

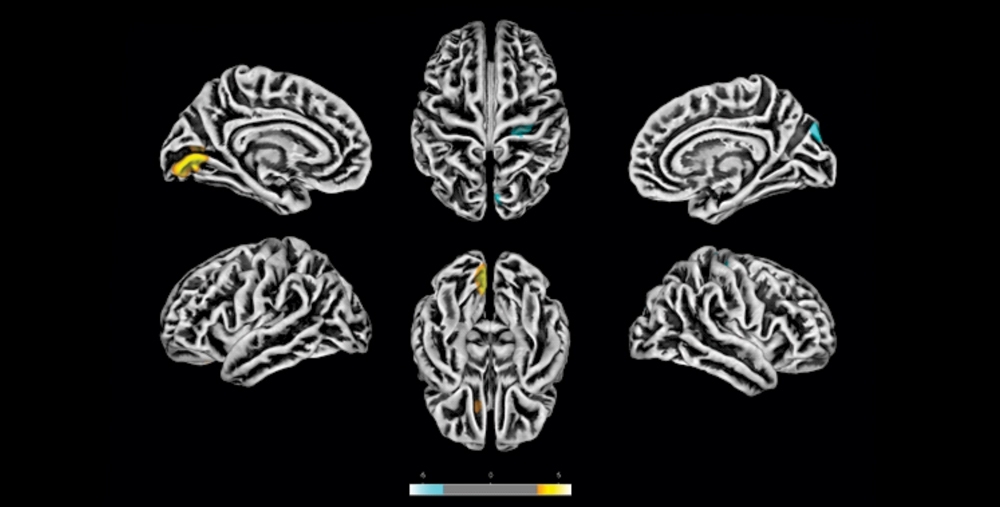
Led by research groups from the universities of Campinas and São Paulo, the investigation combined MRI scans of mild COVID-19 patients, analysis of brain tissue samples from patients who died from COVID-19, and experiments performed with human nerve cells infected in the laboratory.
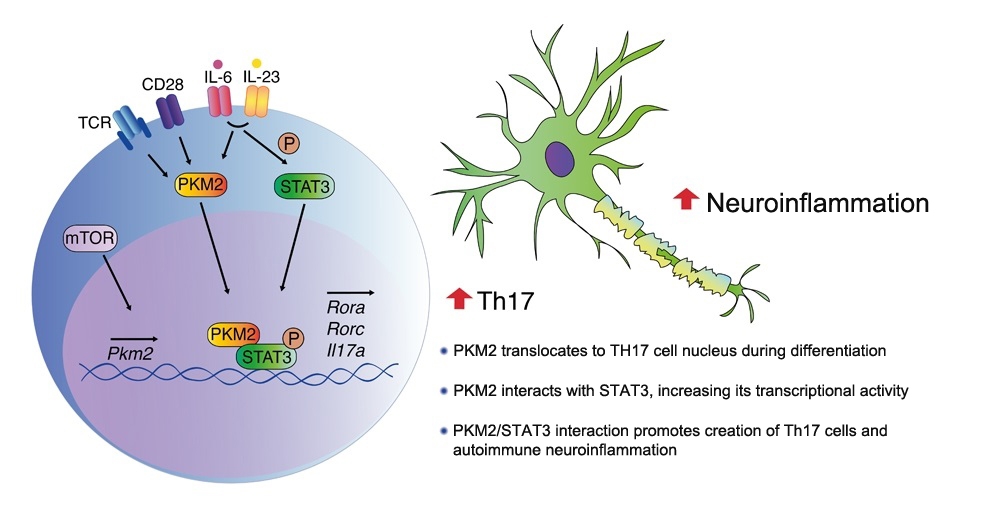
In an article published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, a group affiliated with a FAPESP-supported research center reports that an enzyme associated with energy production in cells also participates in the differentiation of immune cells involved in exacerbated inflammation. The discovery could lead to more effective treatment.
Study conducted at São Paulo State University demonstrates for first time that simple and inexpensive strategy yields better results than conventional treatment and avoids indiscriminate use of antibiotics.

Methodology developed by Brazilian researchers is based on analysis of metabolites in blood serum. Innovation has been patented and reported in Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Study led by researchers at Oxford University suggests that after successive infections by the coronaviruses that cause common colds throughout life the defense system becomes specialized and cannot recognize emergent varieties such as SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion presented by Brazilian researchers in Obesity Research & Clinical Practice is based on analysis of nine clinical studies involving 6,577 patients infected by SARS-CoV-2 in five countries.

Model developed by Brazilian researchers predicts spatial and temporal evolution of epidemic diseases and can help plan more effective social isolation programs with less socio-economic impact.

An article in The Lancet stresses the vulnerability of these health workers, whose readiness to counter fake news with trustworthy information, and to monitor COVID-19 patients in home isolation, has been neglected.
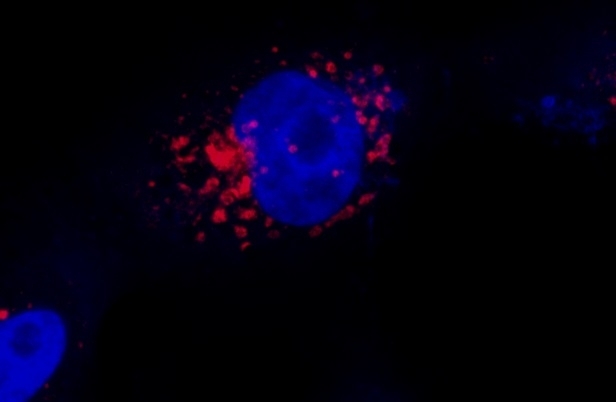
Protocol developed by Brazilian researchers shows SARS-CoV-2 replicating near cell nucleus. Methodology helps scientists understand coronavirus’s action mechanism and could also be used to study other viruses.

In the fourth phase of EPICOVID-19 BR, the proportion of the population with antibodies against the novel coronavirus fell from 3.8% in June to 1.4% in August in 133 cities. According to the authors, the methodology accurately estimates contagion rates in the previous 45 days.
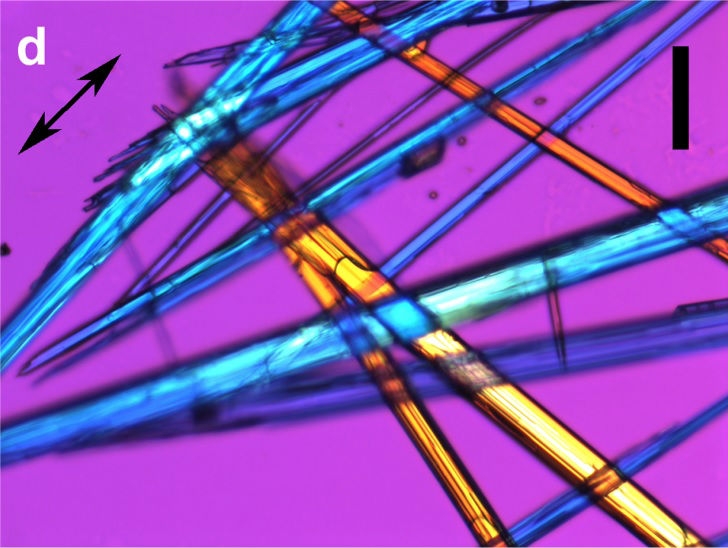
Brazilian research group shows that valproic acid (VPA), used to treat epilepsy since the 1960s, modulates gene expression in tumor gene models and acts on DNA conformation and the histones in chromatin.
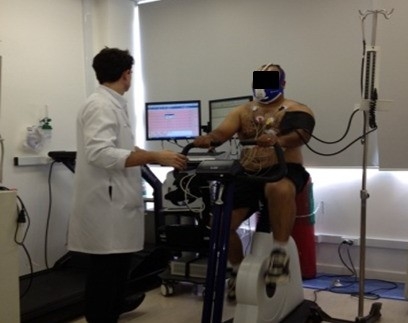
Brazilian researchers’ finding that exercising in the evening reduces blood pressure more than in the morning can help health professionals choose the time of day for aerobic training depending on the type of anti-hypertensive drug they take.

Researchers affiliated with institutions in Brazil and elsewhere analyzed blood work from almost 179,000 people who were tested for the novel coronavirus. They obtained the data from COVID-19 Data Sharing/BR, an open-access repository established by FAPESP.
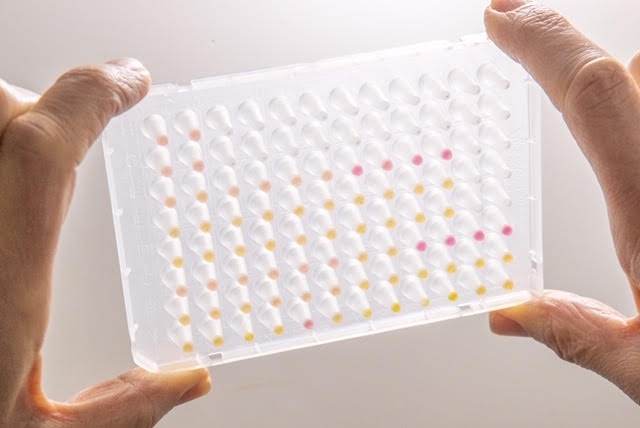
Designed by the Human Genome and Stem Cell Research Center, the novel test may cost a quarter of those based on RT-PCR, considered the gold standard for diagnosis of the disease.

Brazilian researchers use complex training program to stimulate different motor and cognitive skills simultaneously and restore brain regions associated with freezing of gait in advanced-stage patients.
Project led by researchers from Brazilian and American institutions will collect primary data during the pandemic to create a repository that will serve as a basis for future studies. The findings of the comparative analysis will be published in book form.
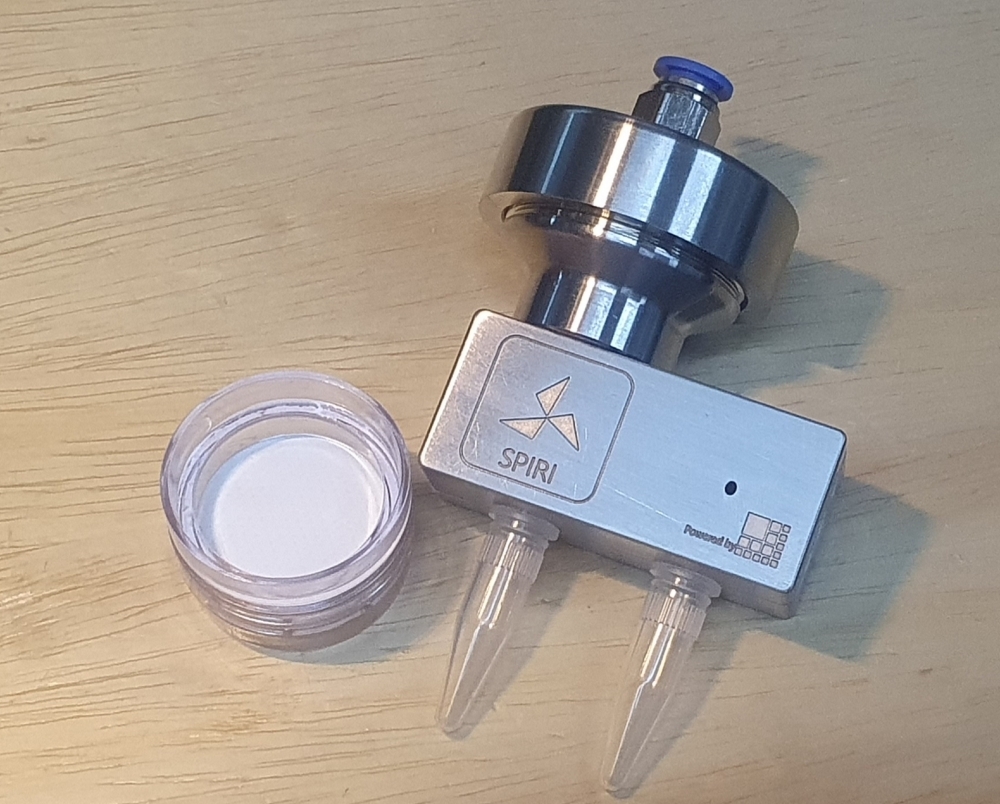

Integrated with the air quality management tool created by startup Omni-electronica, a collector captures viruses suspended in the environment and submits the air samples to RT-PCR testing. Monitoring of crowded locations combined with indicators created by the firm can contribute to a safer economic reopening.
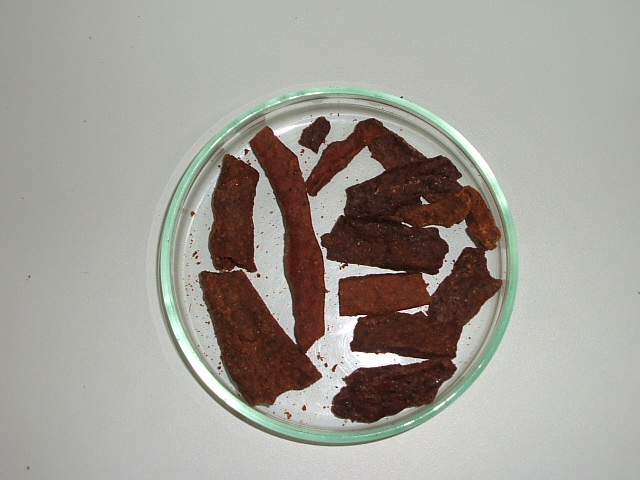

Researchers isolated eight novel polyphenols from the rarest type of propolis. Two of them were found to inhibit tumor cell proliferation in laboratory assays.
Brazilian researchers observed that in uninfected adipocytes, the hormone irisin altered the expression of genes that regulate ACE-2, which encodes a protein to which the virus binds in order to invade human cells.
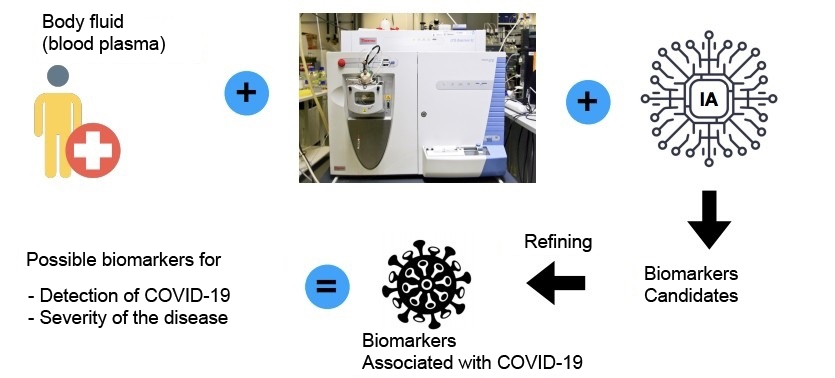
The automated system developed by Brazilian researchers is based on an analysis of patterns of molecules in patient blood plasma.

A study conducted at the FAPESP-funded Center for Research on Inflammatory Diseases (CRID) will identify key processes triggered by SARS-CoV-2 in human cells.
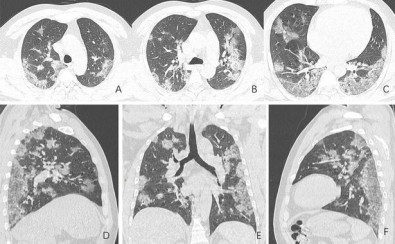
In a project supported by FAPESP, researchers at São Paulo State University (UNESP) will assess the potential of peptides and other bioactive molecules to inhibit the infection of cultured cells.
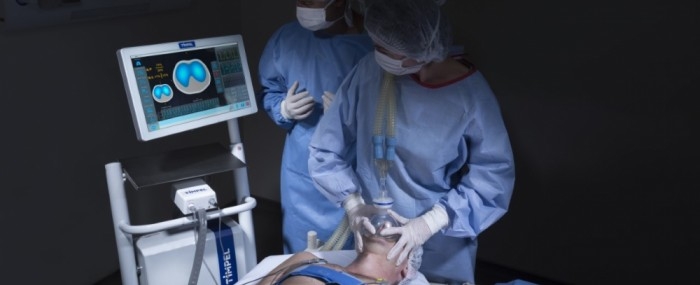
An electrical impedance tomography system was developed by a São Paulo-based startup to monitor the lungs of patients on mechanical ventilation uninterruptedly and noninvasively.
Benefits were observed in a clinical trial involving 38 volunteers treated at the teaching hospital of the University of São Paulo’s Ribeirão Preto Medical School. The drug is cheap and can shorten ICU stays but should not be used outside hospitals, the researchers warn.

A study is being conducted by a research center supported by FAPESP to determine whether people who develop severe forms of the disease have risk genes and whether asymptomatic people or patients with only mild symptoms have protective genes.