

Testing has begun in Brazilian volunteers of two candidate vaccines at an advanced stage of development. In an online seminar co-organized by Agência FAPESP, researchers involved in Phase 3 clinical trials said the more vaccines are approved, the better mankind’s chances of controlling COVID-19.

Platform created by FAPESP in partnership with University of São Paulo, Albert Einstein Jewish Hospital, Hospital Sírio-Libanês and Fleury Group begins providing access to data for more than 177,000 patients, 5 million clinical examinations and 9,600 outcomes.

Project supported by FAPESP aims to help triage suspected COVID-19 patients.
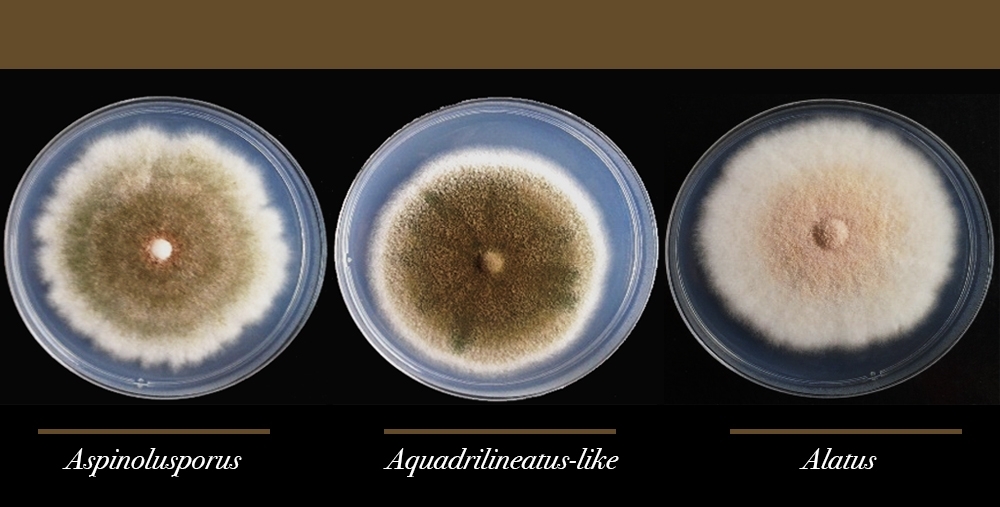
This is the first time Aspergillus latus has been found in a hospital. The species is more drug-resistant than its two parents and highly dangerous for patients with respiratory diseases and compromised immune systems. The researchers will now investigate the role of fungi in COVID-19.
Assembled over a five-year period by the University of São Paulo’s Medicinal Chemistry Group, the material will be tested for treating infected cells. The goal of the research is to find a compound that inhibits the key enzyme in the replication of SARS-CoV-2 without affecting human cells.
The open-access tool was developed in Brazil by researchers at the Center for Mathematical Sciences Applied to Industry to minimize the risk of shortages and overspending.

In laboratory tests, the material inactivated 99.9% of SARS-CoV-2 in two minutes. The technology developed by the startup, which is supported by FAPESP, will be used to produce face masks and hospital apparel.
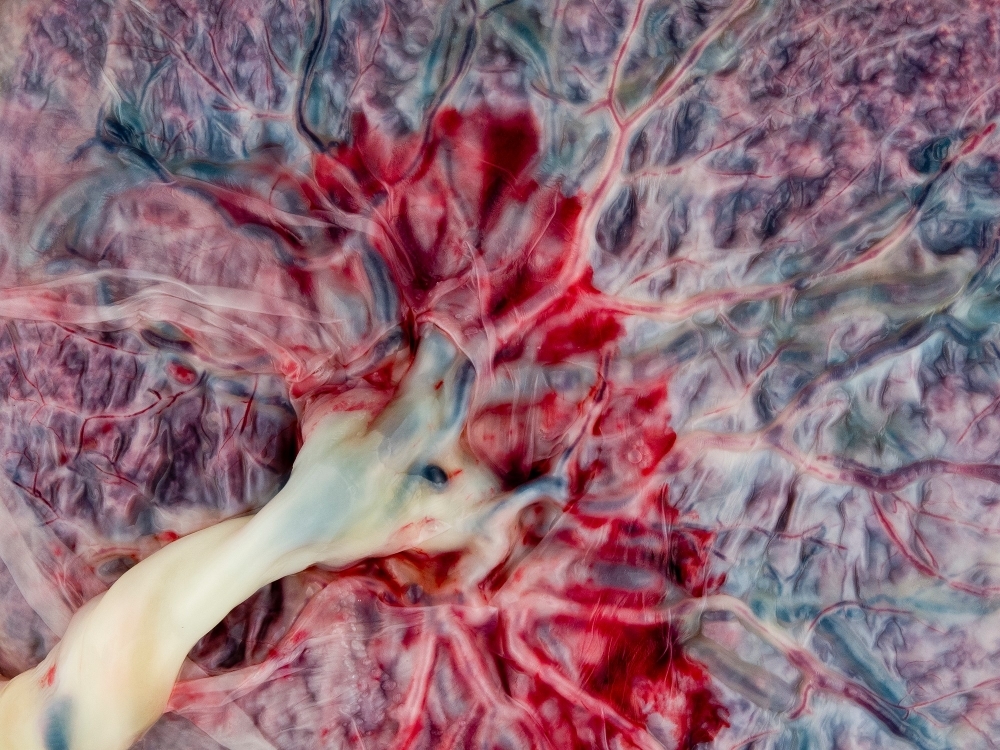
Based on placental cell gene expression data and computer simulations, Brazilian researchers concluded that the virus may use the placental proteins DPP4 and CTSL as an alternative point of entry into human cells.

The study will analyze how the disease affects different communities in Brazil and the US based on social and demographic characteristics related to drivers of environmental vulnerability.
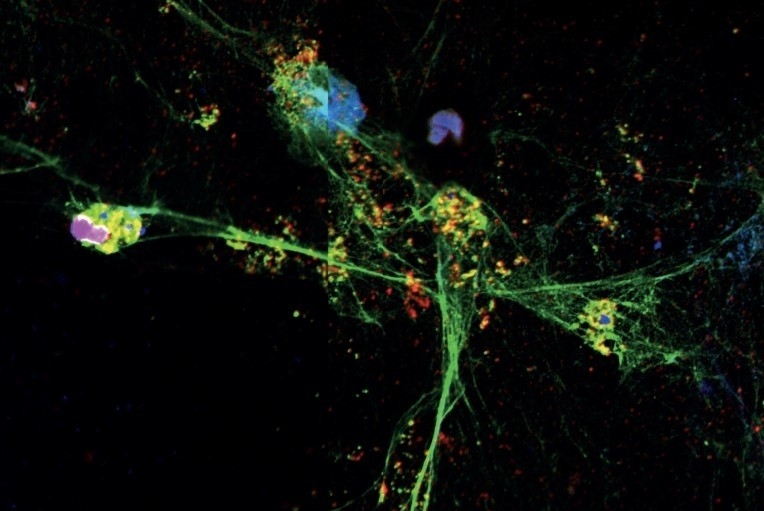
Study conducted by the FAPESP-funded Center for Research on Inflammatory Diseases (CRID) shows that drug currently used to treat cystic fibrosis can help prevent complications from infection by SARS-CoV-2.

The website developed by researchers at the University of São Paulo includes videos, illustrations, texts and posters with information on the right way to put on and take off masks, gloves, gowns and other items.

Synthetic compounds and molecules derived from natural products belonging to Brazil’s biodiversity are being screened by teams at the Center for Innovation in Biodiversity and Drug Discovery, which is supported by FAPESP.
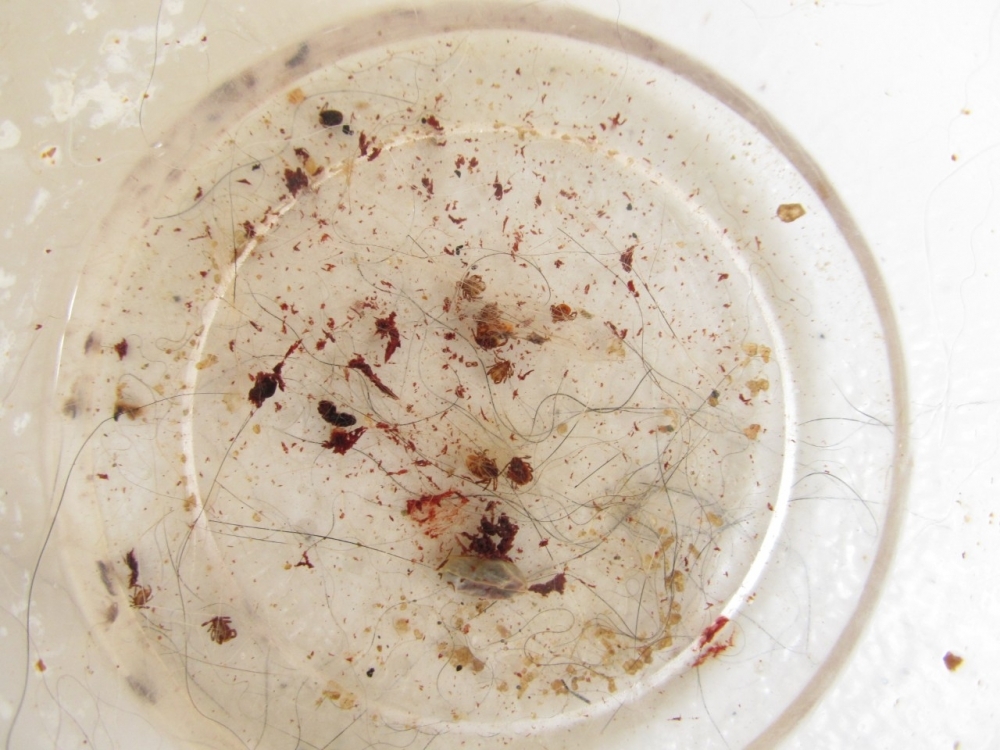

Experiments were conducted by scientists affiliated with the Center of Excellence in New Target Discovery, a research center supported by FAPESP, involving five animals with spontaneous skin tumors.
The project is supported by FAPESP’s Innovative Research in Small Business Program. The firm plans to produce ELISA kits that will detect antibodies against the novel coronavirus in blood serum.
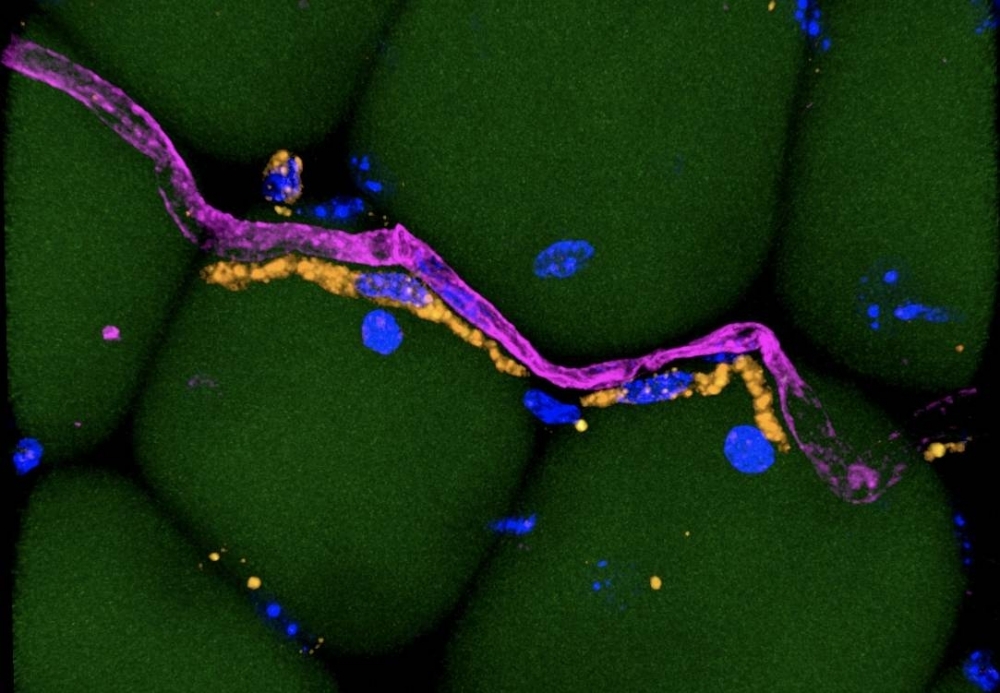
Brazilian researchers are the only Latin American group to have had a project selected in an international request for applications by the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative. Funding of more USD 175,000 has been awarded to the study, which will be the first in Brazil to use single-cell analysis.

Researchers at the University of Campinas tested the Brazilian immunotherapy drug OncoTherad on five patients who contracted the disease while being treated for bladder cancer. The drug attenuated the inflammation in their lungs and shortened their hospital stay.
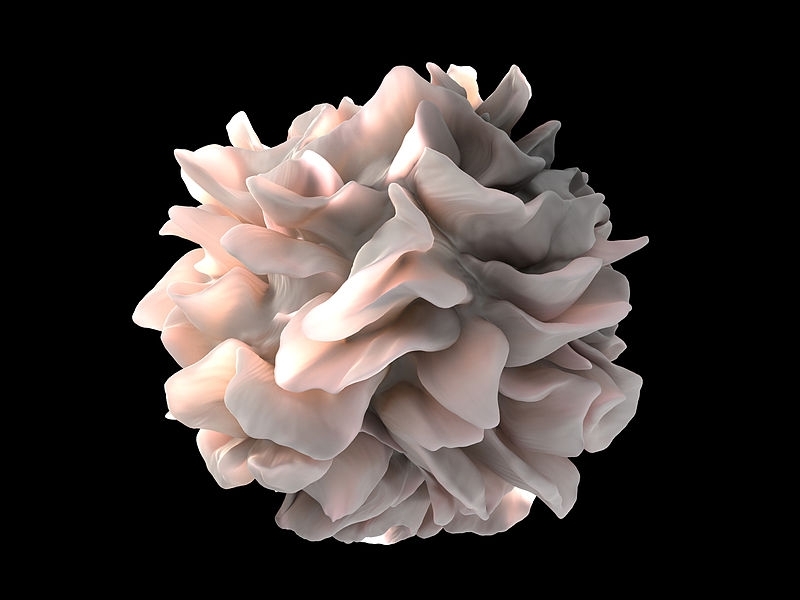
A formulation could be used in patients at risk of respiratory failure to prevent their condition from deteriorating. This methodology has been used to treat HIV/AIDS by an international group of scientists led by Brazilian researchers.

In a review article published in the American Journal of Physiology, Brazilian researchers present scientific evidence on the impact of short periods of inactivity on the cardiovascular system and recommend exercise to stay fit at home during the pandemic.
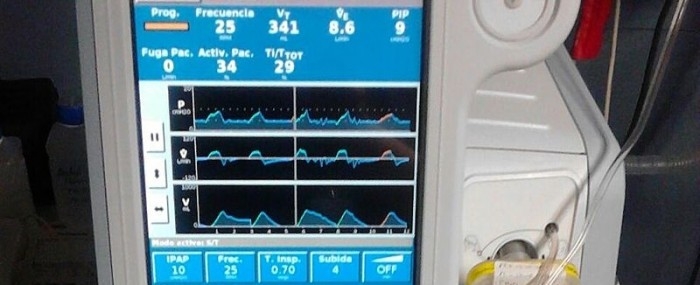
Through a project supported by FAPESP, the São Paulo-based firm Setup is developing two portable ventilators. More robust and easier to operate than standard devices, they are designed for use in ICUs and field hospitals.

Company supported by FAPESP is developing a smart visible and thermal spectrum imaging system to spot people with fever in schools, malls or offices.

Pre-clinical trial will identify the formulation and concentration capable of inducing a rapid and lasting immune response, before further development and testing.
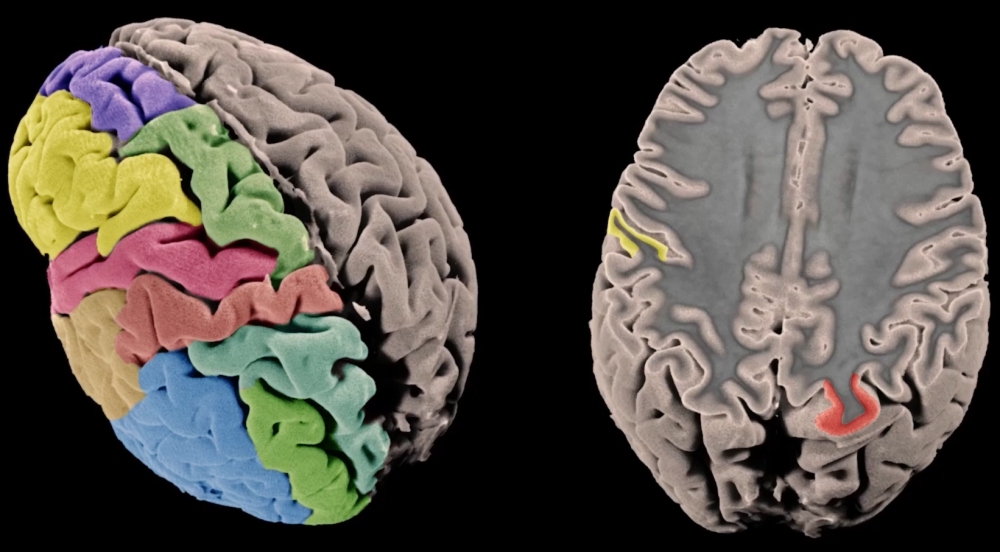
Based on quantitative MRI, researchers measured cortical volume in 51,665 participants and correlated the data with genetic markers.
Scientists affiliated with a research center supported by FAPESP set out to understand the strategies used by immune cells to combat the most severe phase of the disease.
A study supported by FAPESP is investigating the possibility that estrogens inhibit the progression of the disease. The goal is to find medications for the treatment of COVID-19.
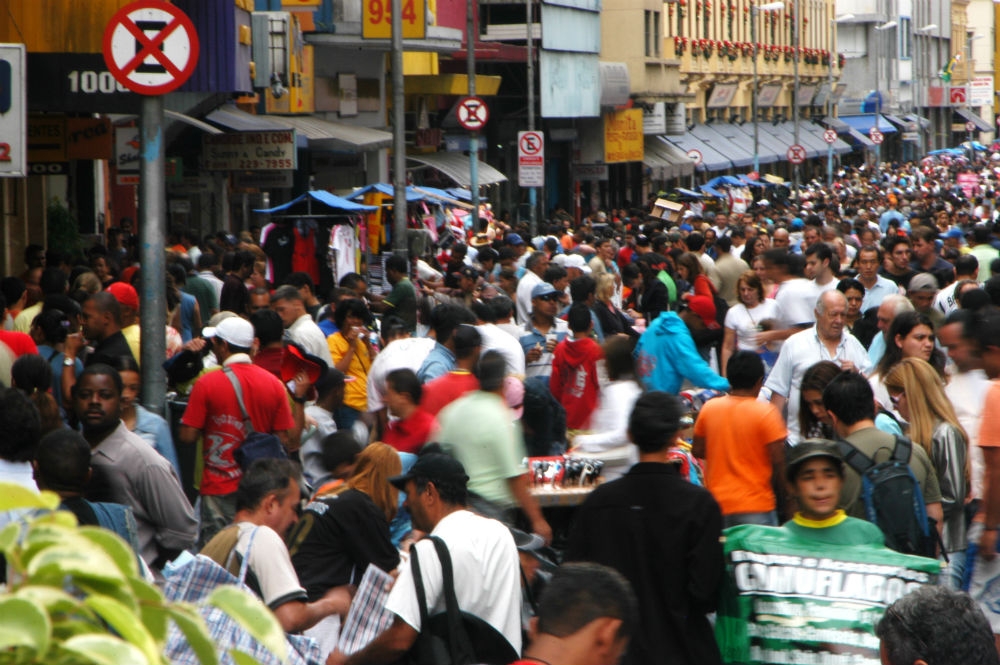

Only 13.8% of the workforce has jobs in sectors not badly hit by social isolation according to a research network set up to propose ways of improving the quality of government policies for dealing with the crisis.