

Specialists discussed the situation in a webinar held by Agência FAPESP and Canal Butantan. However, they stressed that achieving herd immunity should not be public policy, as clearly shown by the tragic death toll suffered in Manaus, the state capital of Amazonas.

The method identifies and distinguishes between flaviviruses that cause many diseases in humans and animals in Brazil.

Participants are members of the São Paulo arm of a study conducted in six Brazilian states beginning in 2008. The goal is to compare mental health before the pandemic to that during the pandemic in both healthy individuals and subjects suffering from anxiety and depression.
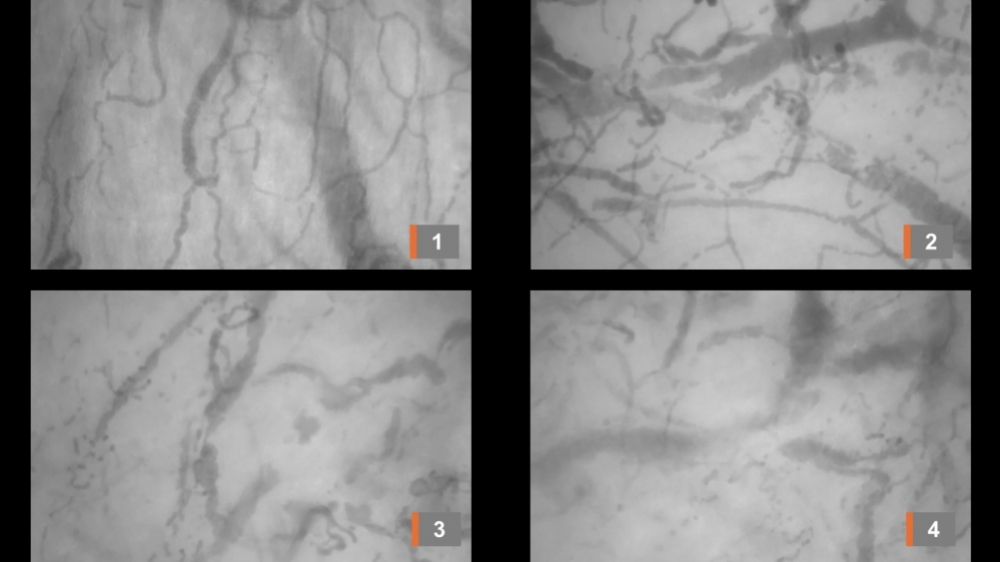
A study involving 13 patients requiring intubation for mechanical ventilation reinforces the theory that coagulation disorders resulting from an exacerbated inflammatory response to SARS-CoV-2 may explain some of the most severe symptoms of the disease.

A study of São Paulo city shows that neighborhoods with more hospitalizations and deaths from coronavirus coincide with areas whose inhabitants have been unable to shelter at home.

Applied to skin as a piece of sticking plaster, the device developed by Brazilian researchers can be used to monitor human metabolism and administer drugs.

Through a project supported by FAPESP, the São Paulo-based firm is developing an RT-qPCR diagnostic kit in which all reactions take place in a single tube.
In a laboratory experiment with rats, Brazilian researchers succeeded in reversing natural processes associated with aging that lead to loss of bone density and strength.

Ten units of the device developed at the university’s Engineering School (POLI-USP) began operating at Hospital das Clínicas in July.
Researchers from Portugal, the UK and Brazil produced the estimate using a mathematical model that takes into account variations in the risk of catching the disease within different population groups. Despite being good news, the finding does not diminish the importance of non-pharmaceutical interventions to contain transmission, the authors stress.
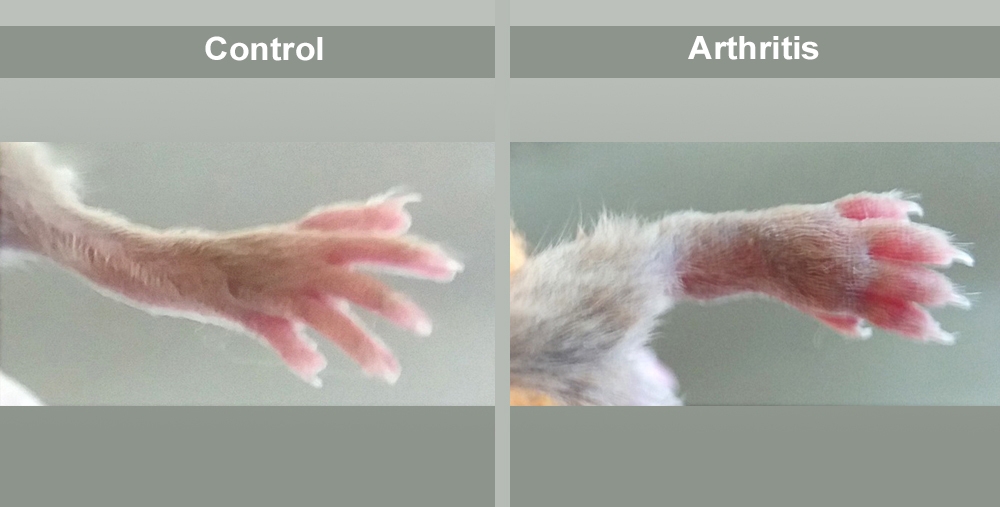
Tested in mice with genetically induced arthritis, the substance decreased the area affected, reduced local swelling, and assuaged the pain associated with the inflammatory process.
Autopsies performed on COVID-19 patients treated at the largest hospital complex in Latin America show that some died mainly as a result of cardiovascular alterations.
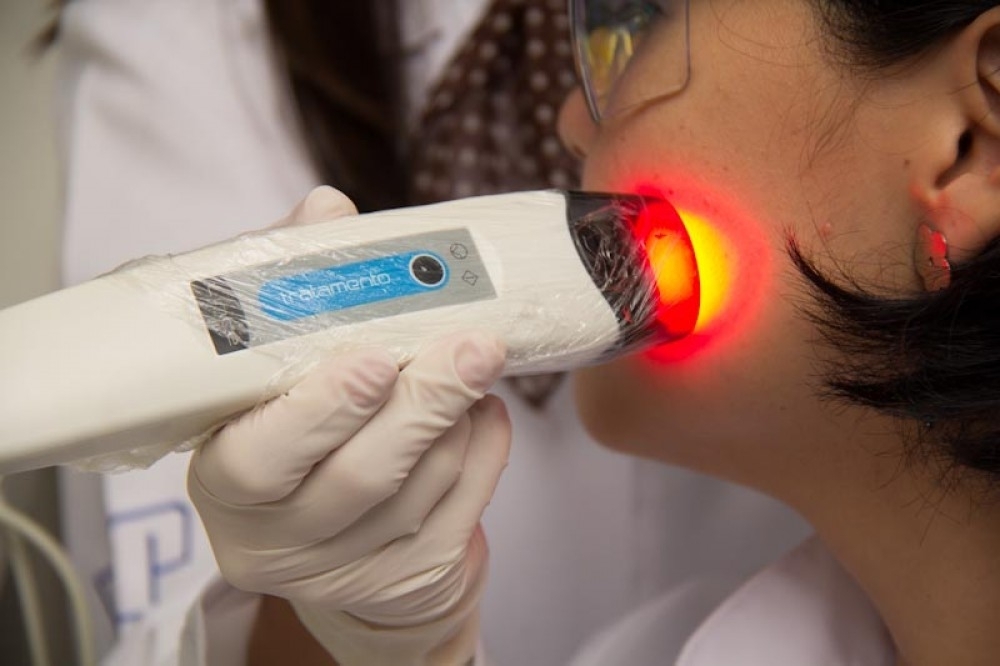
Researchers at the Optics and Photonics Research Center, supported by FAPESP, advocate the technique as an additional treatment for patients with the disease.
Researchers from Brazil, Mexico, Nigeria and the US took part in a webinar organized by FAPESP to discuss privacy and data security and how people’s behavior shapes the pandemic
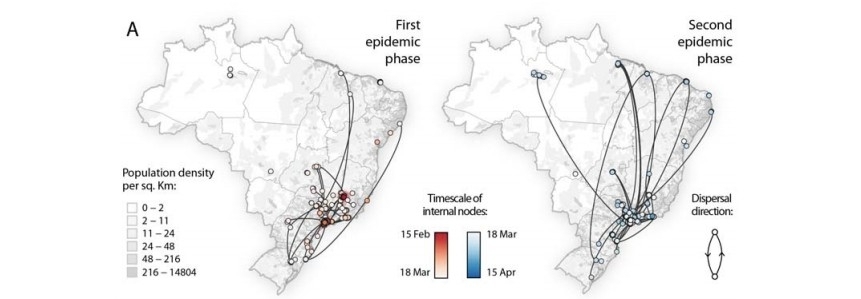
Study determined how the disease was transmitted using genomic data for SARS-CoV-2 obtained by sequencing almost 500 viral isolates from Brazilian patients and cross-referencing this with air travel data and deaths from the disease in the period.

Researchers have correlated information on drugs, genes and diseases to identify potential candidates for psychiatric and neurological treatment. The methodology they developed will be used to search for drugs against COVID-19.
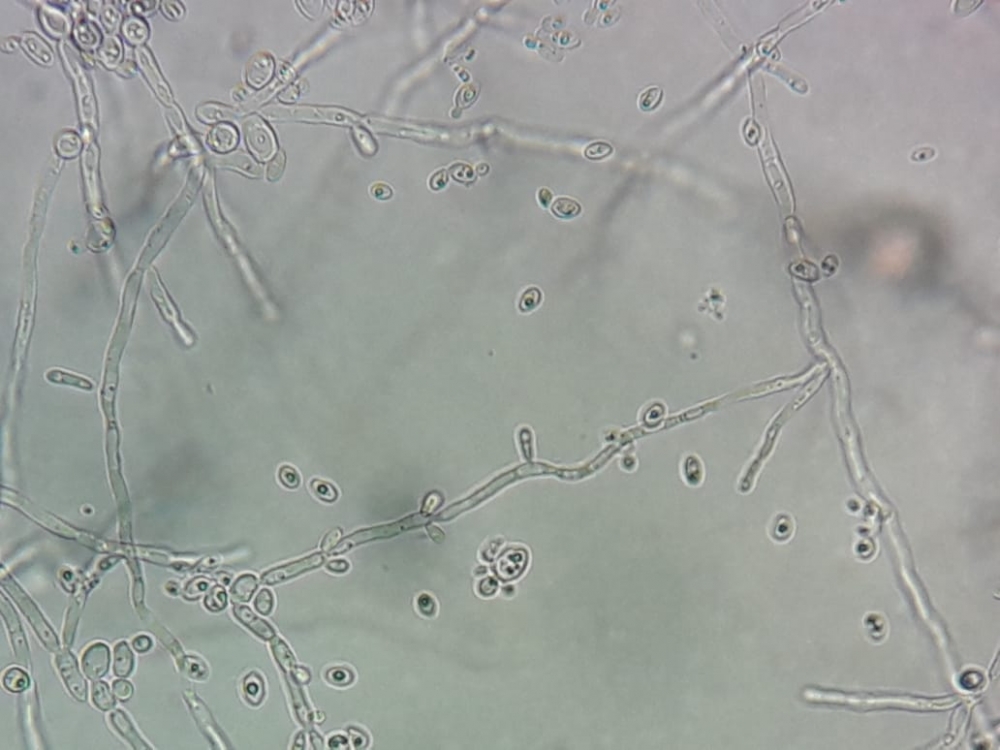
Present in the human digestive tract, species of Candida can cause bloodstream infections in patients treated in intensive care units. An international study involving 16 hospitals found isolates with high levels of virulence.
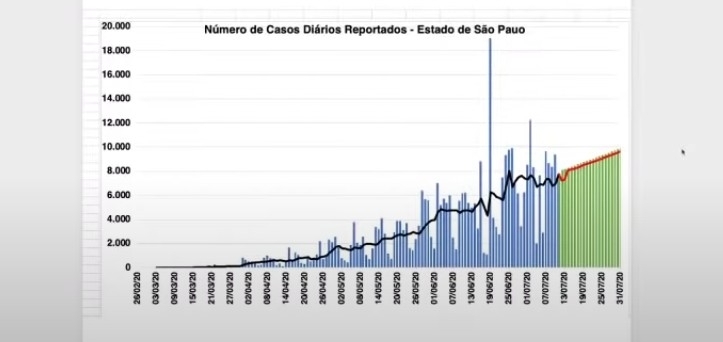
The contagion curve in Brazil appears to have plateaued and is set to remain at the current level until at least the end of 2020. Investing in the identification and isolation of infected people and their close contacts, keeping schools closed and improving the quality of the information offered to the public are measures governments should take to make sure the situation does not become even worse.
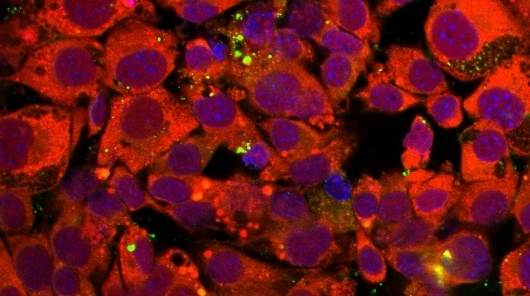
A study showed that the novel coronavirus can infect human adipocytes and that the viral load is three times higher in aged adipose cells. The results may help us understand why people with obesity and those who are older are more at risk of developing the severe form of COVID-19.

Online survey with 11,863 respondents also shows that feeling sad or depressed became routine for 39%, while overall health worsened for 26%.

Researchers used statistical techniques to analyze data of 126 countries. The variables that intensified contagion at the start of the outbreak included low temperature, a large proportion of older people, foreign tourist arrivals, and greeting habits involving physical contact.
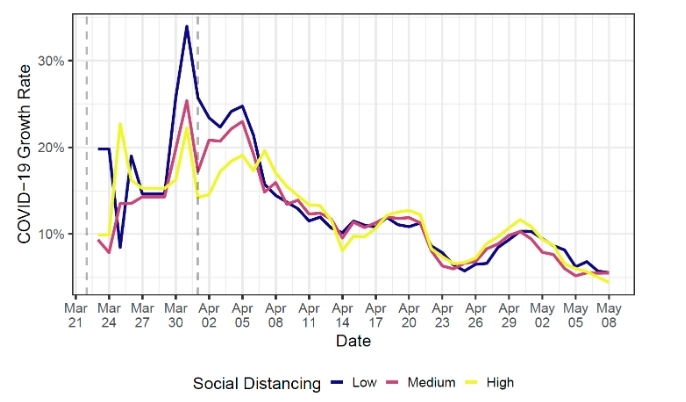
The reduction resulting from implementation of these measures in São Paulo has been calculated for the period between mid-March and early May using a mathematical model developed by a FAPESP-funded research center. The scientists also estimated that these two public health measures reduced the peak of transmission by 25% in Brasília.

Program developed by startup with FAPESP’s support was initially designed to train cognitive skills and help improve physical fitness but will now have extended functionality.
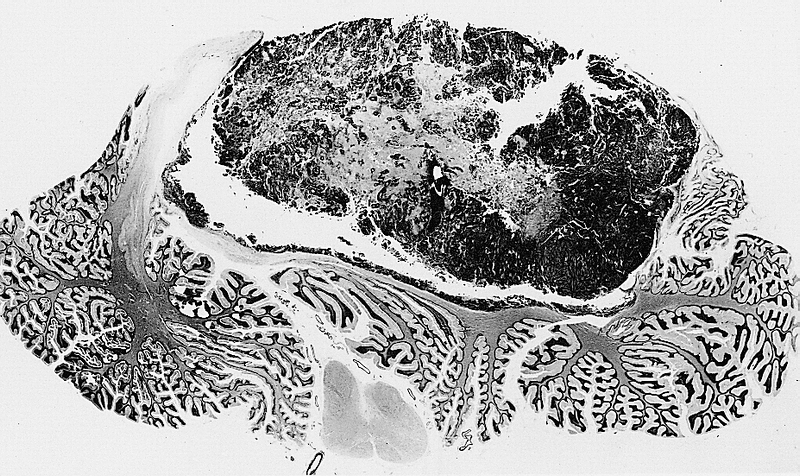
When tested in vitro, arsenic trioxide killed tumor cells and prevented the formation of new colonies. This leukemia drug also boosted the effect of radiation therapy on medulloblastoma, a type of central nervous system tumor most common in children
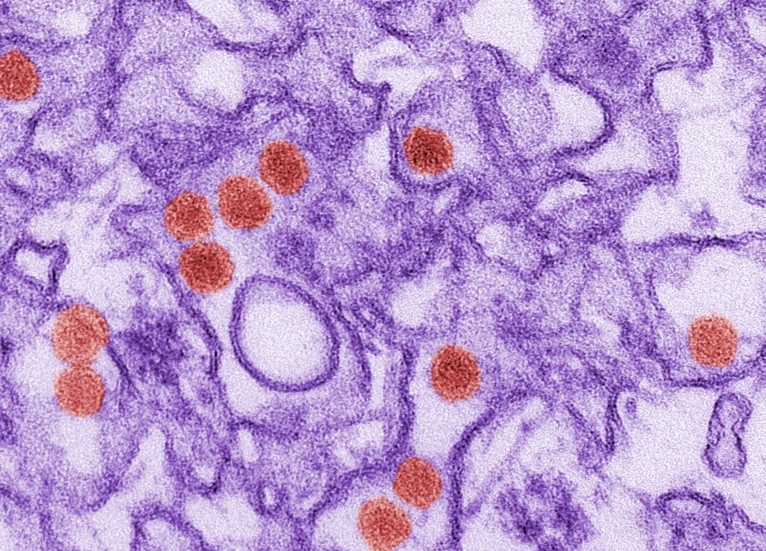
The compound inhibited the action of a protein activated by the virus to suppress the host’s immune response. The therapy also proved effective against dengue virus and will be tested at the University of São Paulo against coronavirus.