

Preliminary results of patient tissue analysis show that the virus infects adipocytes and alters the quantity of signaling molecules released by these cells into the bloodstream.
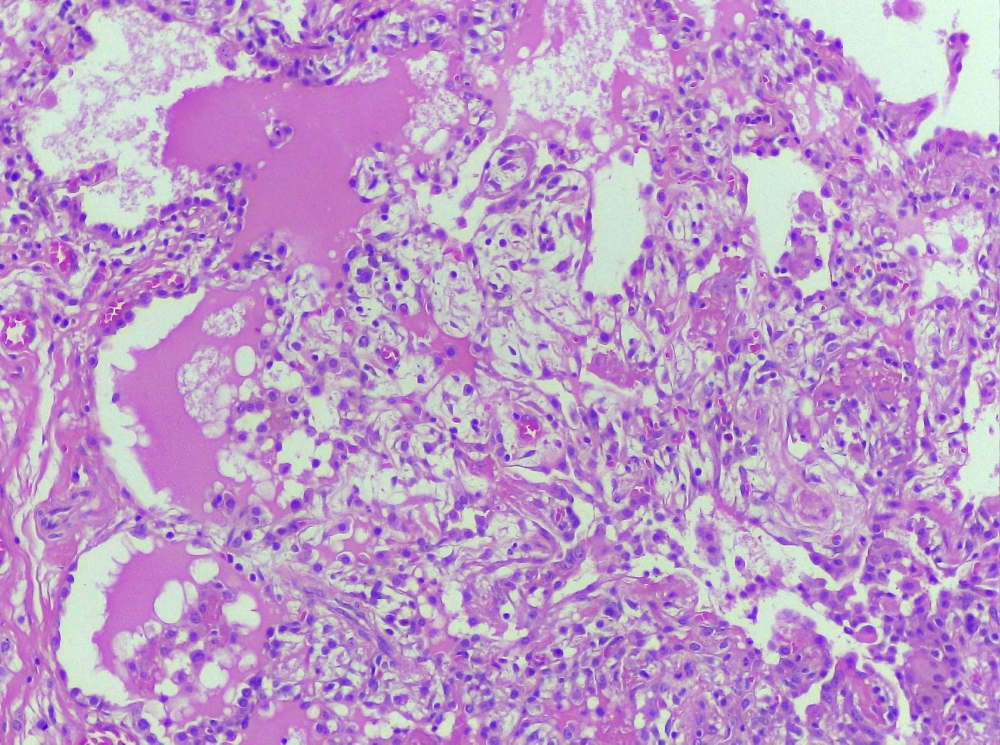
Scientists at a research center supported by FAPESP identified a non-inherited mutation in blood cells from a patient with GATA2 deficiency that may have prevented bone marrow failure and other clinical manifestations.
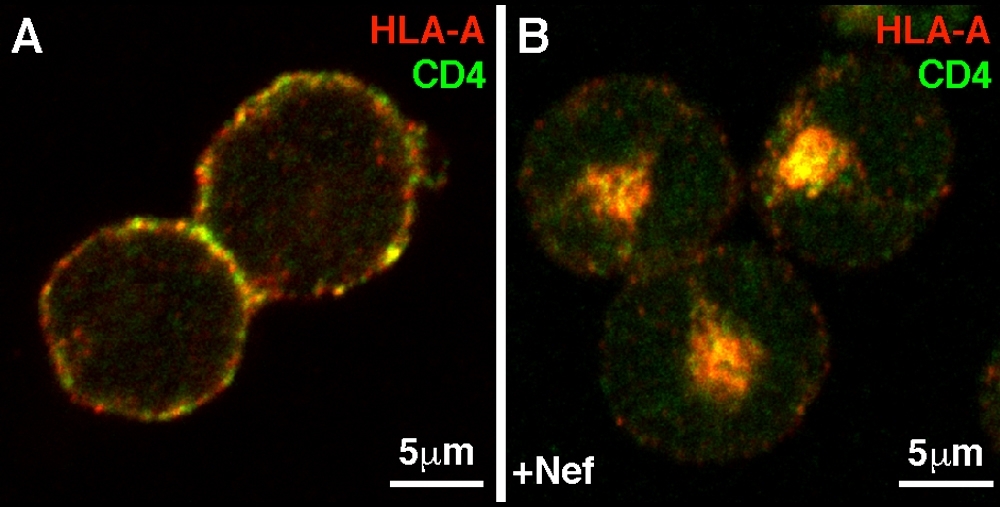
Research shows how Nef subverts human cells’ defense mechanisms to enable HIV to advance; Brazilian scientists comment on progress in this area in Nature group journal article.
Monoclonal antibody tested by researchers at University of São Paulo and experimental drug given to patients in Italy by University of Pennsylvania research group promoted rapid improvement of respiratory function in patients hospitalized in severe condition.
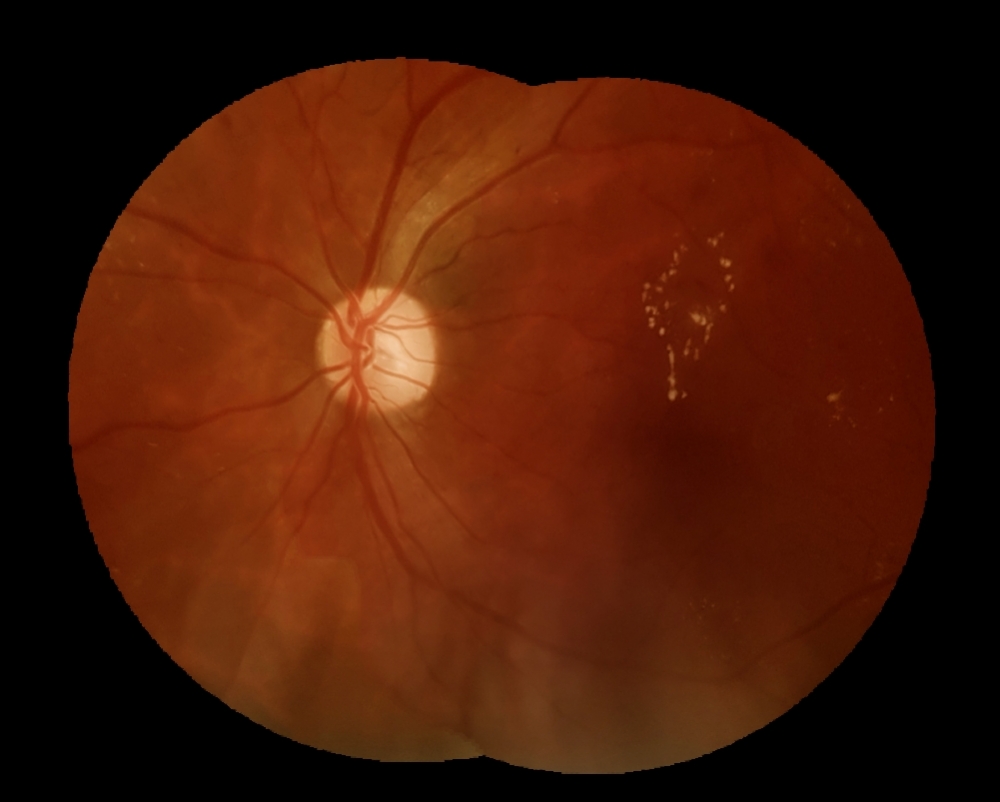
Researchers examine retinas and find high prevalence of type 2 diabetes as well as ocular problems caused by the disease.
Brazilian researchers discovered that sTREM-1 protein in immunoglobulin family could be a very useful biomarker to help medical teams make clinical decisions.
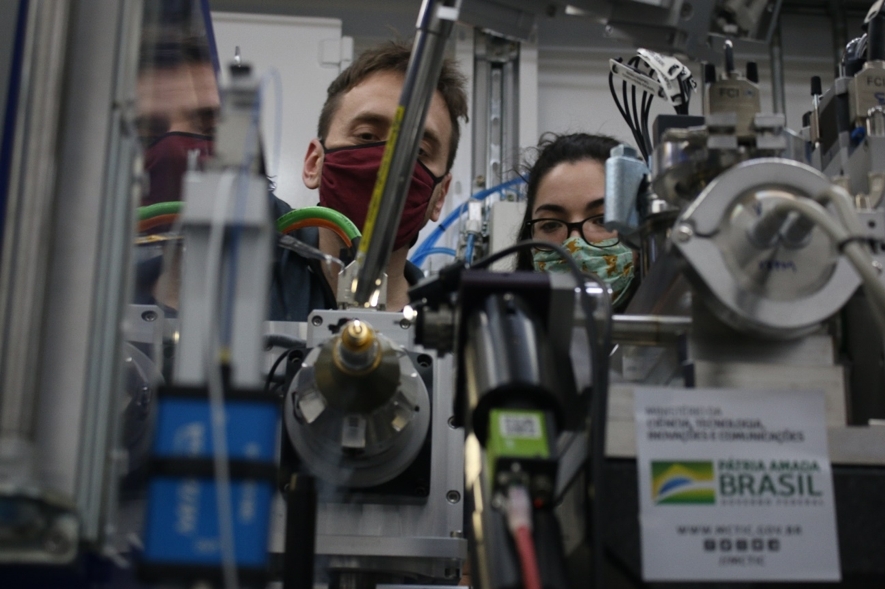

Sirius’s protein crystallography beamline analyzed more than 200 protein crystals from the novel coronavirus as they were exposed to tiny fragments of widely used drugs. If a compound fits perfectly into a target protein, its action can be blocked in the virus.

Devices developed by Brazilian startup BioLambda decontaminate face shields, surfaces, workspaces and air.
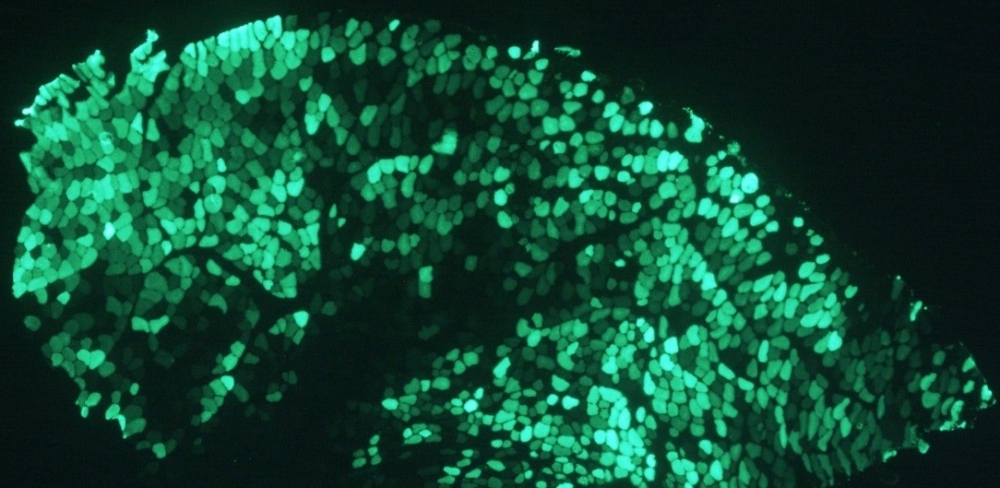
Intervention was tested in mice by Brazilian researchers. Study showed that targeted stimulation of PKA production promoted muscle growth and enhanced resistance to fatigue.
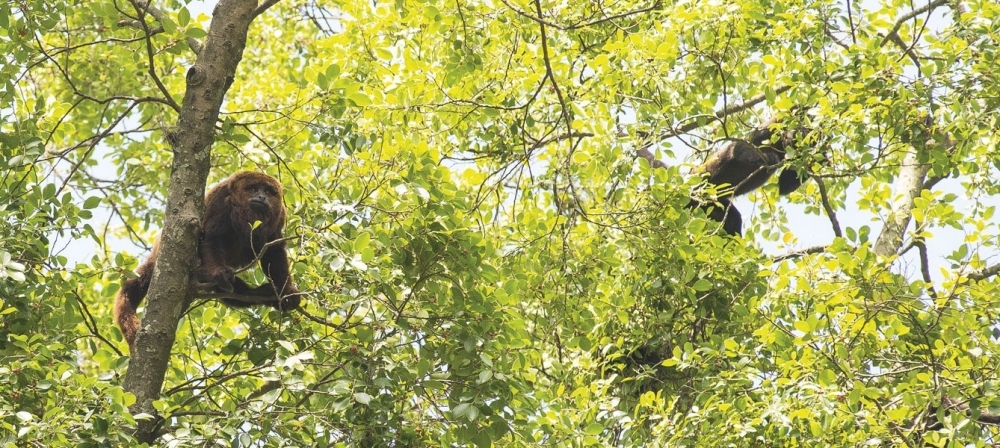

Three waves of the disease swept the state between 2016 and 2018. An international group of researchers described how the virus spread in a study published in PLOS Pathogens based on the sequencing of 51 viral isolates extracted from mosquitoes and monkeys.
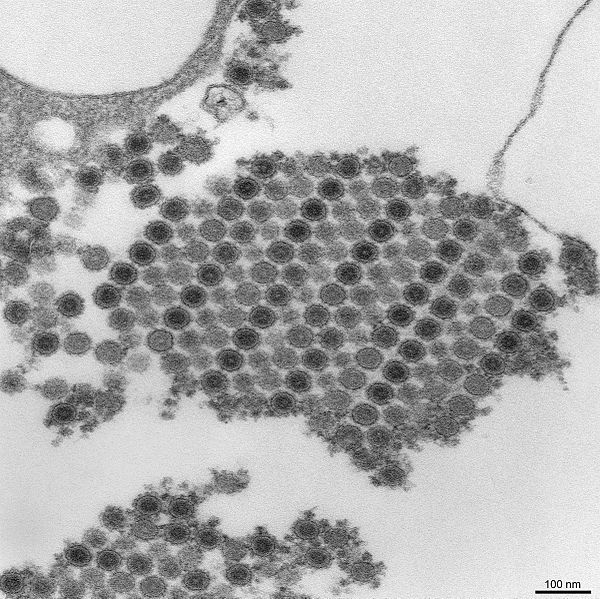
Investigation conducted by international group of researchers showed that chikungunya virus can cause neurological infections. Risk of death in subacute phase is higher for patients with diabetes and significant for young adults.
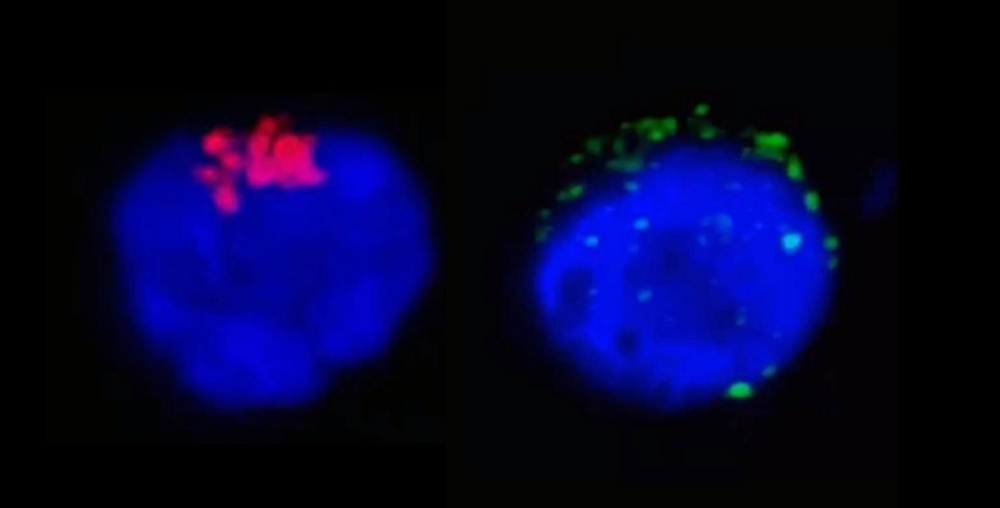
Experiments conducted by Brazilian researchers with lymphocytes isolated from COVID-19 patients showed the virus using the protein CD4 to invade cells that play a key role in coordinating the immune response.
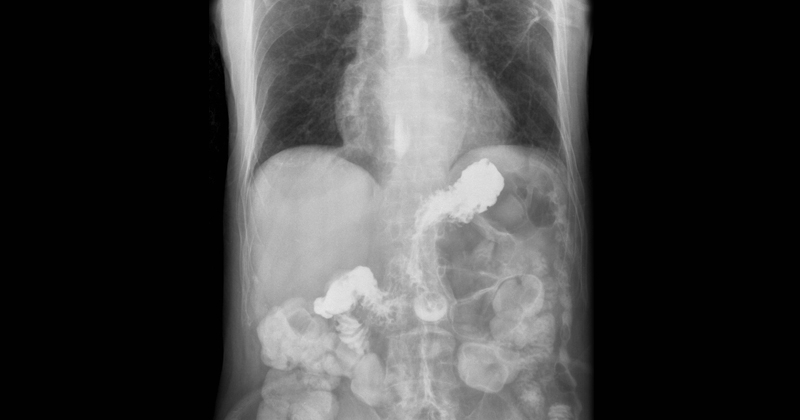
Analyses by Brazilian researchers suggest alterations to pH caused by stomach acid lead to increase in expression of ACE2 and make cells more susceptible to infection by novel coronavirus.

Analysis identified 525 genes encoding proteins that act on the nervous system, cardiovascular system and cell walls. One of the molecules proved effective against cancer cells in preliminary test results.

Renowned scientists will address topics related to how society has been coping with this threatening environment and will discuss factors that influence behavioral change.

Adaptation of muscle tissue to aerobic exercise alters the metabolism of muscle stem cells, helping them recover from injury. Findings may contribute to treatment of cachexia, sarcopenia and other conditions associated with lean mass loss.
Findings reported by Brazilian researchers in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases help explain why only some babies whose mothers are infected during pregnancy are born with microcephaly and other anomalies.
Brazilian researchers found the novel coronavirus replicating inside immune cells from patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Experiments on lymphocytes infected in the laboratory showed that viral entry induced programmed cell death.
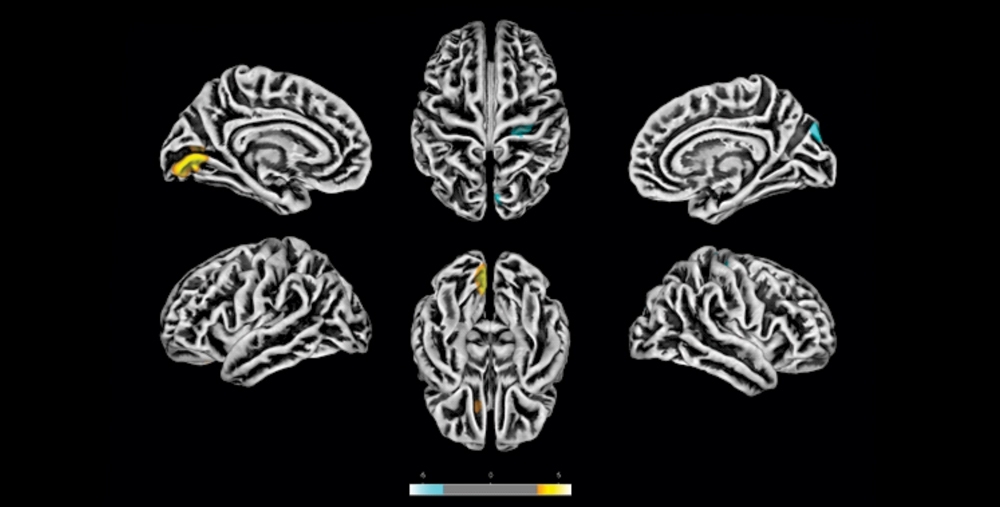
Led by research groups from the universities of Campinas and São Paulo, the investigation combined MRI scans of mild COVID-19 patients, analysis of brain tissue samples from patients who died from COVID-19, and experiments performed with human nerve cells infected in the laboratory.
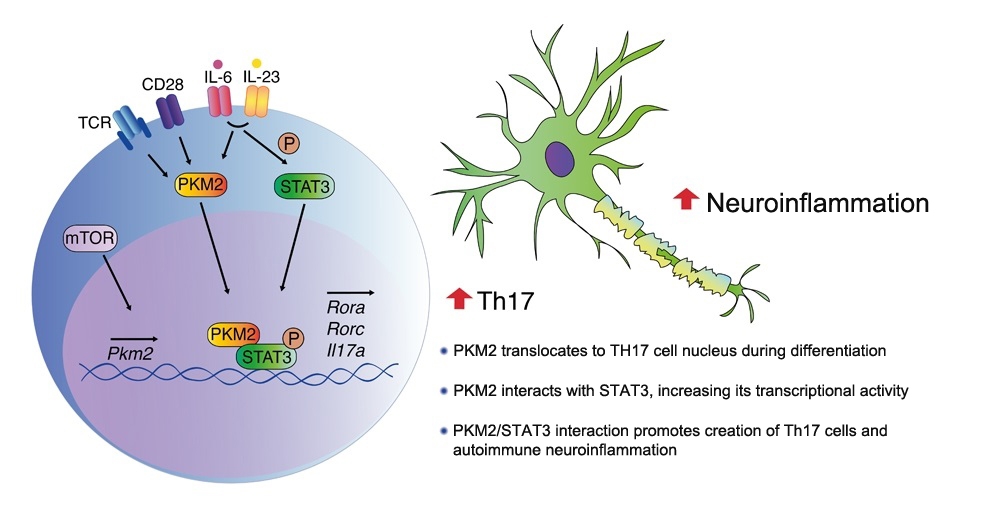
In an article published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine, a group affiliated with a FAPESP-supported research center reports that an enzyme associated with energy production in cells also participates in the differentiation of immune cells involved in exacerbated inflammation. The discovery could lead to more effective treatment.
Study conducted at São Paulo State University demonstrates for first time that simple and inexpensive strategy yields better results than conventional treatment and avoids indiscriminate use of antibiotics.

Methodology developed by Brazilian researchers is based on analysis of metabolites in blood serum. Innovation has been patented and reported in Journal of Psychiatric Research.
Study led by researchers at Oxford University suggests that after successive infections by the coronaviruses that cause common colds throughout life the defense system becomes specialized and cannot recognize emergent varieties such as SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion presented by Brazilian researchers in Obesity Research & Clinical Practice is based on analysis of nine clinical studies involving 6,577 patients infected by SARS-CoV-2 in five countries.

Model developed by Brazilian researchers predicts spatial and temporal evolution of epidemic diseases and can help plan more effective social isolation programs with less socio-economic impact.