


Researchers followed 286 volunteers during a wave of COVID-19 in the Northeast region of Brazil in the first quarter of 2022. The number of cases fell among those who had been vaccinated with three doses, and they had more neutralizing antibodies than subjects who had not completed the vaccination scheme even when previously infected.

An article by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo argues that the analysis should consider not just the quantity but also the size and shape of plastic particles in water samples, as these variables influence the impact of plastic pollution on ecosystems.

The novel material was synthesized at the Center for Development of Functional Materials. The aim of the study was to combat the contamination caused by inappropriate disposal of pesticides and pharmaceuticals.
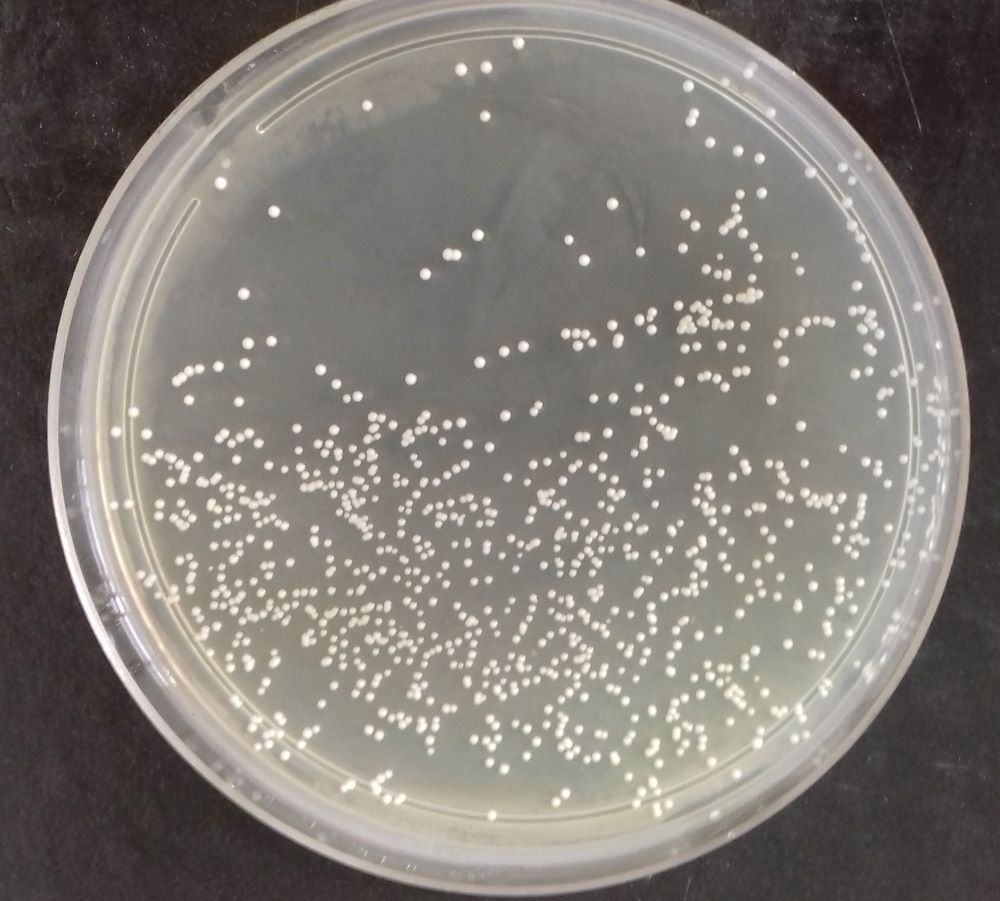
Brazilian researchers conducted preclinical trials involving mice to find the ideal dose and administration regime. The results suggest high daily doses of the probiotic are needed to obtain the benefit.
In a Brazilian study involving 800 children, researchers found that extended breastfeeding protects the baby’s teeth as long as it is not given sugary food.

A study conducted at the University of São Paulo provides knowledge for use in diagnosing and treating chronic fatigue syndrome, which affects 10%-20% of patients who recover from COVID-19.
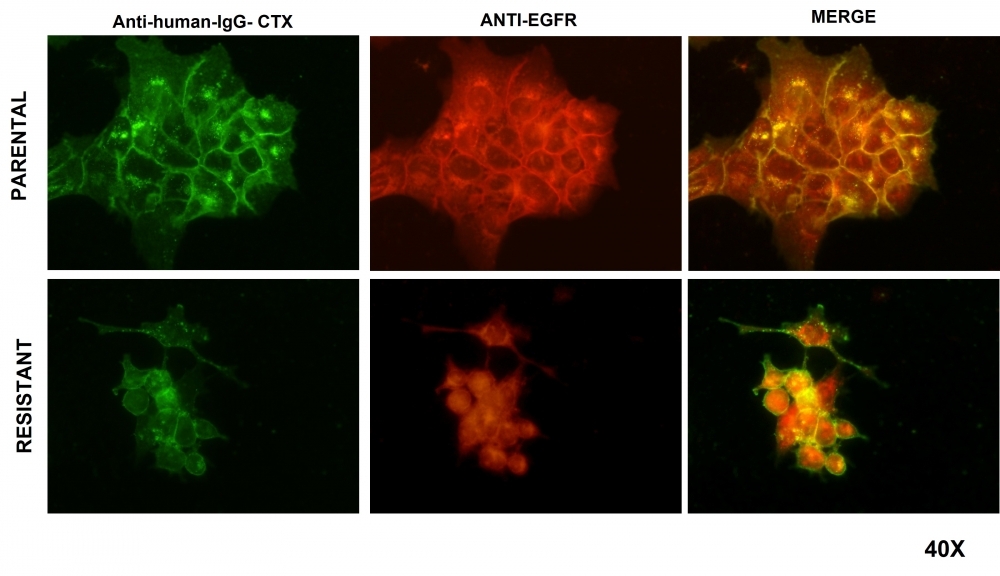
Cetuximab is one of the few drugs approved for this type of cancer, but it is expensive and effective only for 40% of patients. An article in the journal Cells describes molecular alterations observed in tumor cells that indicate resistance to the drug, paving the way to the development of a predictive test.

Based on an analysis of data for nearly 1,000 participants in the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing born in the 1950s and 1960s, researchers concluded that children’s relationships with parents influence longevity, although the impact is different for men and women.
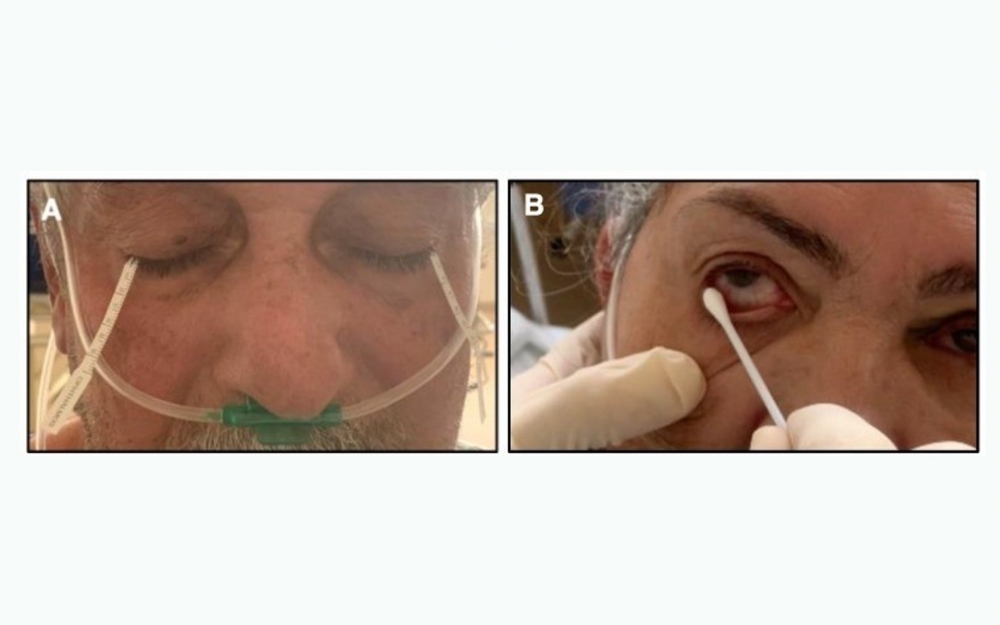
Researchers at the University of São Paulo detected SARS-CoV-2 on the ocular surface in 18.2% of samples taken from patients hospitalized with the disease. The findings point to an alternative to nasopharyngeal swabbing and highlight the need for health workers to protect themselves from infection by ocular fluids.

An article by researchers at the State University of Campinas in Sport, Education and Society investigates the dark side of Olympic fame. The lead author’s PhD research included interviews with former gymnasts in the Brazilian team.
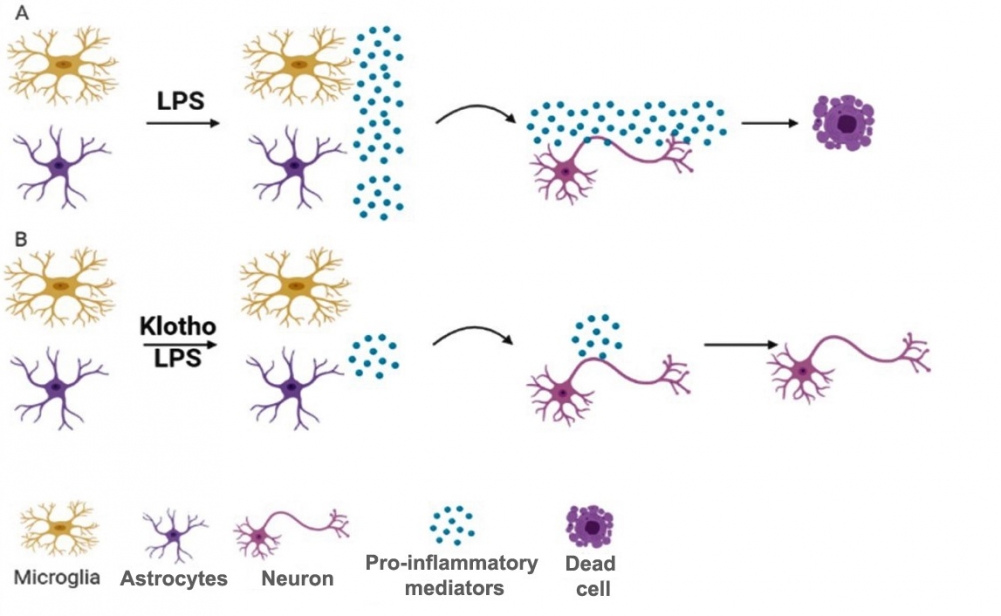
Results of in vitro tests are described by researchers at the University of São Paulo in the journal Scientific Reports point to avenues for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
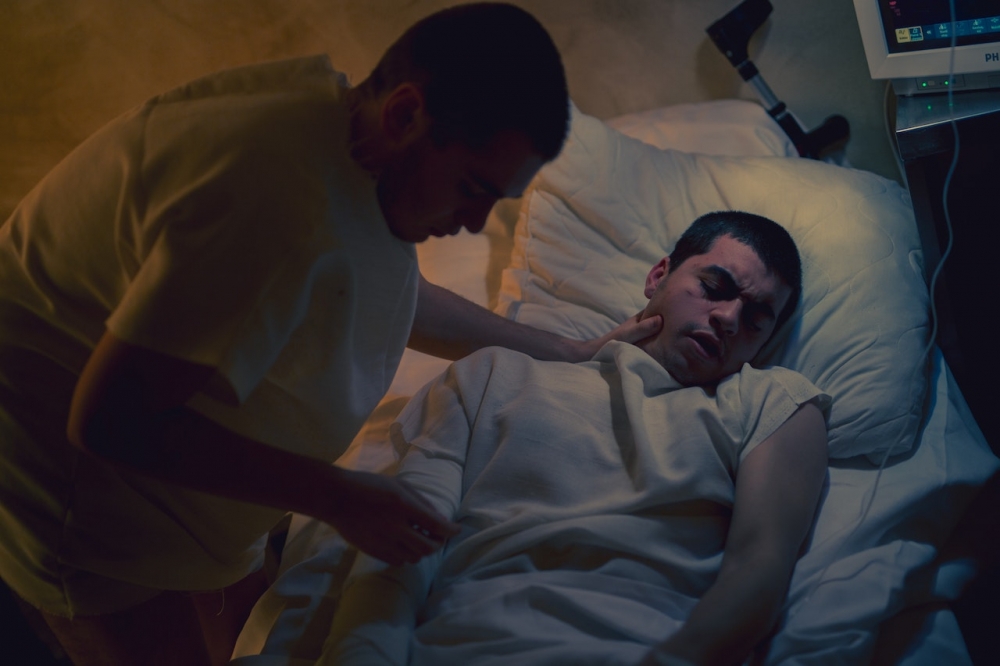

Scientists who analyzed the combined use of two drugs – paclitaxel and immune checkpoint inhibitors – made discoveries that could pave the way for future research to combat the pain caused by other diseases.

A study analyzed changes to the built environment to promote physical activity in Brazil’s largest city between 2015 and 2020, using data from online public libraries as well as the city and state governments.
In Brazil, researchers tracked 80 patients with moderate and severe forms of the disease for up to six months after they left hospital. Muscle impairment during hospitalization was also a predictor of higher healthcare costs in the ensuing months.

In experiments conducted by scientists at the University of São Paulo, the performance of a model obtained in a 3D printer was equivalent to that of the conventional model produced manually. The biomimetic material can be produced on a large scale, reducing animal testing by the cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries.
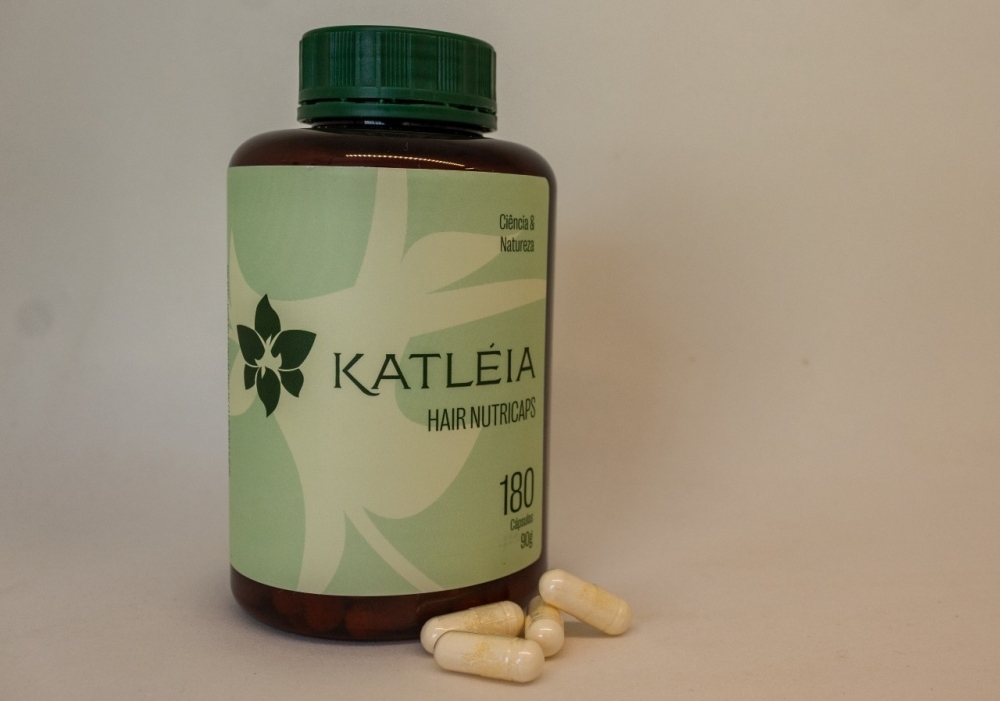

A company funded by FAPESP’s program to support innovation by small businesses is launching a dietary supplement for consumer hair care.
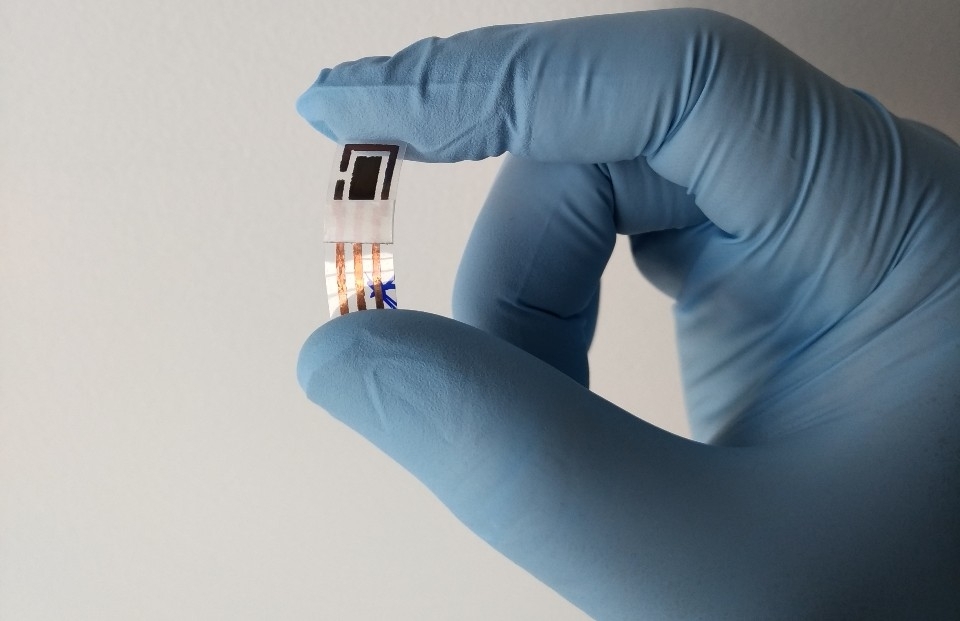

Flexible copper device identifies lead and cadmium in sweat and can be used by untrained personnel to monitor exposure to toxic materials.
Stress, burnout, pain and poor sleep were some of the most frequent symptoms reported by nursing and other staff who care for patients in a study conducted by researchers at the Federal University of São Carlos in São Paulo state, Brazil.
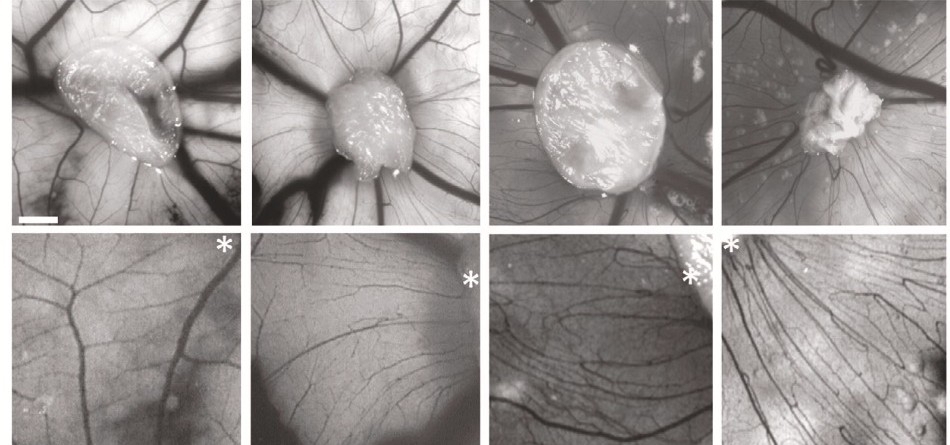
Brazilian researchers have discovered that central nervous system cells from patients with schizophrenia secrete substances that reduce the thickness of blood vessels in the brain, possibly leading to diminished metabolic flux in some parts of the CNS.
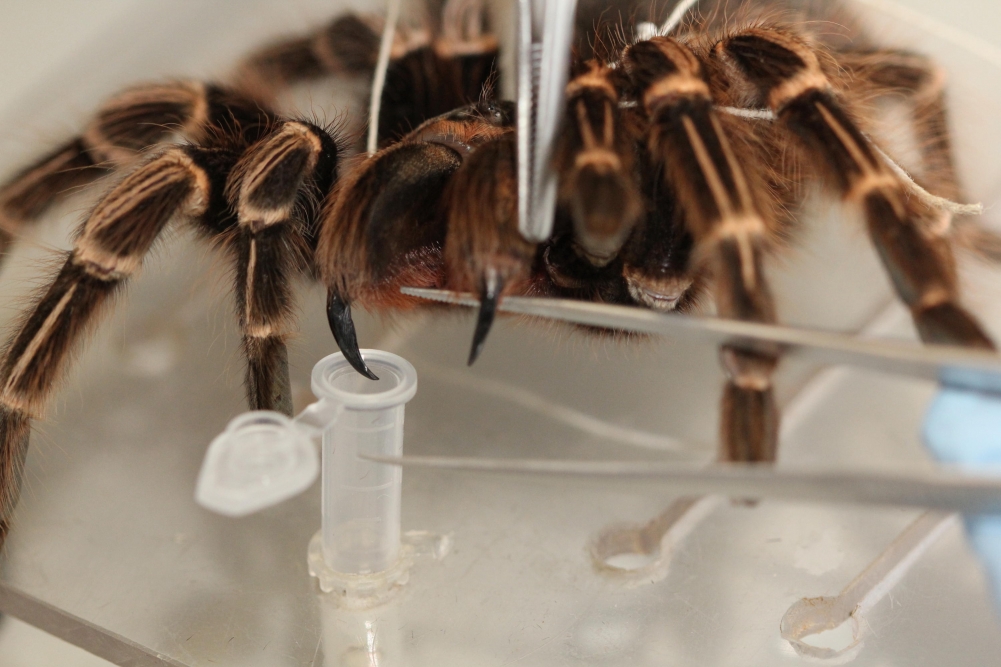

Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo and Butantan Institute used several advanced techniques to analyze the venom of the Orange banded tarantula Acanthoscurria juruenicola and tested its capacity to paralyze crickets. The findings could contribute to the development of biodiversity-based solutions.

Neuropathic pain is chronic and caused by injury to the nervous system, affecting between 3% and 15% of the population. The only treatment options currently available are drugs originally developed for other conditions, such as epilepsy or depression.
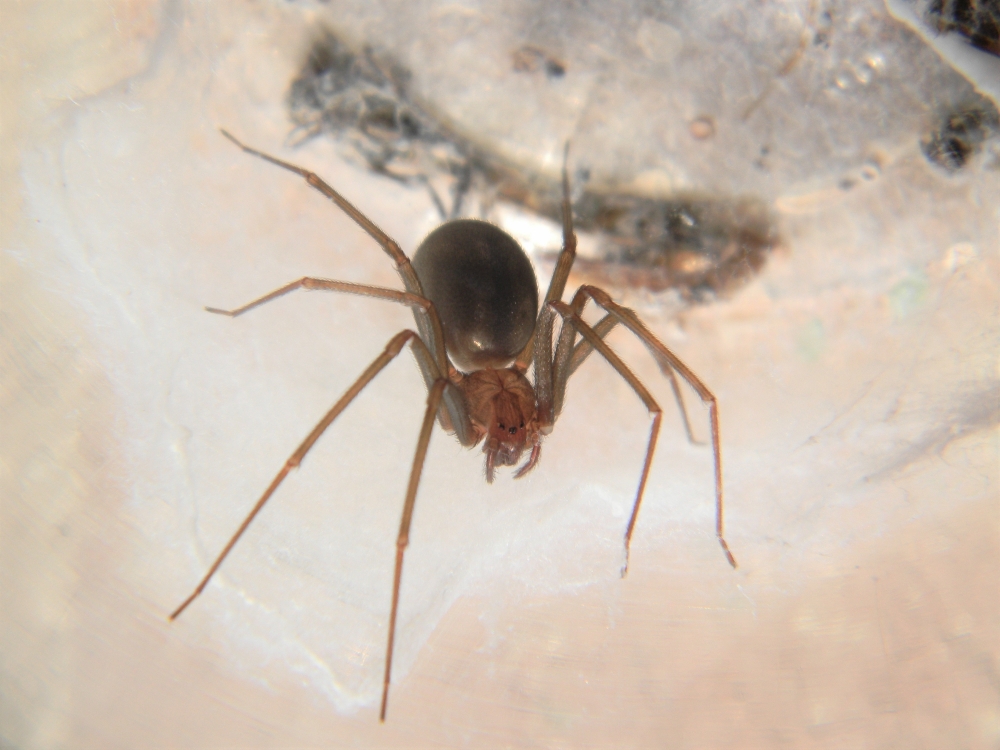

The study involved 146 patients, 74 of whom were treated with an antivenom produced by Butantan Institute in São Paulo. The results showed the antivenom to be safe and effective, especially if it is administered within 48 hours.
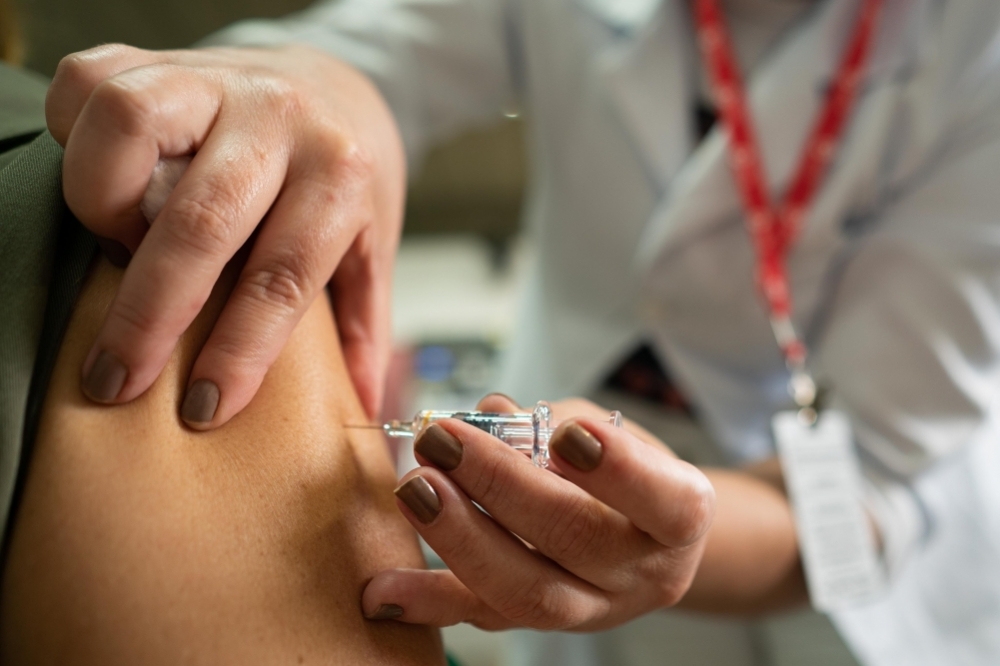
The dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 variant substitution in the town where a clinical trial of vaccination effectiveness was conducted matched the pattern seen elsewhere in the country, but most cases were mild. The researchers analyzed 4,375 whole genomes of the virus.
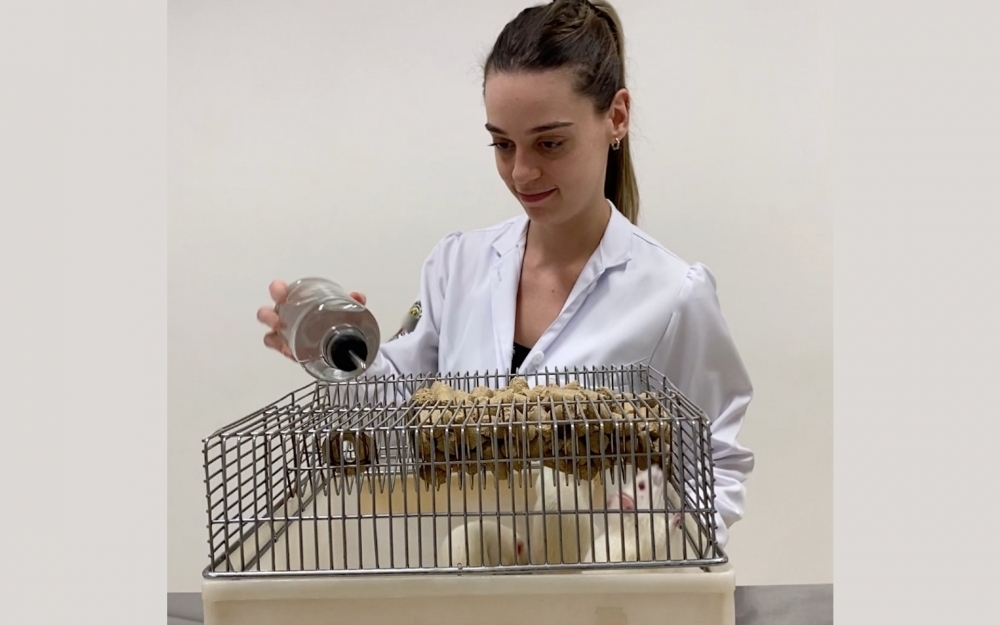

In experiments involving rats, researchers at the University of São Paulo analyzed the effects of celecoxib and indomethacin. The results are published in Scientific Reports.
A group of researchers in Brazil and the UK have developed a method to track seroprevalence in real time. An article in the journal eLife shows how this was done in the case of SARS-CoV-2, providing a “portrait” of the first year of COVID-19 in Brazil.