

Study conducted at a FAPESP-supported research center shows that anti-inflammatory peptide TnP could lead to drug development.
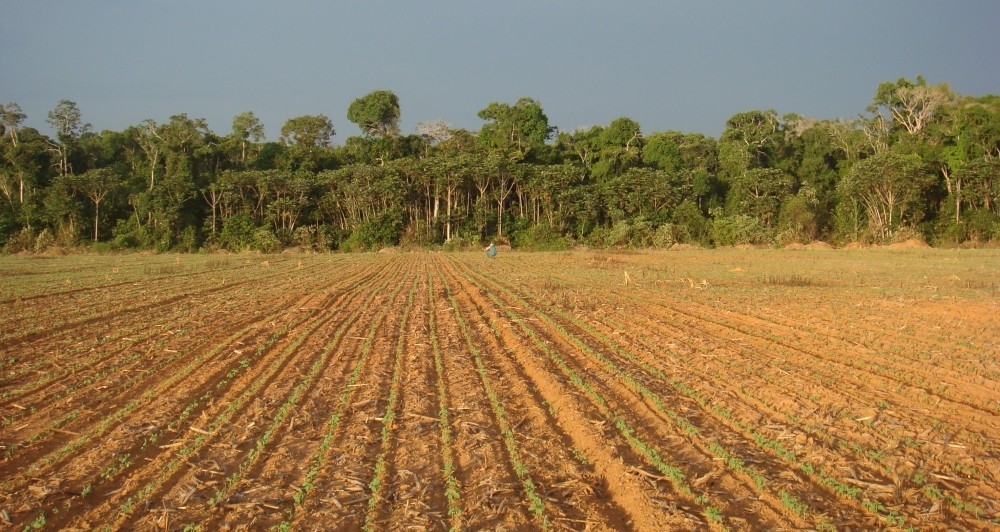

Study suggests that replacing native vegetation with pasture or crops increases competition among microorganisms, favoring those with antimicrobial resistance genes. Brazilian scientists advocate more research to find out whether bacteria can migrate to food and reach humans.

In October the CDC recommended ten instead of 14 days of isolation for patients with mild or moderate symptoms, but Brazilian researchers found viable viral particles in 25% of samples collected from patients on the tenth day of symptoms.
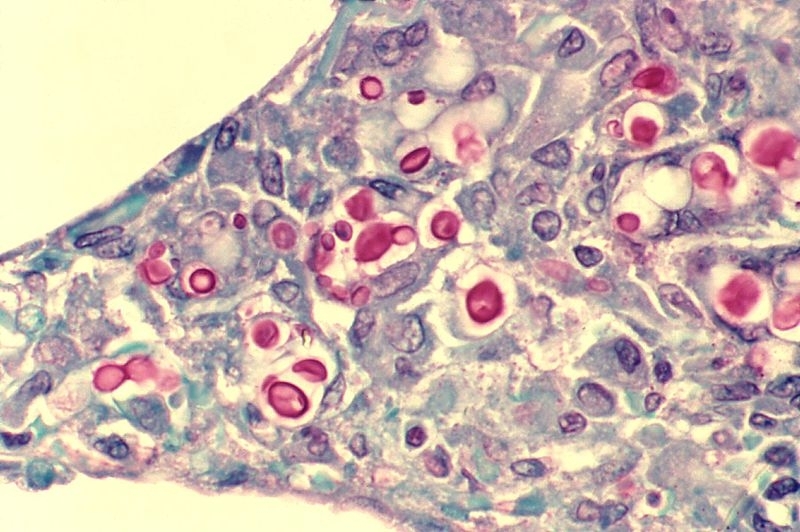
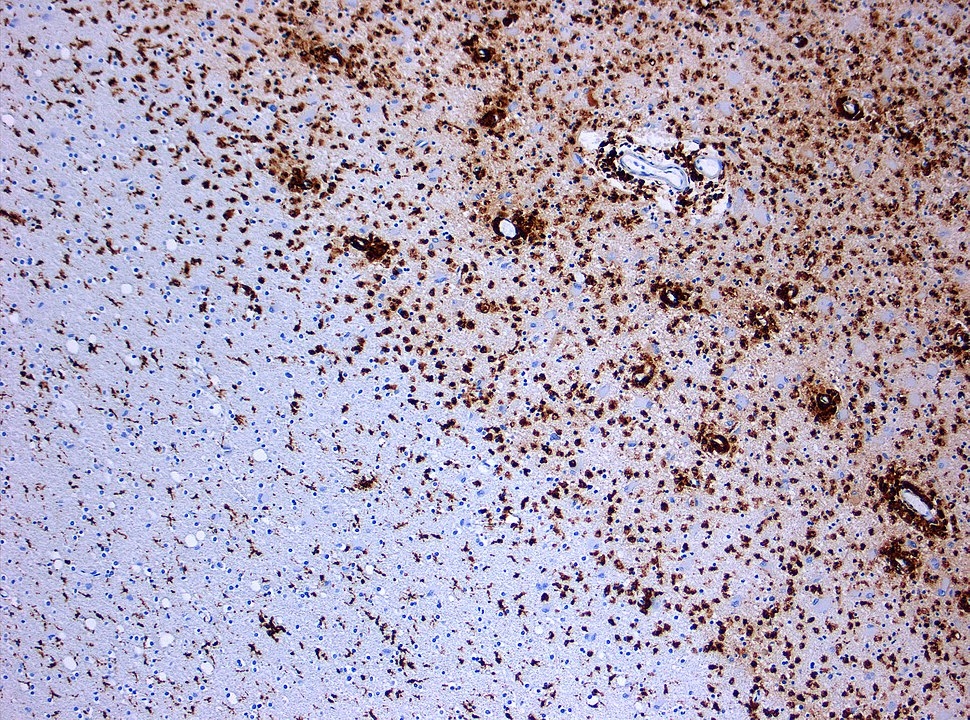
The use of CAR T-cells reprogrammed to “recognize” Cryptococcus spp. proved effective to combat the infection in vitro and in mice.

Scientists will monitor areas in which these diseases are endemic, such as São Paulo, the Amazon, the Pantanal and Panama, to investigate the factors that trigger outbreaks.
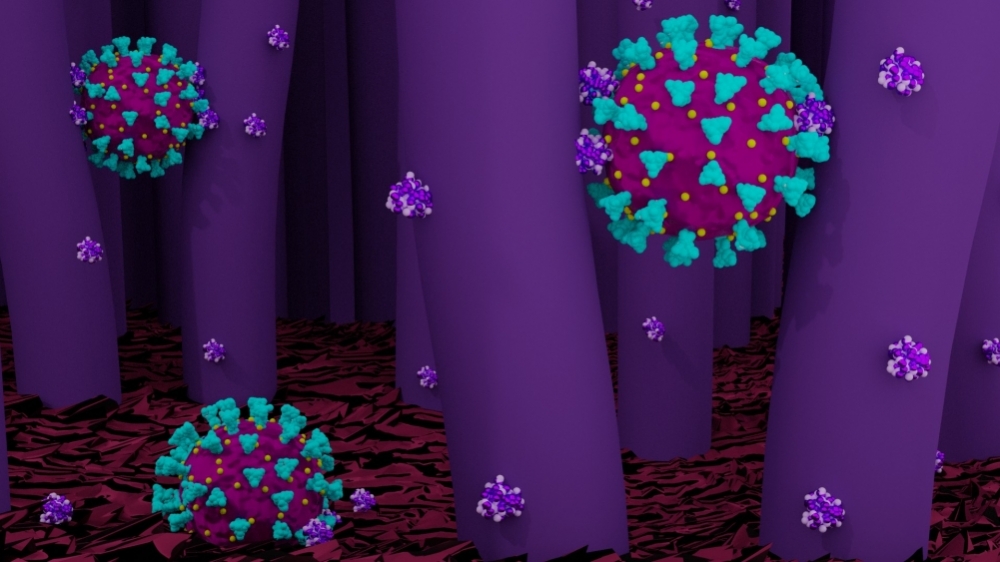

According to a paper by Brazilian researchers published in Nano Today, the spatial arrangement of proteins on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 assures highly efficient interaction with target receptors on human cells.
The different criteria used in Phase 3 clinical trials of the vaccines approved so far were explained by scientists in a webinar hosted by FAPESP. The impact of delays in vaccinating Brazilians was one of the topics discussed.

An analysis conducted in the Brazilian state of São Paulo detected seven proteins in plasma from hospitalized patients that could be used in novel treatments and methods of identifying potentially severe or critical cases.
Study involving more than 200 hospitalized patients in São Paulo shows physically active individuals are not fully protected against the disease.
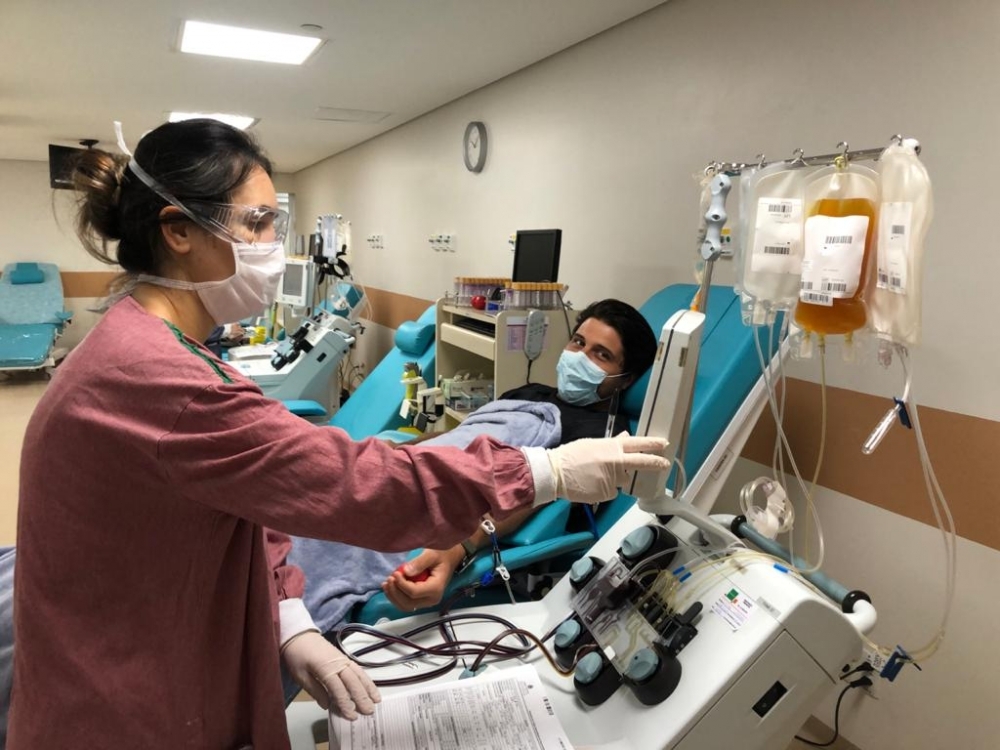
Clinical trial conducted in Brazil suggests the treatment can be beneficial if administered within ten days of symptom onset.
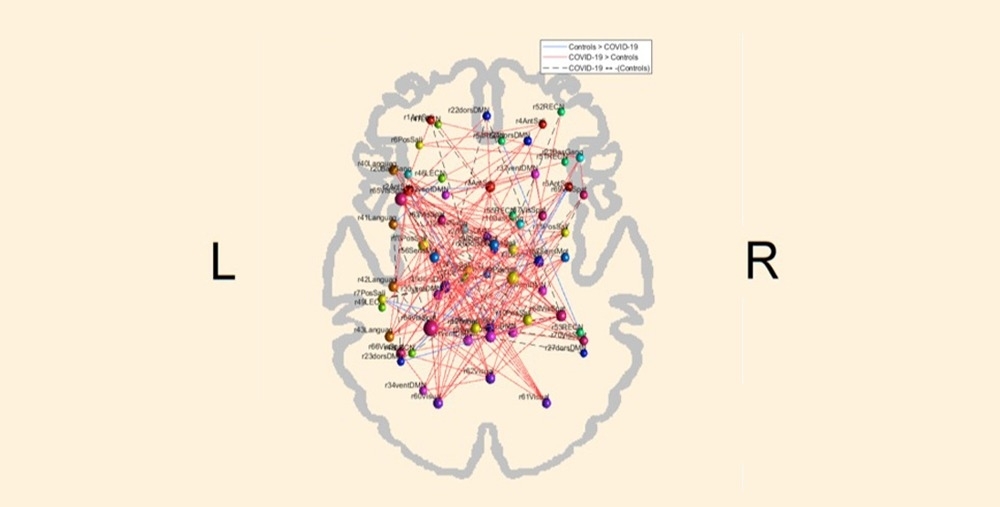
Brazilian researchers used functional magnetic resonance imaging to assess 86 volunteers who had moderate COVID-19 and compared the results with those of uninfected volunteers. Preliminary findings have not yet been published but were presented during a conference held at the University of Campinas.

More than 1,000 volunteers completed an online questionnaire designed by Brazilian researchers. The results show that more women are cooking, sitting down to eat, snacking between meals, and ordering takeaway meals, while dieting and supermarket shopping have declined.

Researchers at a center for neuromathematics say dreams reflect the fear and anxiety fueled by the disease.

Technology based on nanoparticles identifies IgG antibodies and costs only about a fifth of similar devices now on the market. It was developed by scientists at the University of São Paulo and Brazilian startup Biolinker.
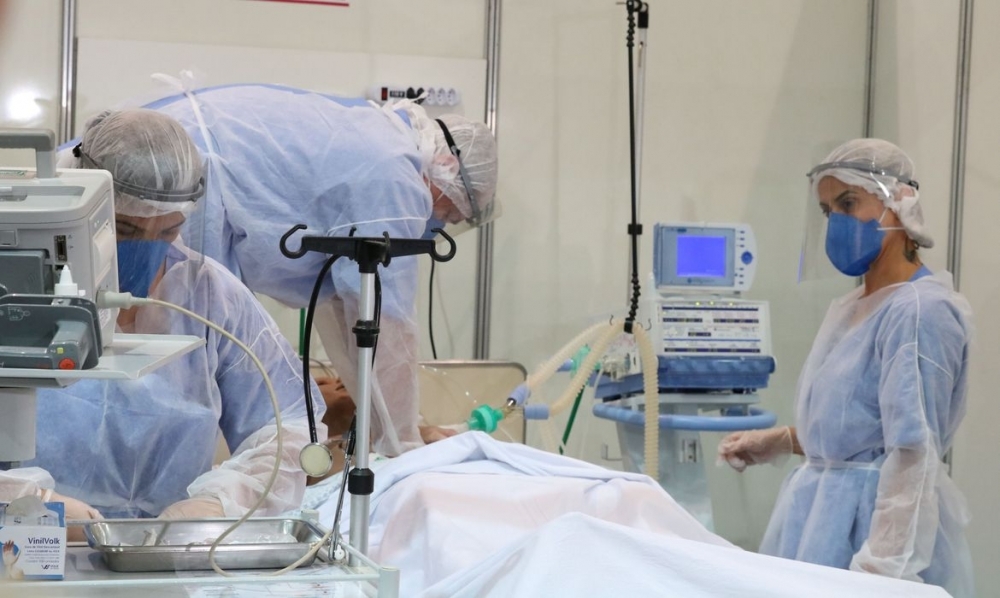
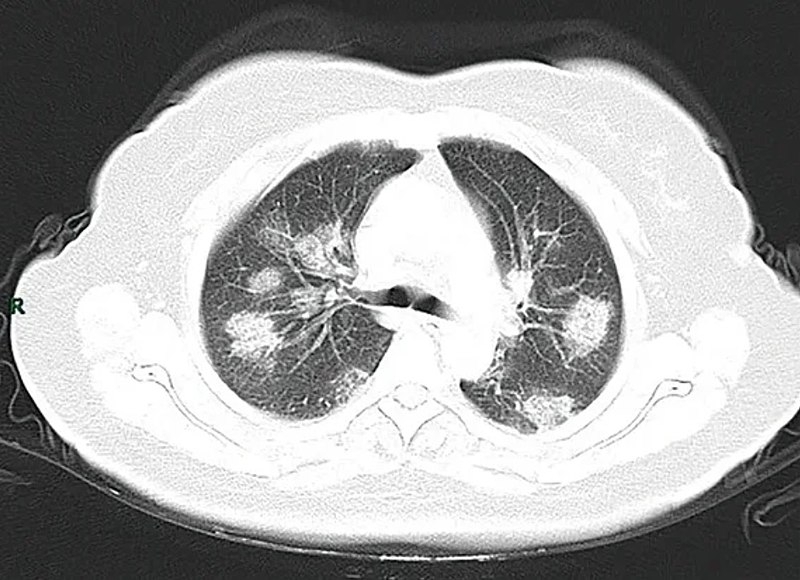
Brazilian researchers applied an examination protocol based on an analysis of 12 lung regions to 180 severe patients and found that the higher the lung ultrasound score the greater the risk of ICU admission, intubation and death.

A study by researchers at the University of São Paulo showed that the blood serum of severe patients contained high levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine and lipid mediators derived from arachidonic acid. The discovery may help improve the prognosis of such patients and the treatment available to them.

According to a study published in Frontiers in Immunology, the reason is their genetic heterogeneity and lack of proportional representation in the Brazilian bone marrow bank.
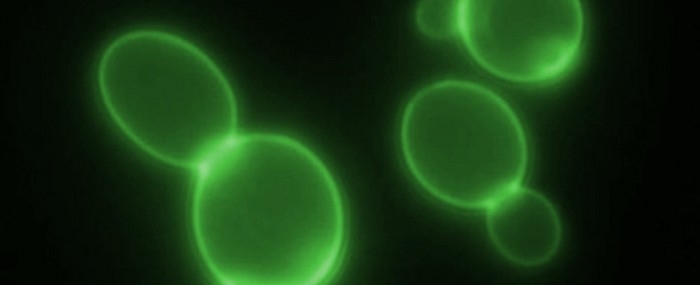
Based on a reaction between yeast and the novel coronavirus, the test will rapidly detect the presence of SARS-CoV-2 in saliva and will be available by mid-2021.
Researchers at York University in Canada and the University of Campinas in Brazil used mathematical modeling to estimate the short-term impact of vaccination. Abandoning non-pharmaceutical interventions too soon could cancel out the benefit, they warn.
The hormone acts as a barrier against SARS-CoV-2, blocking the expression of genes that encode proteins in cells serving as viral entry points, according to a study by researchers at the University of São Paulo.
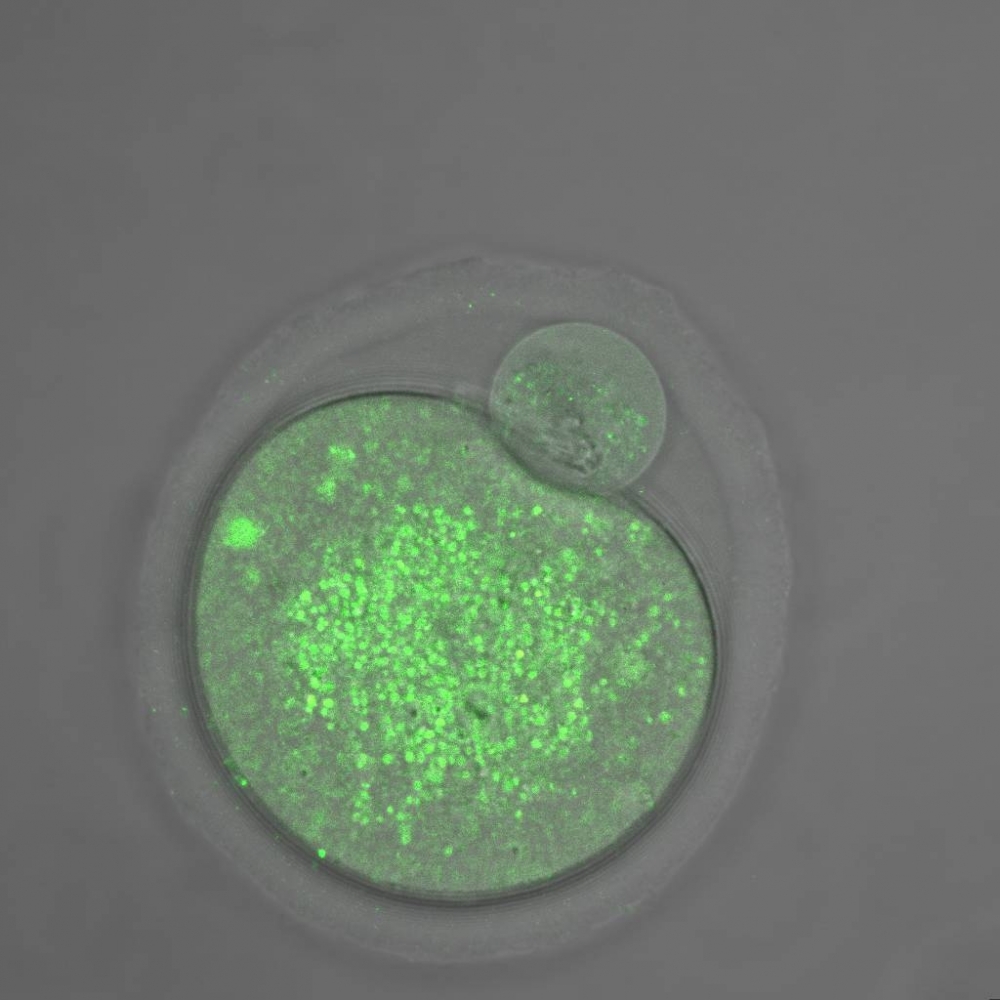
The phenomenon may be associated with a deficiency of the protein mitofusin-2 in the mother’s eggs, which affects the shape and functioning of mitochondria. The finding was based on experiments with mice conducted at the Federal University of São Carlos and reported in the journal Molecular Human Reproduction.

In an article published in Nature Communications, Brazilian researchers show for the first time that in severe cases of scorpion envenomation it is the neuroimmune reaction triggered by the venom that leads to death.
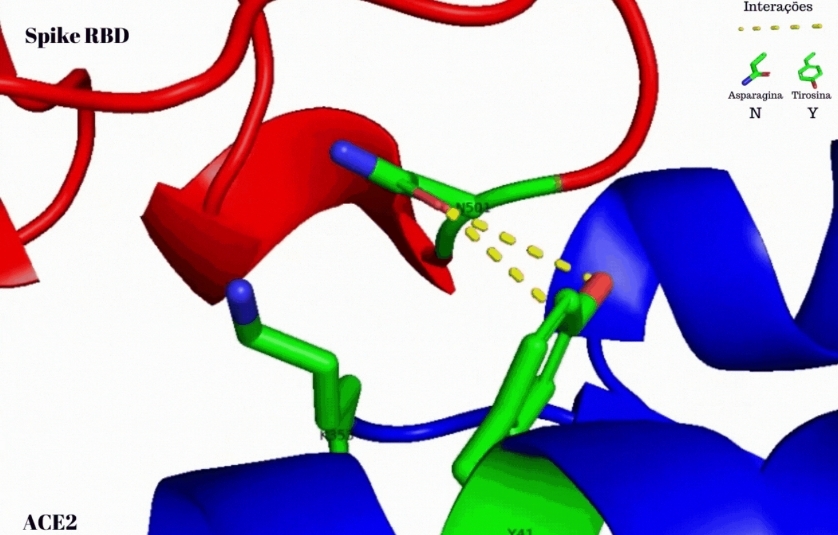
Researchers at the University of São Paulo found that the SARS-CoV-2 variant’s spike protein interacted more strongly with the ACE2 receptor used by the virus to invade and replicate in human cells.

In a review article published in Frontiers of Endocrinology, Brazilian researchers estimate a reduction of 35% in levels of physical activity and a rise of 28% in sedentary behavior in the initial months of confinement imposed by the pandemic.

Experts tell Agência FAPESP about factors that may be associated with the rapid rise in daily case numbers in the capital of Amazonas State, where a six-month state of emergency has been declared.