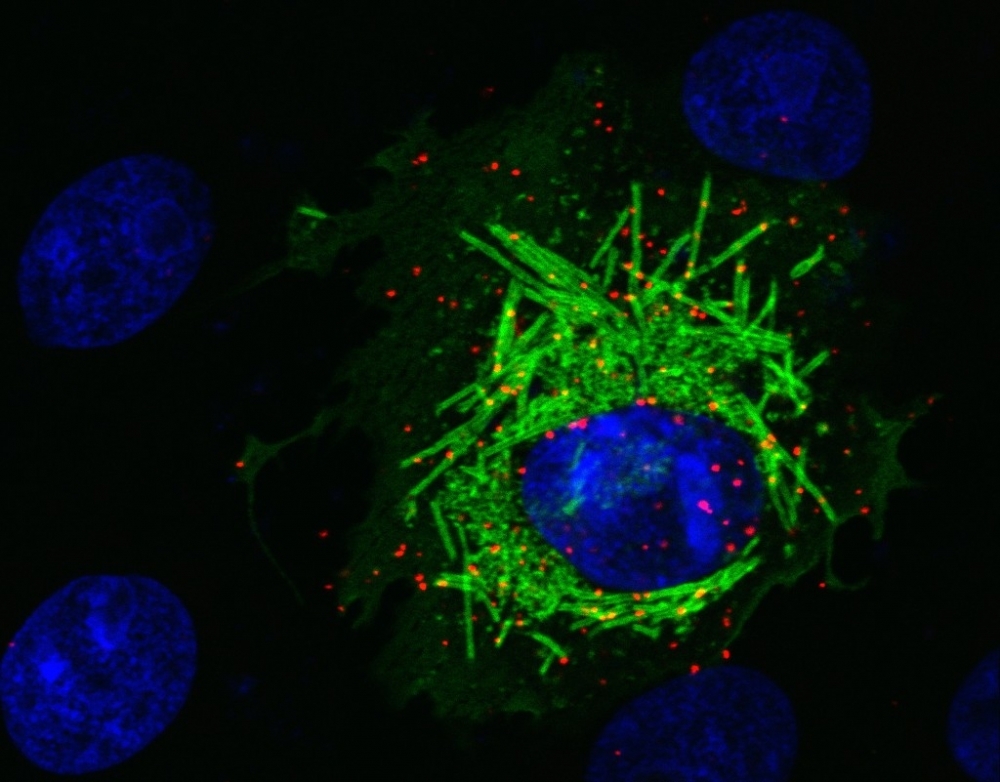
Brazilian researchers have discovered that PCNA, a protein present in the nuclei of human cells, interacts with the SARS-CoV-2 membrane matrix protein M. In laboratory tests, inhibition of this mechanism using a drug reduced viral replication by 15%-20%.
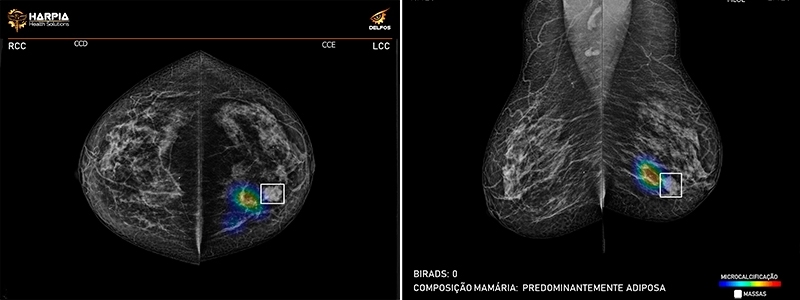
A startup supported by FAPESP has developed a technology based on artificial intelligence that can reduce the time to produce a diagnosis by 40%.

Several substances that killed antibiotic-resistant bacteria were found by Brazilian researchers in a marine sponge native to Fernando de Noronha, an archipelago off the coast of the Northeast.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed 43 scientific articles with data for some 11,500 athletes. The findings point to the need for carefully personalized assessment of athletes and sports players before a resumption of training is allowed, they warn.
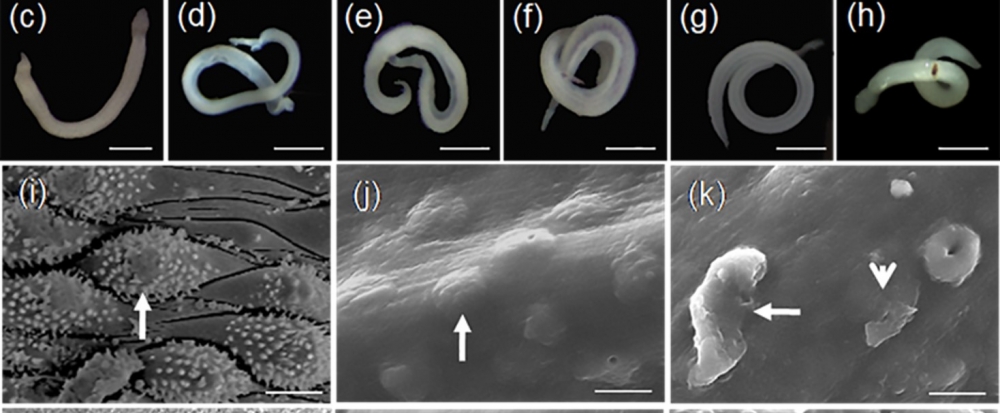
Advanced drug discovery methods have led to advances in the search for treatments for some neglected tropical diseases, including leishmaniasis and Chagas, but research on schistosomiasis and other diseases caused by worms remains at an early stage, according to an article in Drug Discovery Today by Brazilian researchers.
Research that can increase Brazil’s access to CAR T-cell therapy, an increasingly important strategy for treating cancer, is under way at the University of São Paulo’s Center for Cell-Based Therapy (CTC) in Ribeirão Preto, and the Butantan Institute.

In mice fed a high-fat diet, the molecule mitigated weight gain while reducing insulin resistance and liver fattiness. An article describing the results of the study by researchers at the University of São Paulo and collaborators is published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences.

Brazilian researchers surveyed 900 volunteers via an online platform for five months. Most reported feeling that time passed more slowly during home confinement in the early months of the pandemic, associating this perception with feelings of loneliness and a lack of positive experiences in the period.
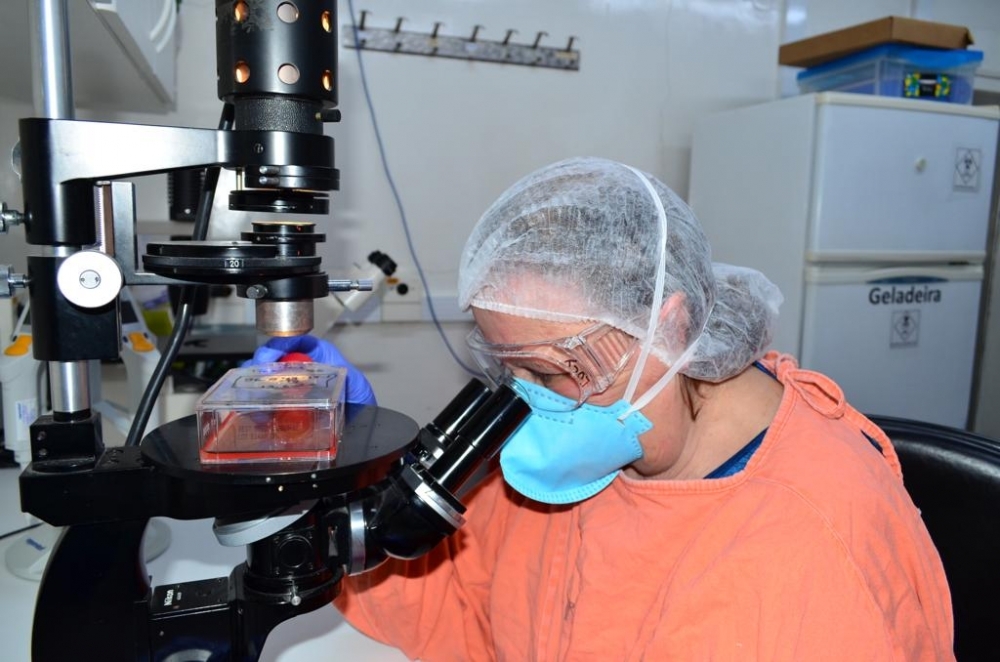

The material can be used for diagnostic testing, research on the evolution of the monkeypox virus, and development of novel treatments and vaccines.
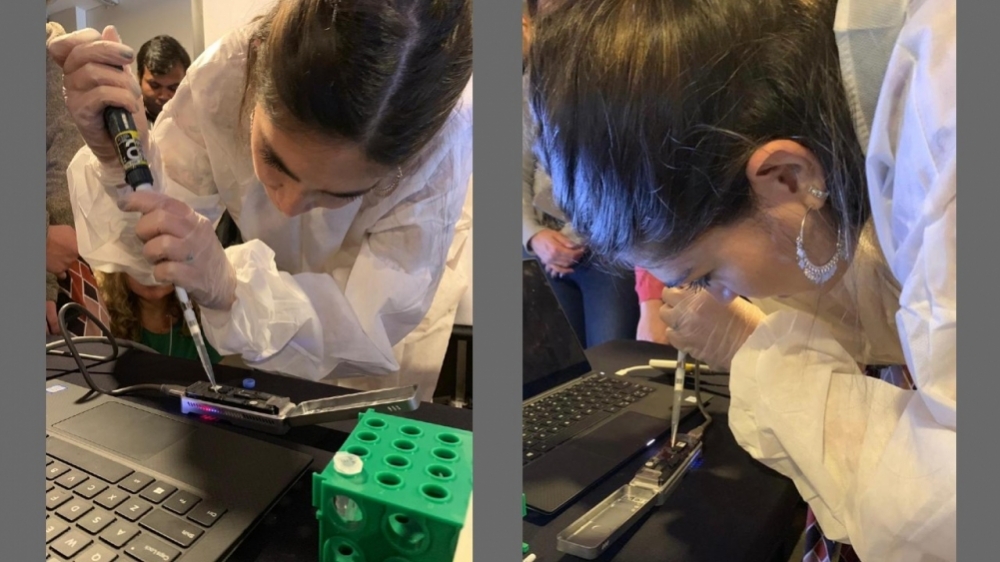

A protocol developed by the Brazil-UK Center for Arbovirus Discovery, Diagnosis, Genomics and Epidemiology (CADDE) was used to analyze a sample from the first Brazilian patient with a confirmed diagnosis. The technology can also be used to detect unknown emerging viruses.
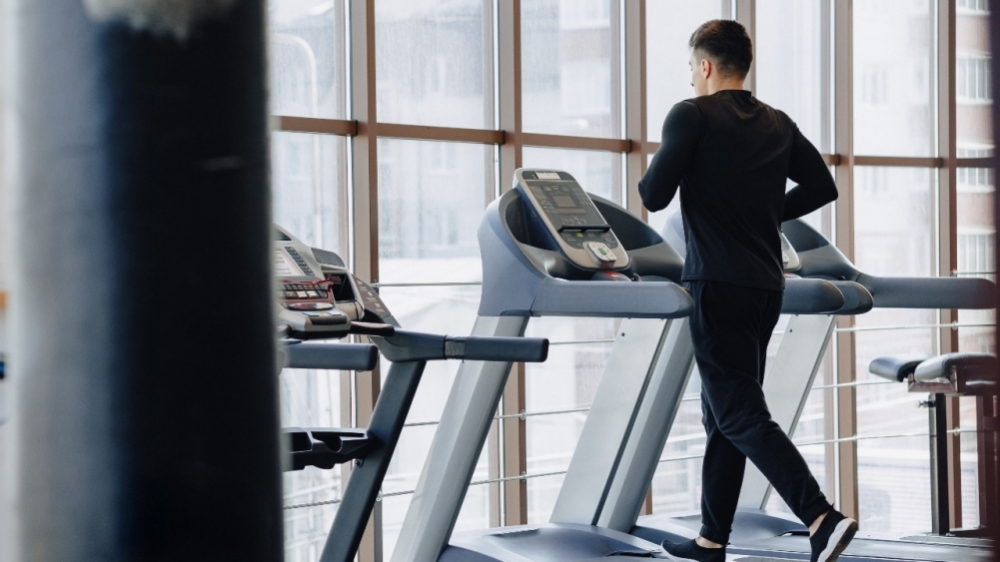

The finding comes from a clinical trial by researchers at the University of São Paulo who recruited 32 male volunteers and have now published the results in Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.
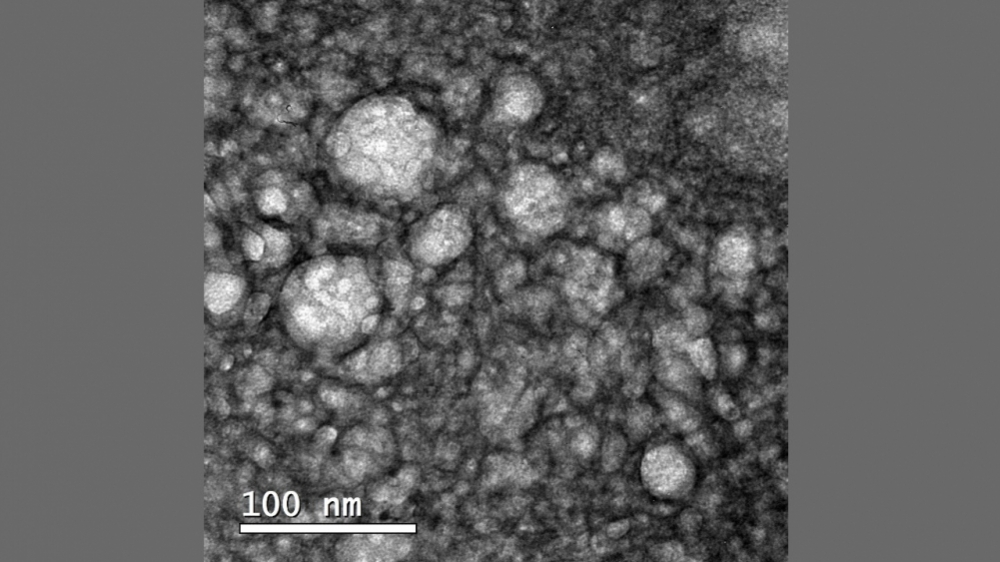
The approach combined nanotechnology, chemotherapy and monoclonal antibodies. It produced promising in vitro and in vivo results against glioblastoma multiforme.
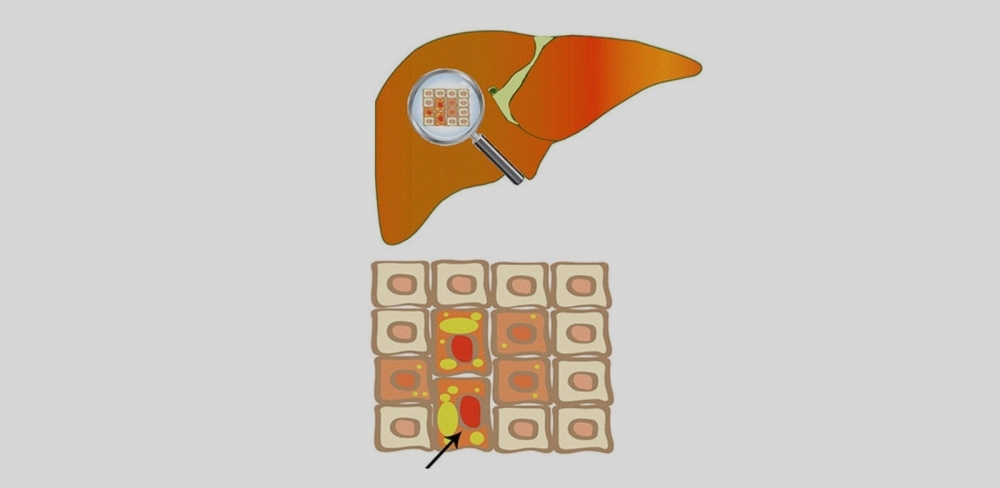
Research reveals the mechanisms whereby methionine-deficient and methionine-supplemented diets can alter gene expression and damage liver cells.
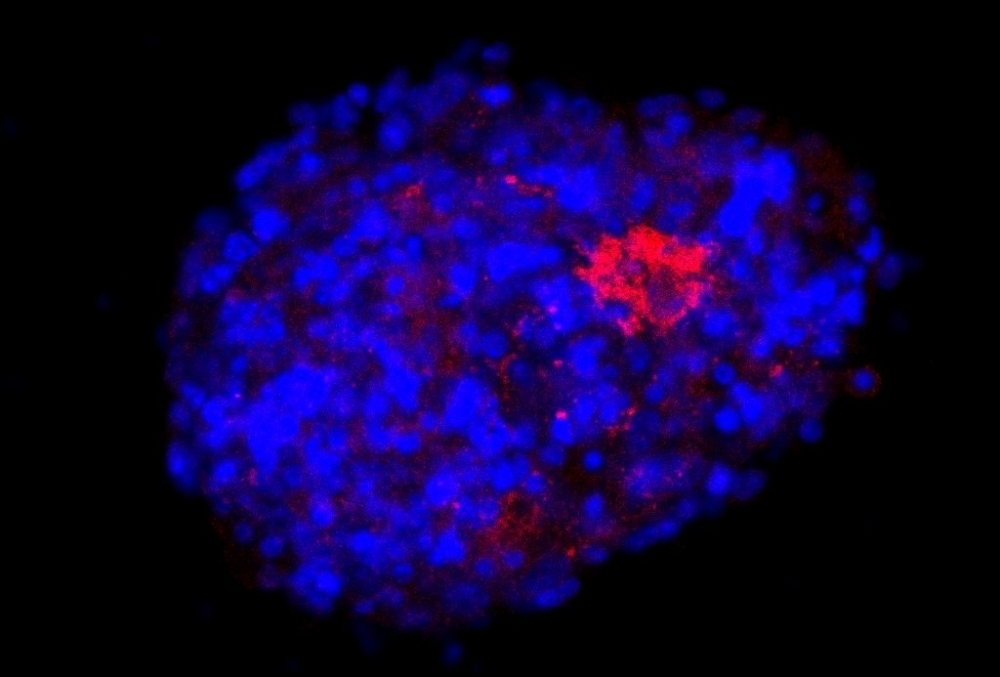
A bioink developed from mouse cells can be used in a 3D printer to create a model that more closely resembles the brain than conventional ones. Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo also obtained an adapted version of SARS-CoV-2 capable of infecting neural cells from mice.
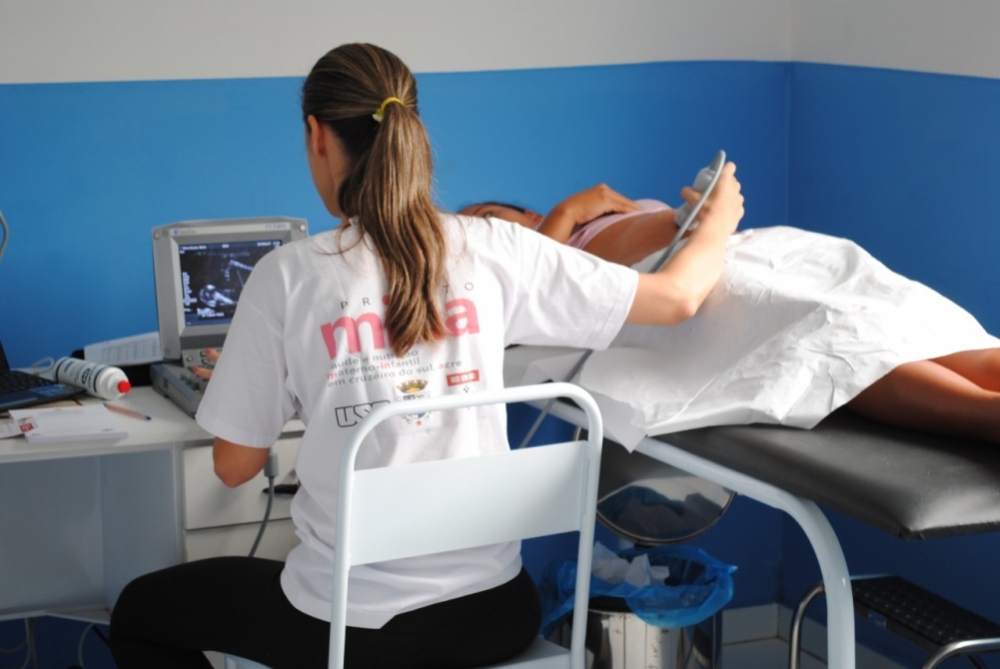
Researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed data for a group of pregnant women in western Amazonia. The analysis pointed to a correlation between at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week and lower birth weight, with less risk of childhood obesity and diabetes.

The results of a clinical trial are reported by Brazilian researchers in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. According to the authors, if corroborated by more robust research, the findings indicate that the method can be used in emergency treatment of hypertensive crisis patients.

Mathematic simulations showed that well-executed non-pharmacological measures reduce the spread of COVID-19 even in places with low vaccination coverage. According to the authors, however, up to 80% of the population could catch the disease if preventive protocols are abandoned.
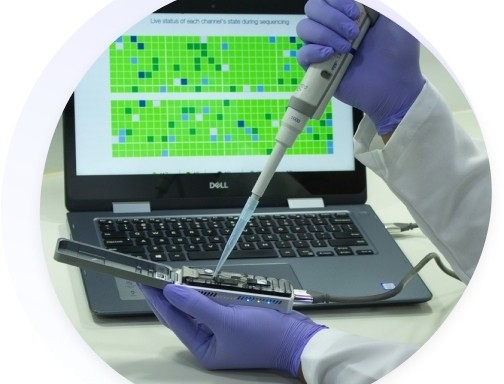
The open-access platform developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo offers access to strategic information on microorganisms classified by WHO as a “critical priority”. The aim is to contribute to the monitoring and control of bacteria that pose a great threat to human and animal health.
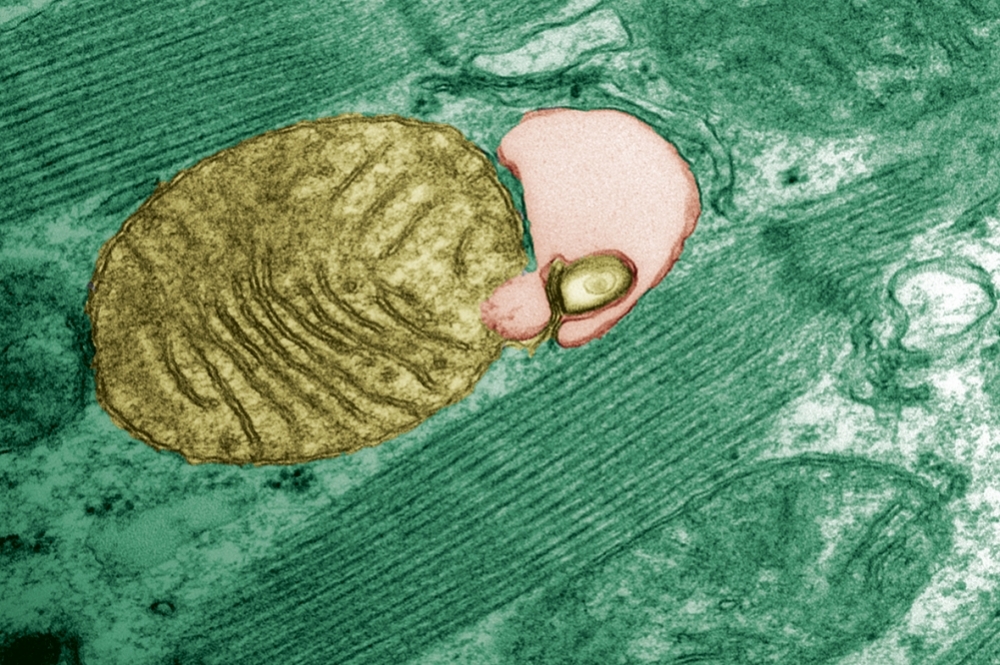
With aging, mutant genetic material tends to build up in the organelles responsible for producing energy, and this can lead to disease. Brazilian researchers have discovered that a cell cleansing mechanism known as autophagy can modulate this phenomenon.
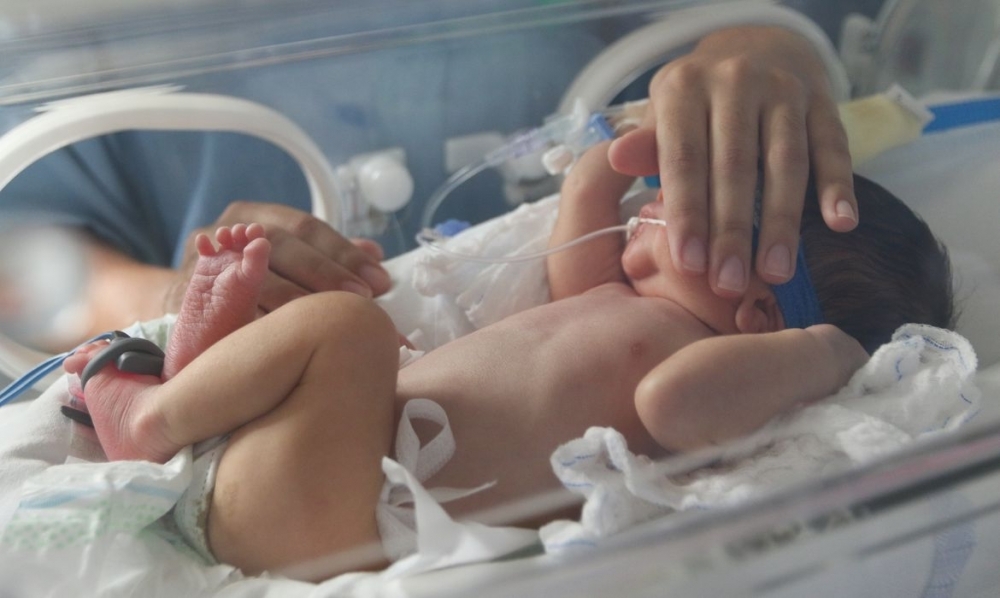
Experiments involving isolated and cultured cells as well as animals and babies suggest that short-chain fatty acid acetate produced in the gut can minimize the effects of infection by respiratory syncytial virus.
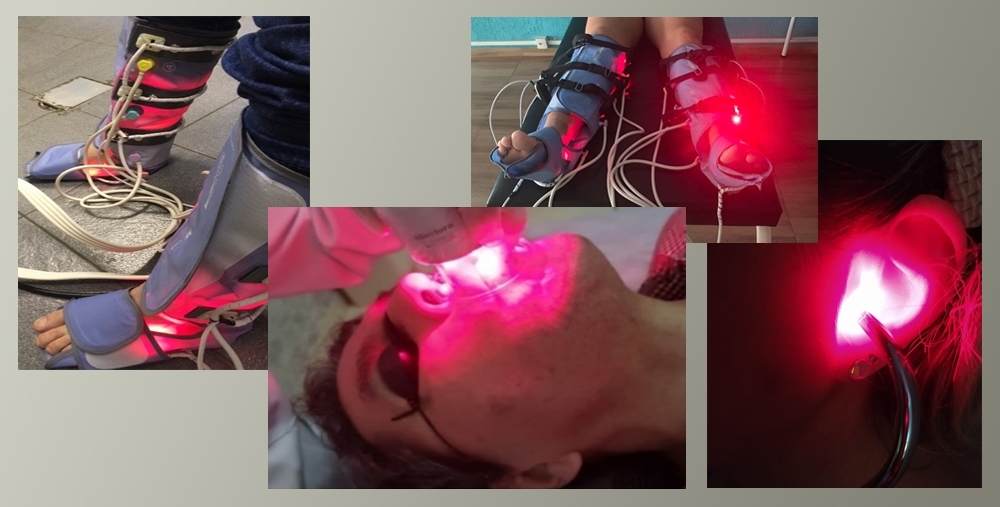
Devices that combine laser irradiation, ultrasound and suction help regenerate tissue and treat muscle, joint, skin, neurological and lung damage. Protocols created via business-university partnerships are being tested and can be applied by treatment centers across Brazil.
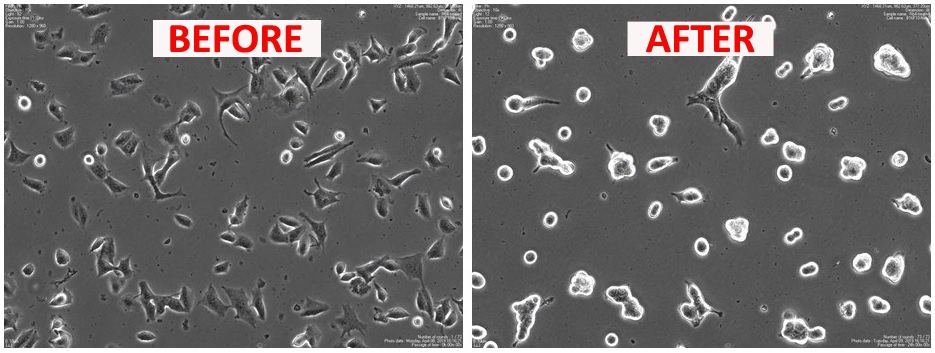
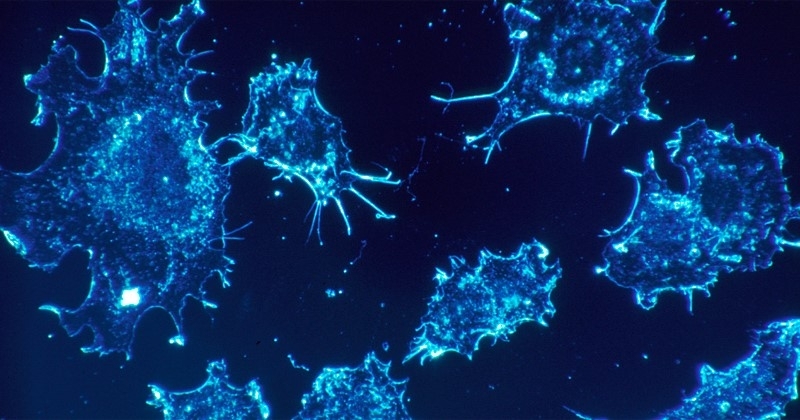
An article in Scientific Reports shows that experimental treatment with a protein-derived molecule reduced tumor growth and metastasis, increasing the survival of mice by 25%.
The discovery is reported by researchers at Harvard University and the University of São Paulo in Nature Neuroscience, and could serve as a basis for the development of treatments for different diseases.
Scientists at a consortium of Brazilian universities show how the enzyme storm triggered by SARS-CoV-2 damages the lungs and may cause lasting complications.