


In laboratory mice, the hormone easily bought from pharmacies and widely consumed as a supplement aggravated Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, depending on the animal’s gut microbiota profile, according to a study by researchers at the University of São Paulo.
Researchers show the importance of political skill on the part of federal research institution Fiocruz and regulatory agency ANVISA in the process that resulted in the signature of an agreement with pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca in mid-pandemic.
In a study with 116 participants, researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo evaluated the genetic material contained in extracellular vesicles possibly secreted by brain tissue. The analysis pointed to patterns of microRNA expression associated with depression, anxiety and ADHD.

Researchers in Brazil and Portugal have been following patients under 40 who had the disease before being vaccinated. Alterations found in immune cells up to 180 days after infection resemble those found in patients with chronic diseases.

This was the main finding of a study involving rats conducted by Brazilian researchers. Mortality was 29% higher for fetuses exposed to a synthetic compound that acts on the brain in a similar manner to natural cannabinoids. Respiratory control and CO2 sensitivity, which influence sudden infant death syndrome, were also altered.

With the support of FAPESP’s Science for Development Center Program, the unit hosted by São Paulo State University will produce pilot batches of candidate biopharmaceuticals and vaccines for clinical trials. The aim is to help researchers and startups survive the “valley of death” in clinical research.

Researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed placental samples from women with and without obesity who contracted the infection while pregnant. The results show that maternal overweight can compromise the placenta’s immune response and impair fetal protection.

Working at the University of São Paulo in Brazil, the researchers used epigenetics to study the mechanism, which could be associated with pathologies such as Alzheimer’s. The discovery expands scientists’ knowledge of the central nervous system.
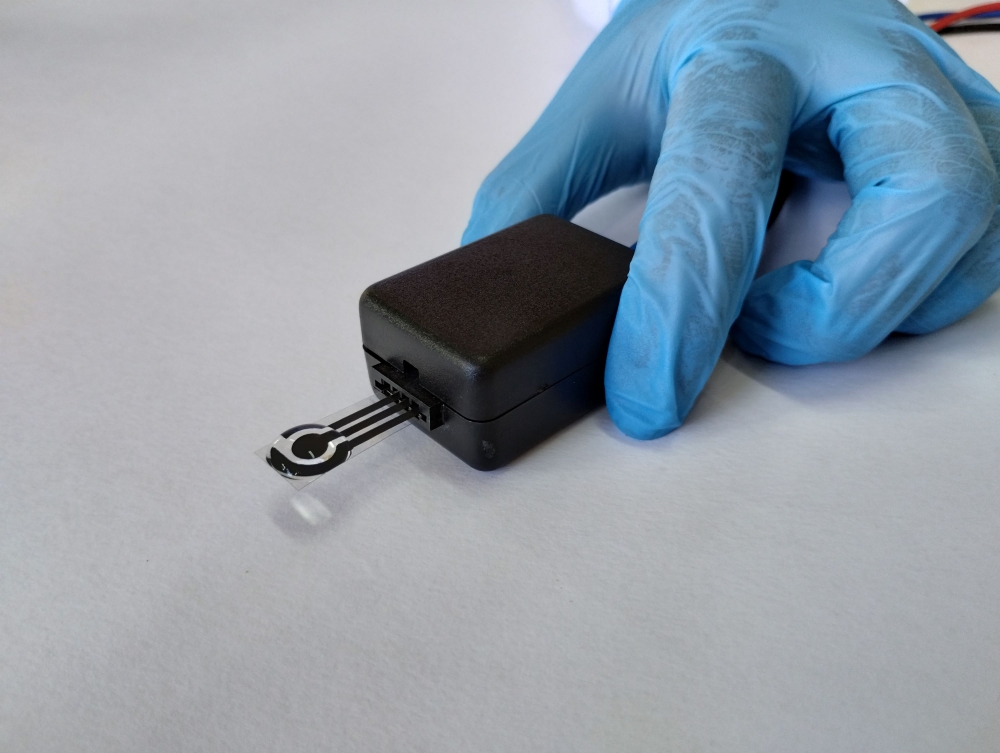

Developed at the University of São Paulo, the device permits corrections to the dosage of the analgesic to improve its efficacy according to the patient’s profile and avoid toxic side effects or overdose.
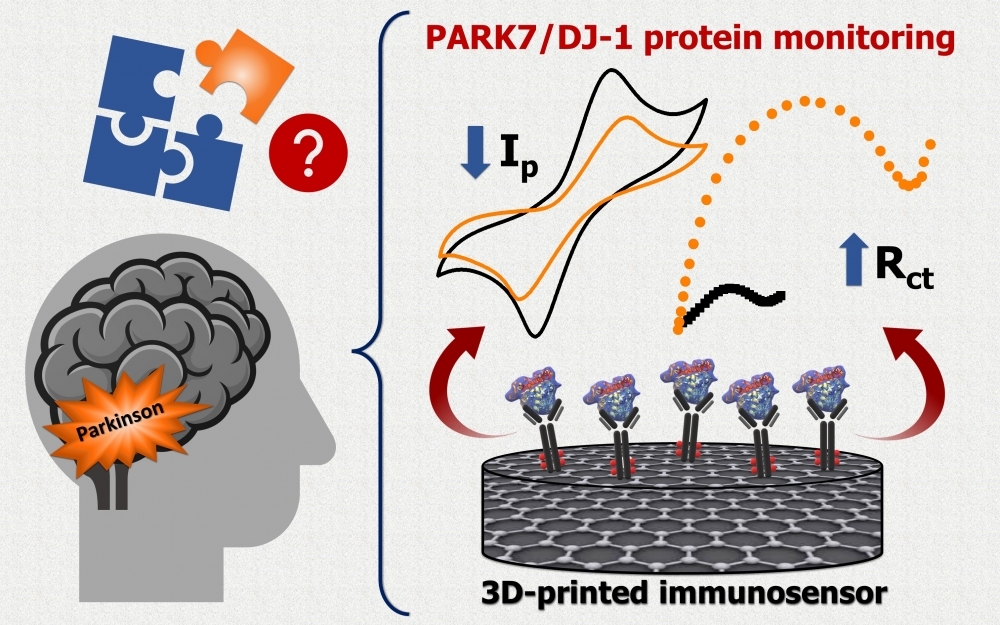
The device, produced by ordinary 3D printing and capable of being miniaturized, detects levels of the protein PARK7/DJ-1, which is associated with the disease. The study used samples of blood serum and cerebrospinal fluid.

A study by a group at the University of São Paulo reported in a scientific journal involved the construction of a database and models. Preliminary results are described in the article.
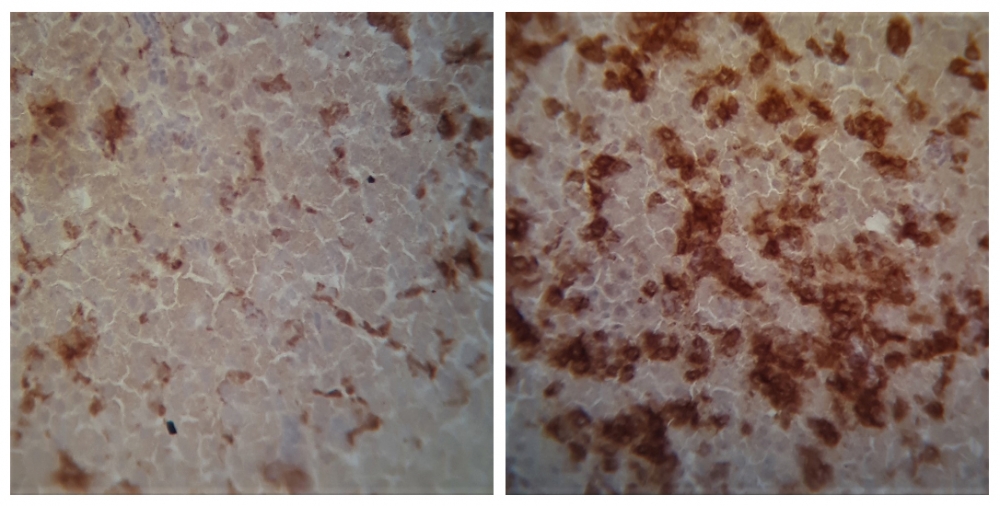
Deletion of two genes, which in mice attenuated the action of the bacteria, made the immune response more exacerbated in broiler chicks. The findings reinforce the need for animal health and hygiene measures throughout the poultry production chain.

The finding is from a longitudinal study conducted in Brazil. Analyzing data for high school students aged 13-18, it concluded that the problem affects girls more than boys and is associated with physical inactivity and low academic achievement.

The center will be hosted by the Federal University of Ceará and will focus on the use of the Internet of Things, big data, digital transformation and cutting-edge technology in prevention, diagnosis and low-cost therapies.

Addition of rosmarinic acid at a mere 0.1% reduced the amount of sunscreen needed to protect the skin, increased the sun protection factor by more than 41% and combined photoprotection with antioxidant activity. The innovation would reduce the volume of chemical substances discharged into the environment.

This conclusion, presented by Brazilian researchers in the journal Scientific Reports, is based on a systematic review of clinical trials held to investigate the effect of strength training on blood pressure in hypertensive patients. All age groups benefited, but the positive effects were most evident in patients aged 50 or less.

With the support of FAPESP and Banco Industrial do Brasil, the National Center for Research and Innovation in Mental Health (CISM) was launched at an event held on March 15.

Experiments involving nematode worms conducted by researchers at the University of São Paulo showed that the benefits of physical activity to muscles are directly linked to processes occurring in mitochondria, the organelles that make energy for cells. Their findings offer possible routes for drug development.
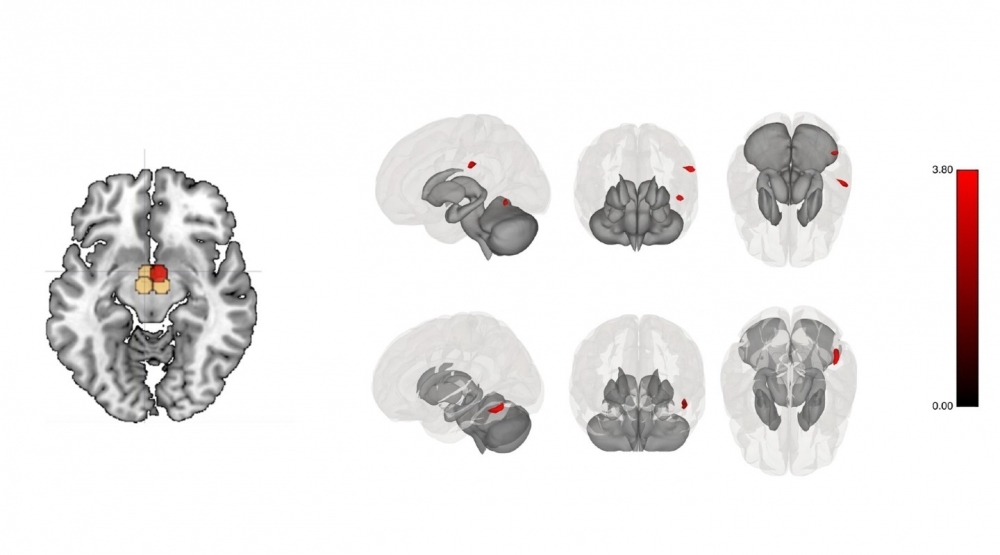
In a study conducted in São Paulo, Brazil, exercise training increased connectivity between the hypothalamus and sensory regions, accelerating satiety, for example.

Analysis conducted in Spain used a methodology developed by researchers at the State University of Campinas to detect many toxins simultaneously.
A study in rats analyzed neural rhythm in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus with machine learning techniques. The results could guide future personalized treatments for psychiatric disorders.
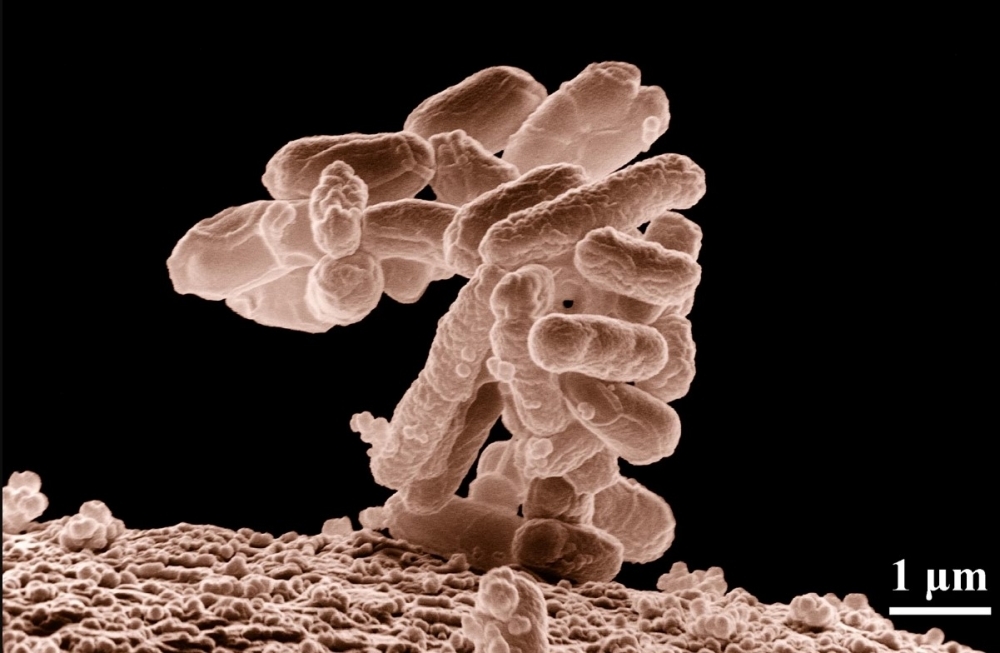
The aim of the study was to analyze the virulence and antimicrobial resistance profile of the main agent of urinary tract infections.

Fatigue, breathlessness and other symptoms that may persist months after recovery from the infection may both favor sedentarism and be more frequent as a result of an inactive lifestyle, according to findings described by researchers at the University of São Paulo in an article in Scientific Reports.

Significant changes in gut microbiota were observed in 42 men with coronary artery disease after they took 250 ml of red wine per day for five days a week over a period of three weeks.

The study involved 28 volunteers diagnosed with sarcopenia, which is characterized by loss of muscle mass and strength.