


The findings of the study, which involved 1,183 physicians in two Brazilian states, point to inequalities in the uses and coverage of telemedicine. Private clinics spearheaded the growth.

Researchers in Brazil and the UK analyzed data for more than 3,000 people aged 50 or more to prove the importance of vitamin D to muscles.

Brazilian researchers advocate trials using mini-brains grown in the lab to investigate the impact of these drugs on fetal neurodevelopment.
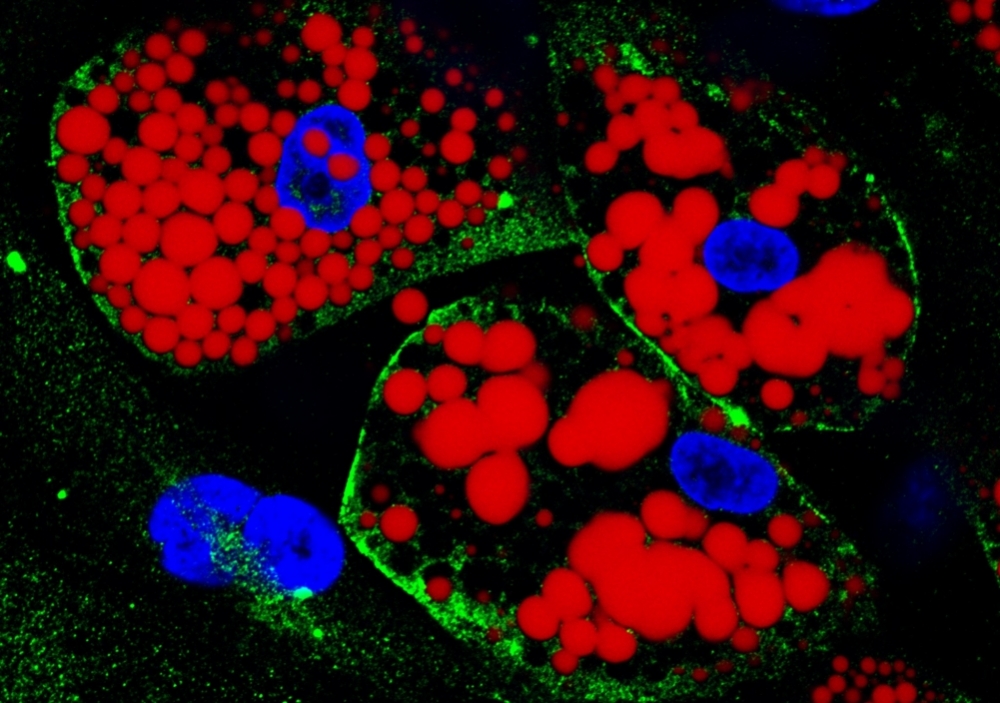
Brazilian researchers infected fat cells from subcutaneous and visceral tissue with SARS-CoV-2. Fat cells from organs in the abdominal cavity had a higher viral load and produced more pro-inflammatory molecules after contact with the virus.
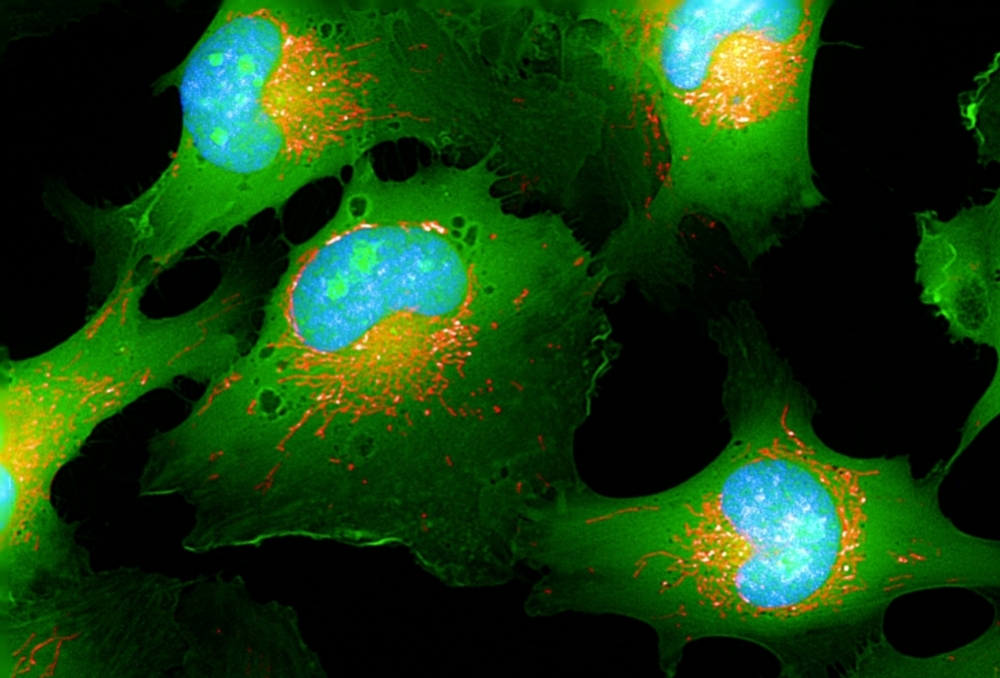
An article on the study is published in Biomedicines. The findings offer an avenue for the development of novel therapies for Chagas megaesophagus.
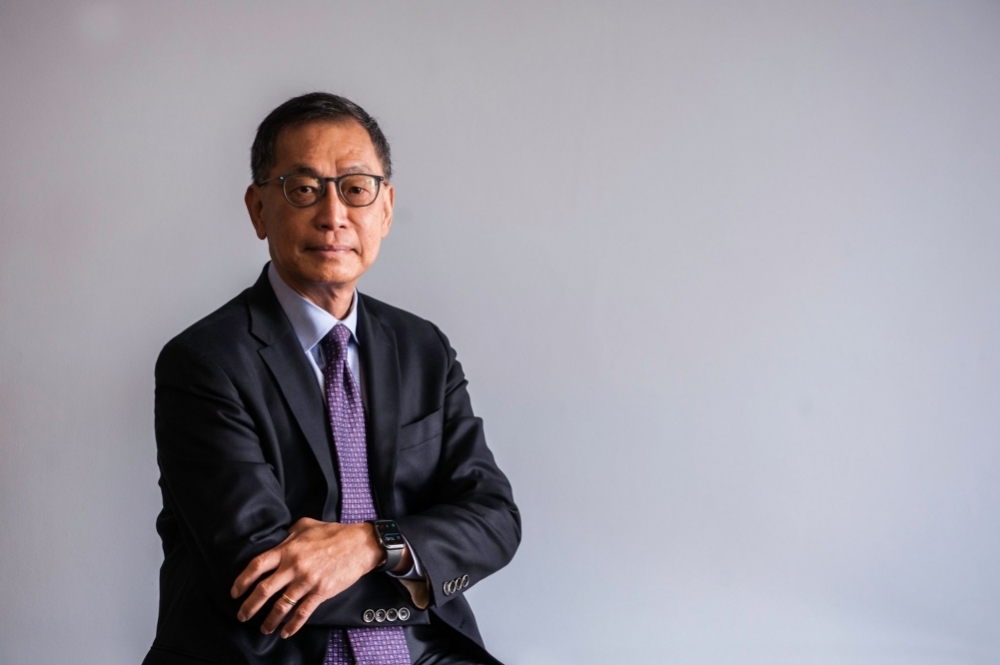

On a visit to Brazil, the scientific director for LICR and one of the most cited researchers in the field of oncology spoke about advances in cancer treatment and the development of tools that in his view enable physicians to detect tumors very early on.
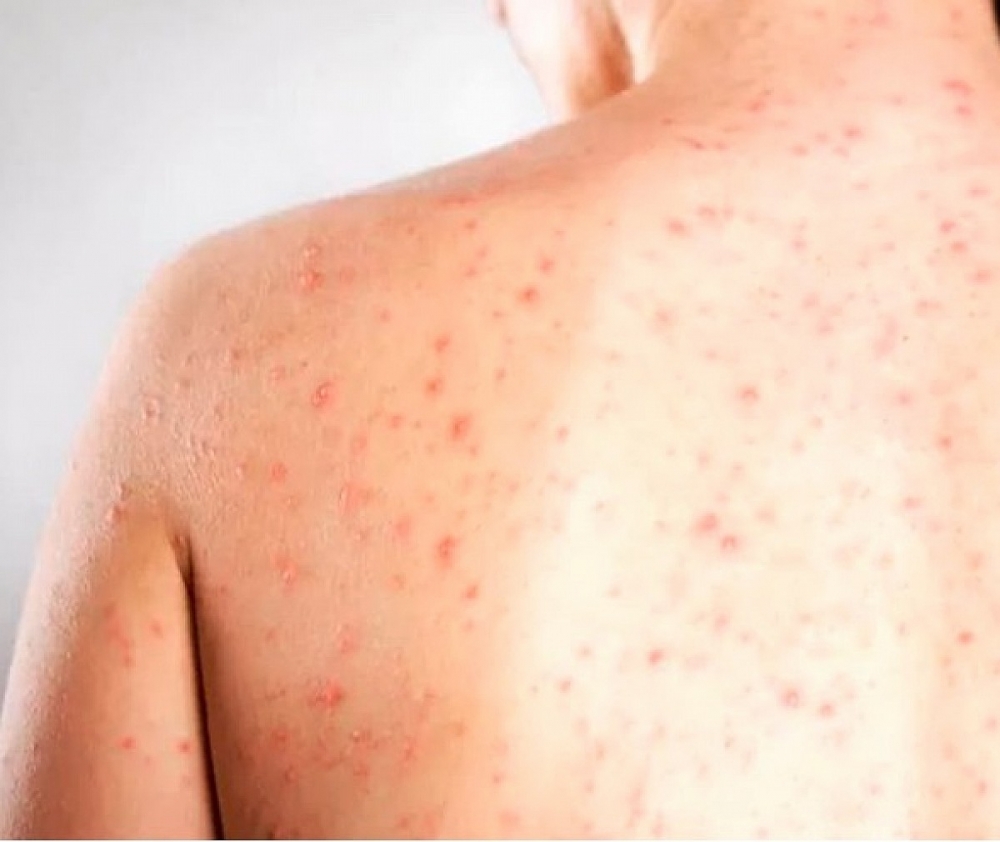
A total of 252 children living in a city in northwestern São Paulo took part in the study, in which blood samples from hospitalized children were analyzed. The percentage with measles antibodies was less than the 94% target considered ideal to prevent outbreaks.
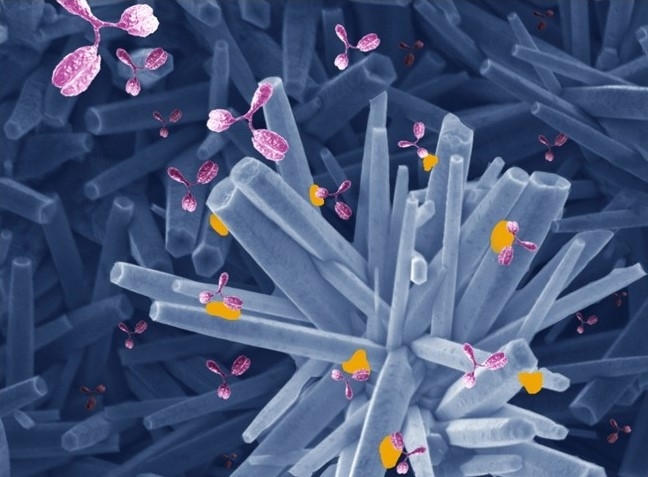
Brazilian scientists have developed a biosensor using zinc oxide combined for the first time with an electron-conducting glass substrate and the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. The results outperformed ELISA, the current gold standard for diagnosing infectious diseases.
The worst-ever outbreak of fungal disease caused by the same strain of Candida parapsilosis in severe COVID-19 patients was reported in a hospital in Salvador. Novel drug-resistant strains of Candida will emerge in Brazil, the authors predict.

The importance of organizing and assuring access to the government’s healthcare data via the SUS was highlighted in a presentation by Ester Sabino, a professor at the University of São Paulo, to a webinar hosted by the São Paulo State Academy of Sciences. Data integration and access would benefit researchers and the Health Ministry, and help to direct investment in the sector.

A study conducted at the University of São Paulo shows that flaws in the metabolization of ATP, one of the main sources of cellular energy, can lead to dysregulation of the immune system and a dangerously exacerbated inflammatory response to infection by the novel coronavirus.
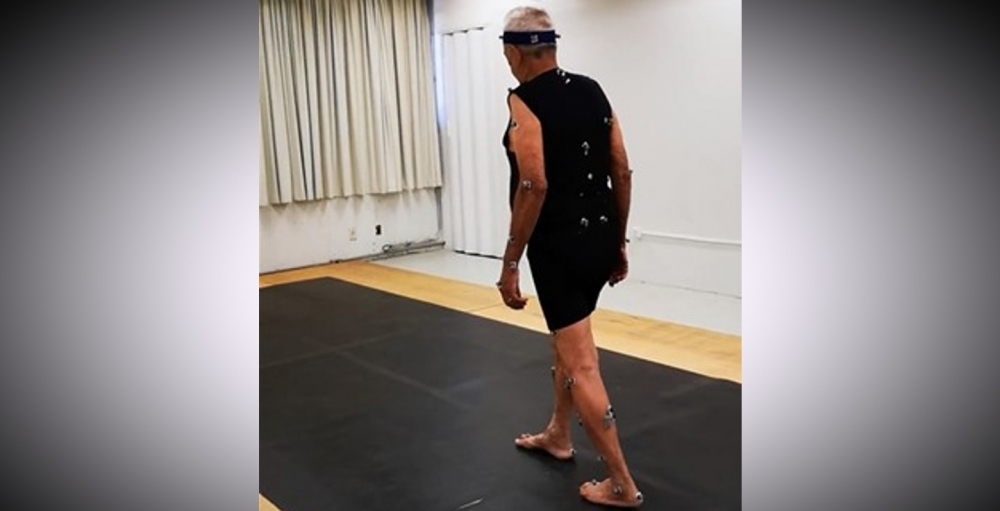

Researchers at São Paulo State University tested machine learning techniques to estimate parameters such as step length, width and velocity. The method makes clinical diagnosis more precise and can determine the stage reached in progression of the disease.
Researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo set out to discover why proteins that should be found in cell nuclei ended up in cytoplasm or elsewhere in certain situations. This unexpected phenomenon may indicate a relevant pattern for diagnostic and treatment purposes.
A team at a FAPESP-supported research center investigated over-90s who were resilient to SARS-CoV-2 and identical twins who had severe COVID-19 with different outcomes, including long COVID. The findings are expected to contribute to the development of vaccines and treatments for this and other viral diseases.
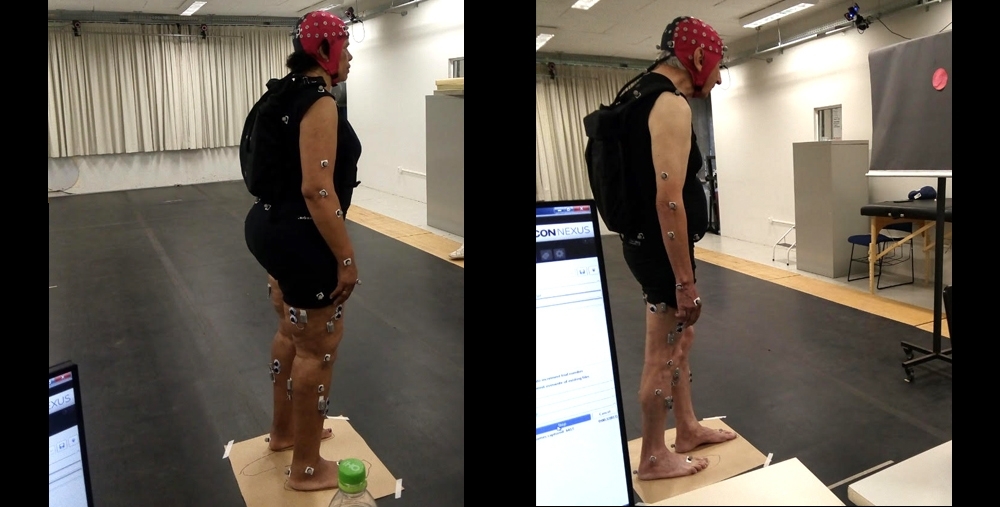
Researchers at São Paulo State University described in detail the positive effects of levodopa on posture and balance, in a study aimed at optimizing treatment. The findings are reported in Brain Research.

An article by researchers at the Federal University of São Paulo describes how the functioning of RNA changes in cells infected by the COVID-19 virus. The findings provide clues as to how different variants can escape the immune system, and serve as a basis for the development of novel treatments.

In partnership with private enterprise and government, scientists in São Paulo state (Brazil) plan to strengthen domestic production and consumption of aquatic products.
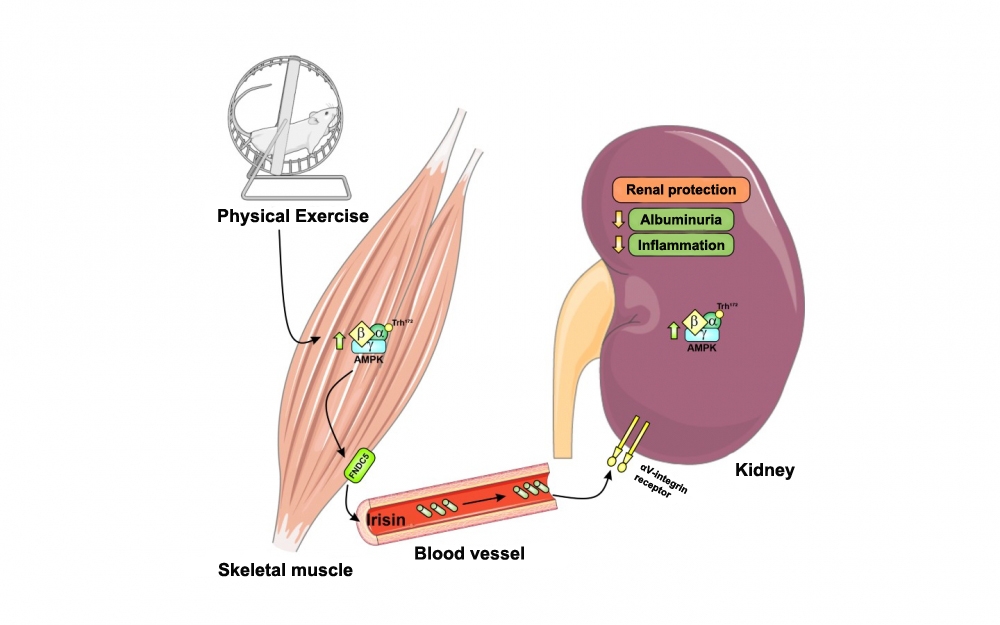
Researchers at the State University of Campinas conducted experiments on rats and human kidney cells. Their findings, published in Scientific Reports, show that irisin, a hormone secreted in muscle tissue during exercise, avoids the cellular degeneration that leads to diabetic nephropathy and kidney failure.
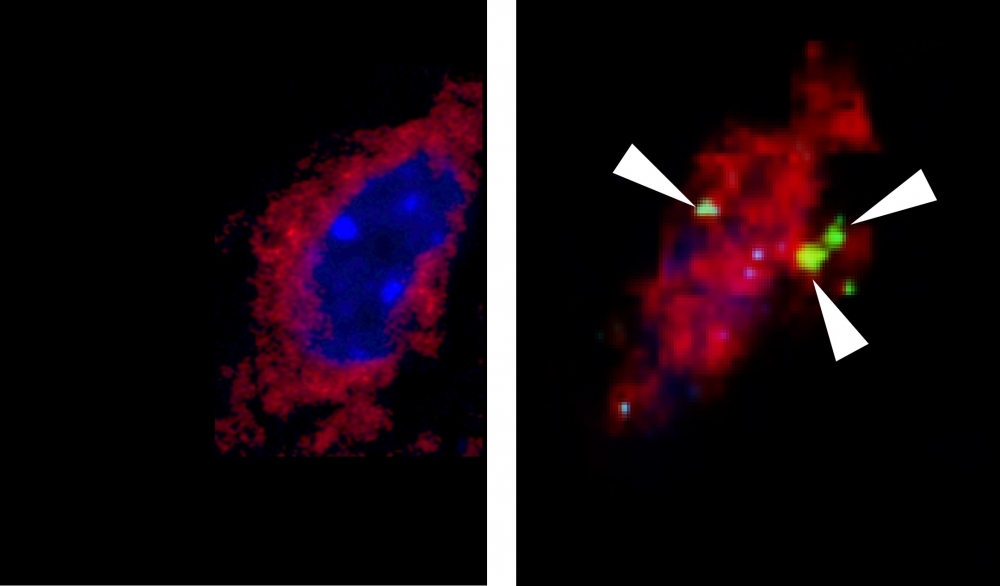
Through experiments involving mice, Brazilian researchers discovered that a molecule released by the brain during exercise breaks down fatty acids in skeletal muscle tissue and continues to do so after the exercise has ceased.
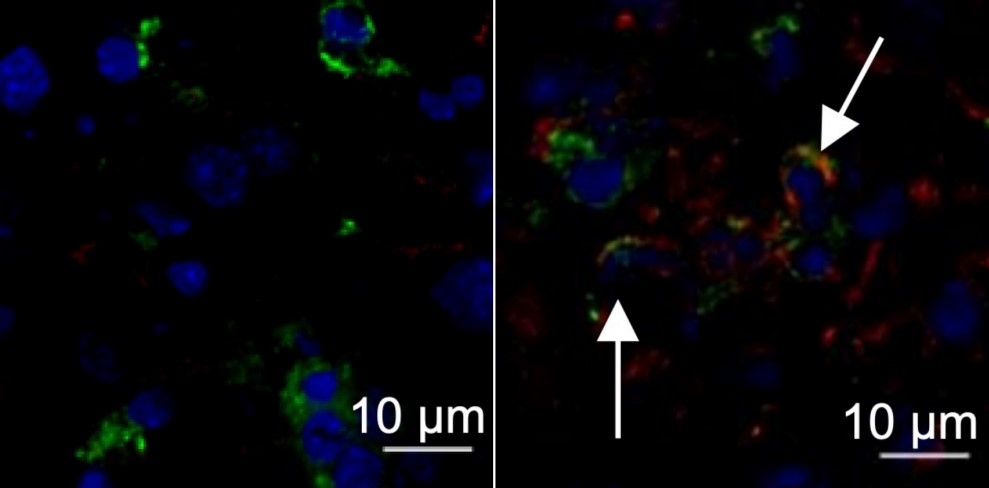
A type of treatment known as immune checkpoint blockade proved beneficial in cells from COVID-19 patients in intensive care and in mice infected by a betacoronavirus similar to SARS-CoV-2. The study is published in Science Advances.

At a meeting held in São Paulo city, researchers from the Brazilian state of São Paulo and the Netherlands described their work on the development of prosthetics and other implantable biomaterials. FAPESP will invest BRL 15.2 million to fund the projects selected in the call.
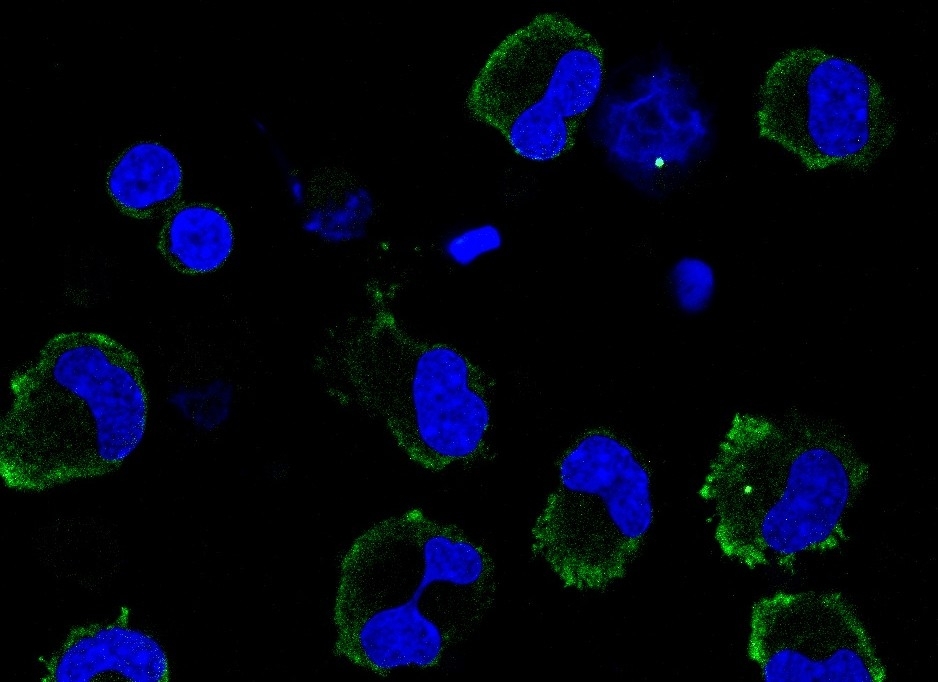
Researchers at the University of São Paulo tested the anthelmintic niclosamide on mice and human blood cells. In addition to exhibiting antiviral action, the drug deactivated the cellular mechanism that triggers a cytokine storm. A novel formulation is required for the active principle to reach the lungs and treat severe COVID-19 in humans.

Measuring handgrip strength is one of the main ways of detecting sarcopenia, a syndrome characterized by loss of muscle mass, force and function. Researchers in Brazil and the UK recommended raising the minimum value considered normal, after analyzing data for more than 6,000 men and women aged 60 and over.
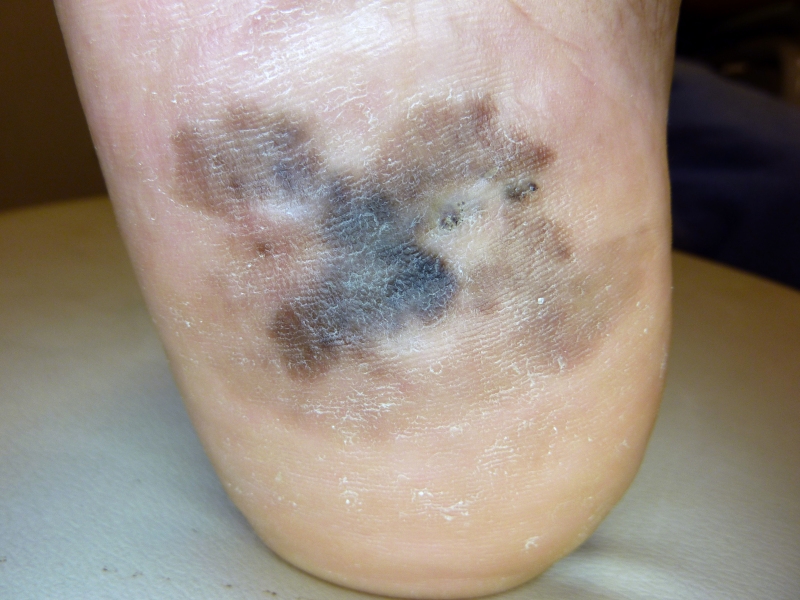
Analysis of skin tumor samples showed correlations between changes in proteins that regulate the organism and prognosis. The results, published in Nature Communications, were obtained by researchers in Brazil and France.
The results of animal trials were published recently in Nature Communications. The researchers have received the green light from the national health surveillance authority to proceed with testing on humans.