


When researchers reanalyzed datasets from more than 1,000 patients, they found differences between men and women in the expression of genes associated with the functioning of immune cells and the production of inflammatory molecules. The findings point to possible targets for treatment of both sexes.
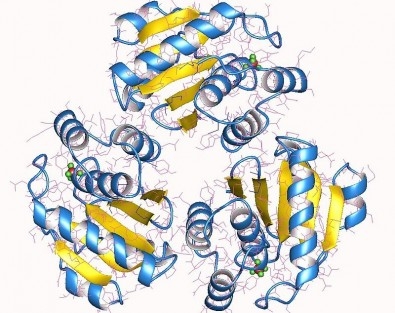
After 14 years studying the action of the enzyme LMWPTP in tumor cells, Brazilian researchers conclude that the molecule is associated with chemotherapy resistance and metastasis.
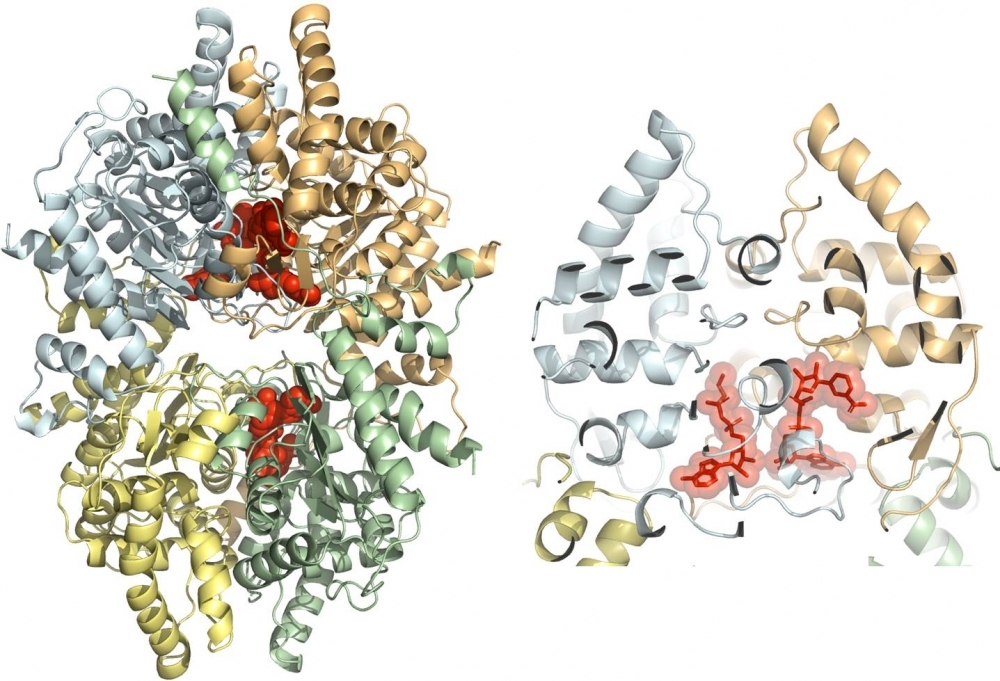
Discovery by Brazilian scientists paves the way for the study of more potent molecules capable of directly destroying parasites underlying elephantiasis and cutaneous leishmaniasis, with fewer adverse side-effects.
Technology to manage hospital flows is being tested by health units in metropolitan São Paulo.

The Brazilian research group used epigenetic modulators to try to “erase” the damage done by stress to neuroplasticity. The study showed that acute intervention in epigenetic mechanisms produces antidepressant-like effects more rapidly than conventional drugs.
The raw materials and inputs for vaccines are produced in different countries and subject to undersupply risk, said speakers in a webinar on Facing the Challenges of Vaccine Distribution organized by FAPESP.
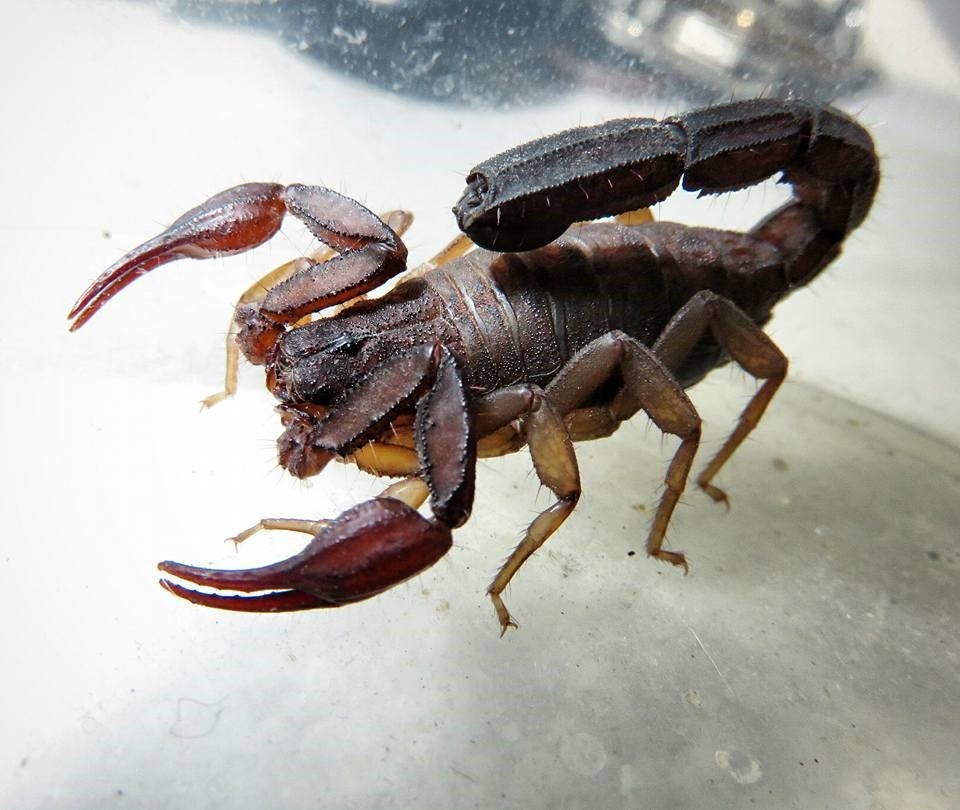

Brazilian researchers tested the antichagasic properties of VmCT1, obtained from the venom of Vaejovis mexicanus, a scorpion harmless to humans, and synthesized novel analogs to redesign the native molecule.

The online survey was conducted in Brazil and completed by 938 survivors of the disease whose diagnosis was confirmed by RT-PCR or serological test. Those who regularly had at least 150 minutes per week of moderately intense aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of high-intensity training were considered sufficiently active, in accordance with the WHO’s recommendations.
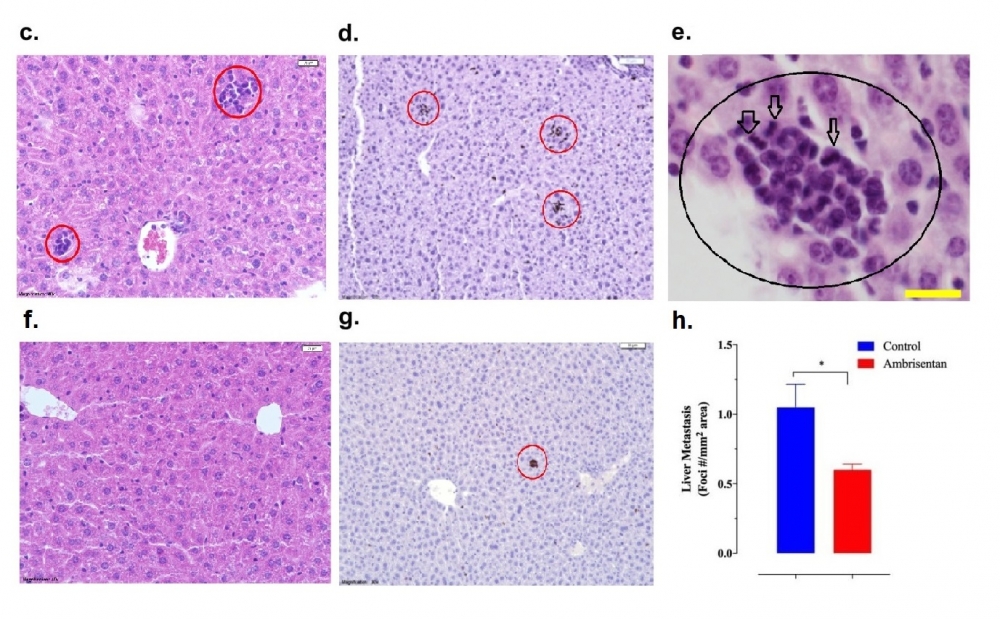
In experiments by Brazilian researchers with mice and tumor cell lines, the drug showed potential to combat metastasis. The scientists are planning to conduct clinical trials with patients who are on chemotherapy.
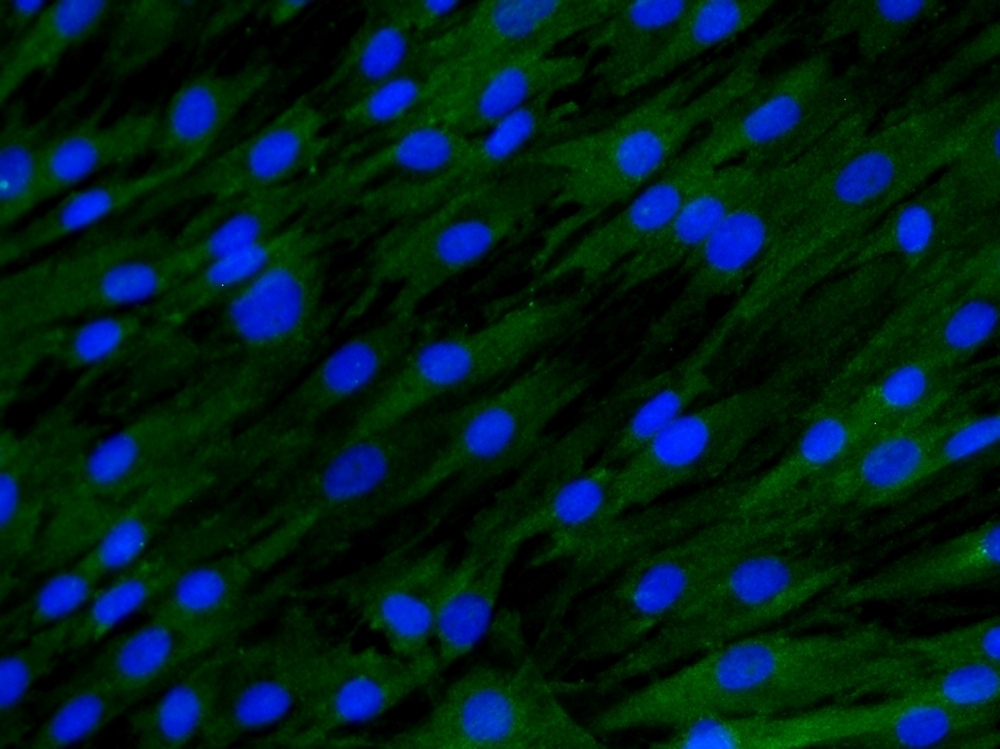
An in vitro study by a Brazilian researcher shows that maresin and resolvin synthesized from fatty acid stimulate periodontal ligament stem cells even in the presence of inflammation.
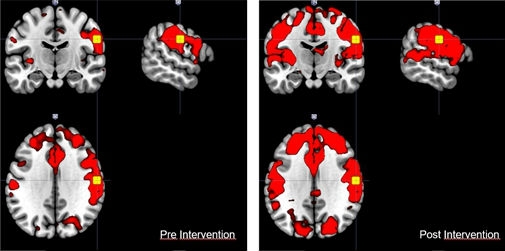
A study performed at one of the Research Centers supported by FAPESP resulted in development of a novel rehabilitation device. The article was recognized as outstanding by the 20th International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications.
Brazilian researchers show that commercial serological tests available in laboratories nationwide can be used to screen donated plasma in order to see if it contains enough antibodies capable of neutralizing the novel coronavirus
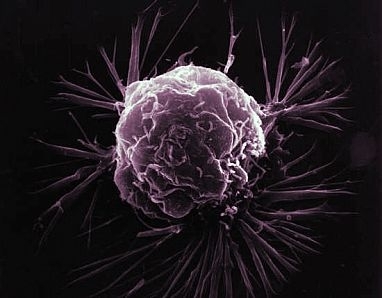
In an article published in the Journal of Pineal Research, researchers at São Paulo State University and collaborators describe a set of genes potentially regulated by the “sleep hormone” in some types of tumor
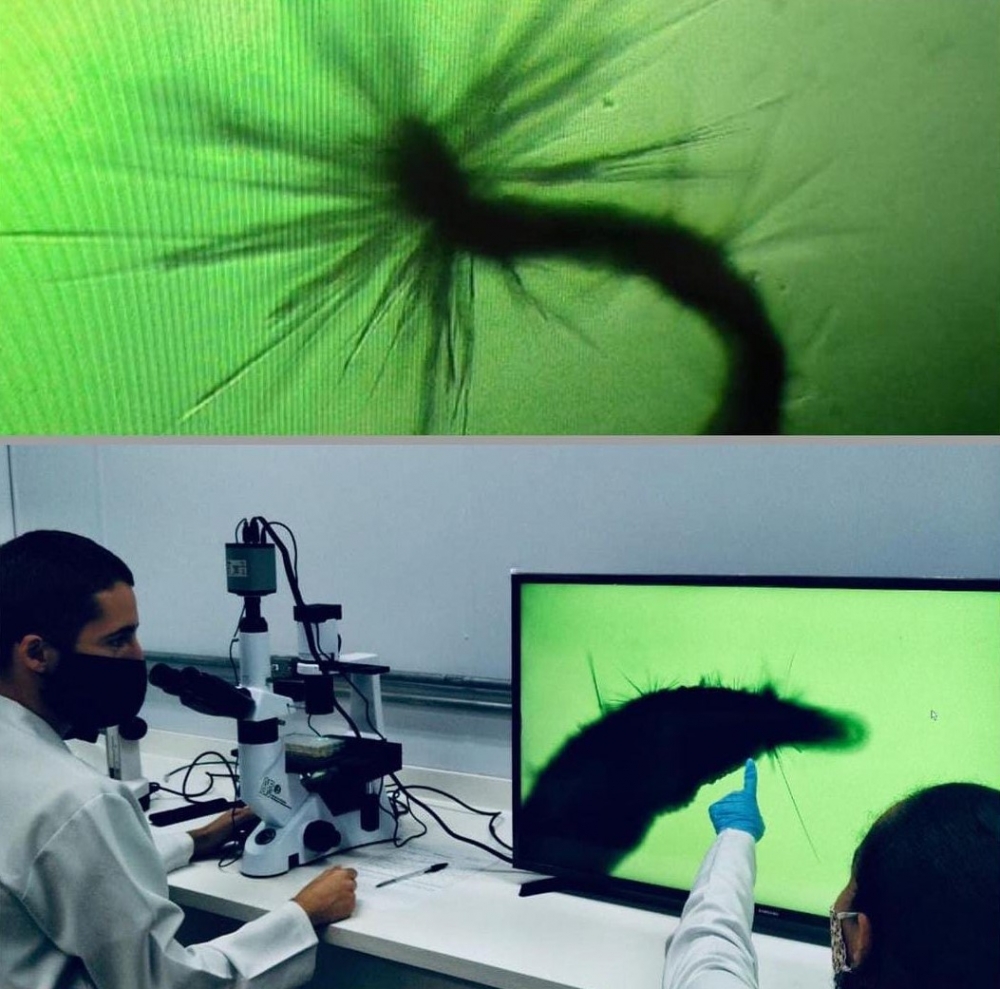
In vitro studies and experiments with mice show that the natural extract was more effective than the only drug available to combat this parasitic disease.
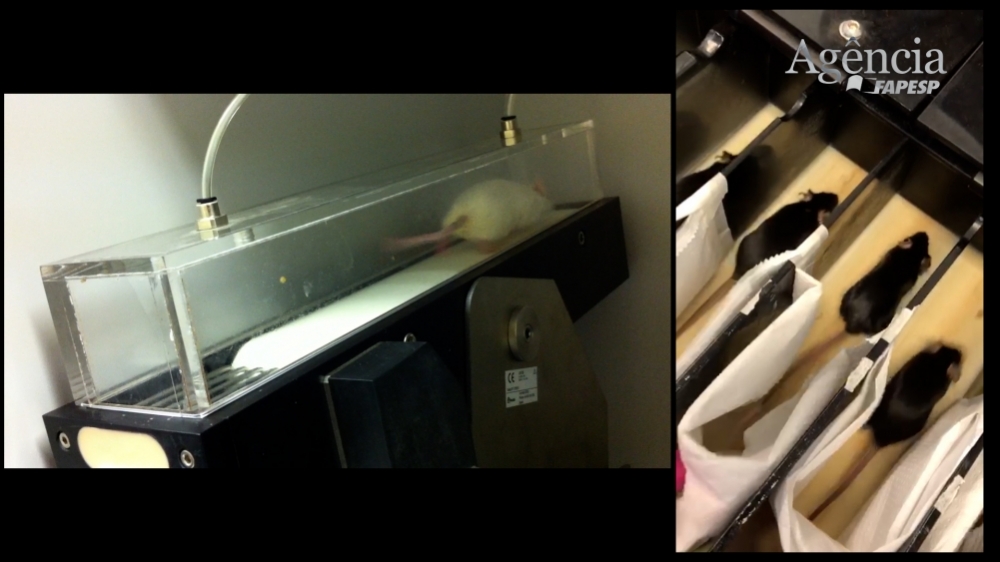

Experiments with mice and humans showed that exercise training increased the expression in adipose tissue of a key enzyme for the organism’s metabolic health, combating the harmful effects of aging and obesity.
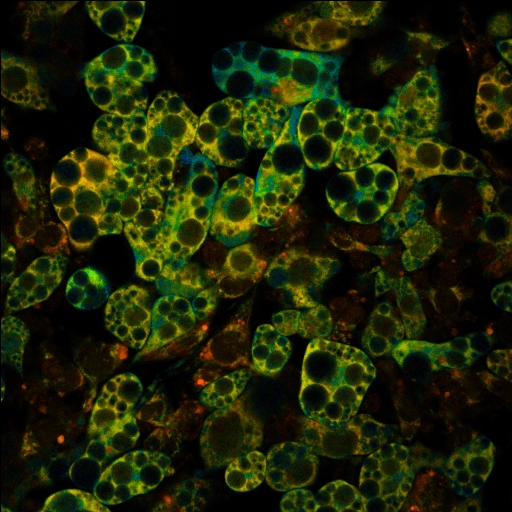
Medication originally developed to kill bacteria displayed the capacity to increase cell energy expenditure in tests with mice. Researchers at the University of Campinas and the biopharmaceutical AstraZeneca are testing compounds with a similar structure that could give rise to novel approaches to the treatment of obesity.
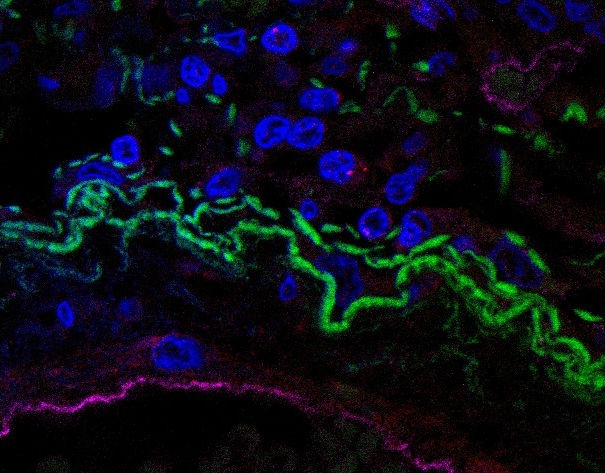
In defense cells from patients hospitalized with the disease, Brazilian researchers found signs of activation of a protein complex called the inflammasome, responsible for initiating the inflammatory response that can damage organs and lead to death. The findings could help identify drugs capable of interrupting the process.
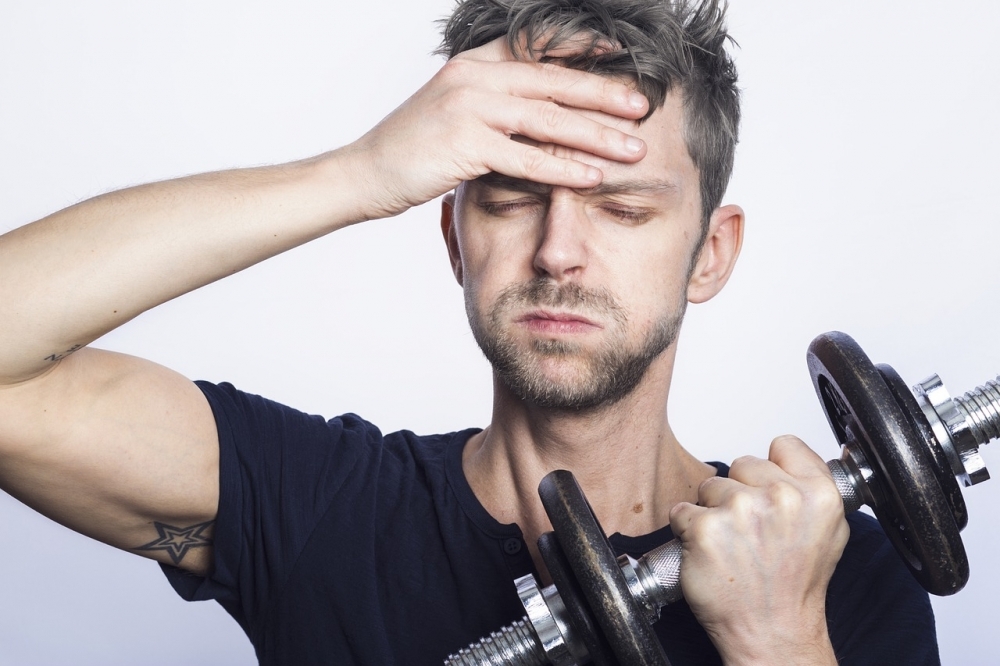

An article in Cell by researchers affiliated with Harvard and the University of São Paulo shows that the metabolite succinate is released by muscle cells during physical exercise and triggers a process of tissue remodeling that makes muscles stronger and enhances metabolic efficiency.
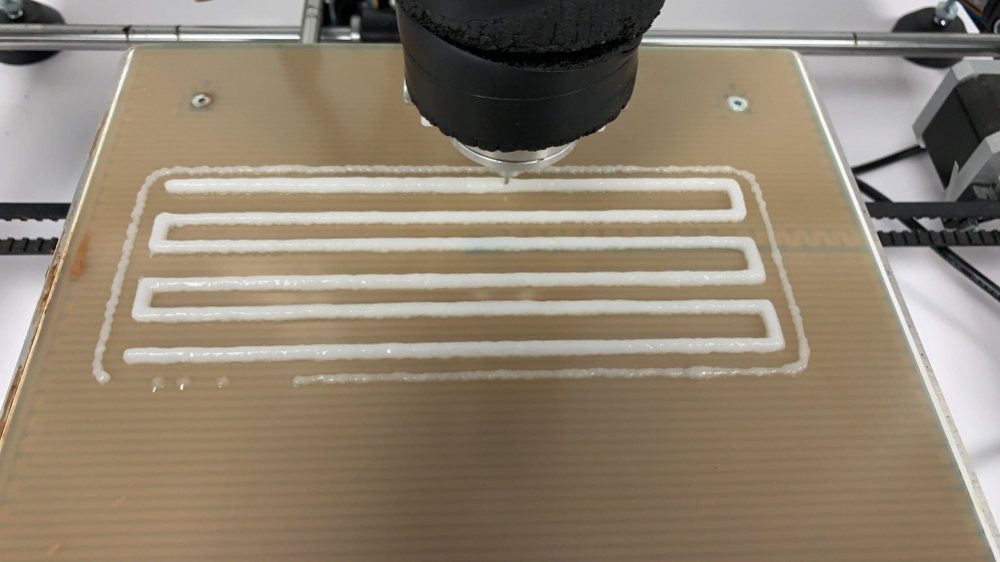
Food engineers in Brazil and France developed gels based on modified starch for use as “ink” to make foods and novel materials by additive manufacturing.

The special series “Field Diary” (“Diário de Campo”) features University of São Paulo scientists Marcelo Urbano Ferreira and Marly Augusto Cardoso on an expedition to Mâncio Lima, a small town in the Amazon where they collect samples from patients to investigate transmission of the novel coronavirus.
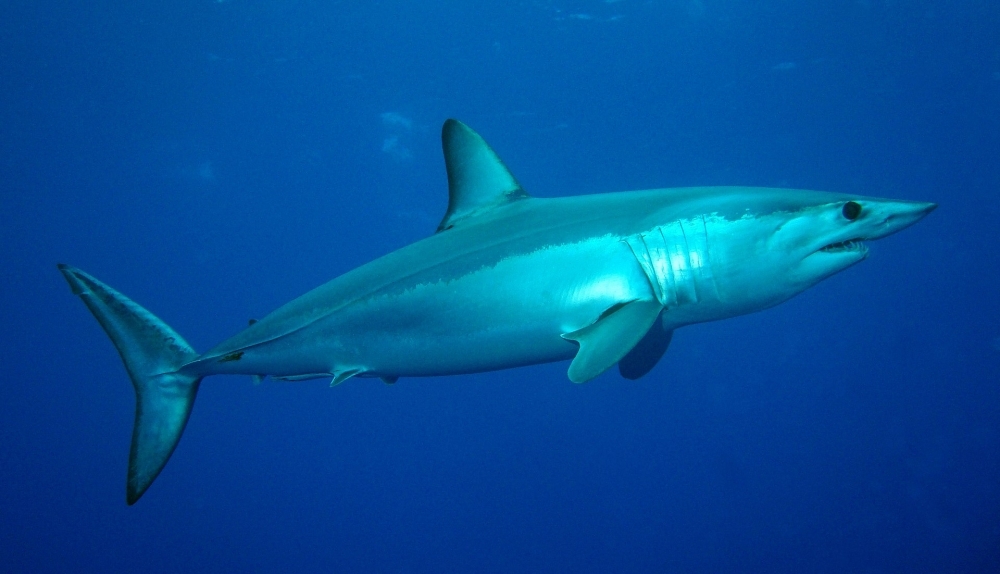

Genetic mapping of the shark’s liver and eye tissue showed overexpression of nine genes known for action in tumor suppression, wound healing, and probable monochrome vision. The species is considered globally endangered and caught on a large scale by industrial fishing vessels.
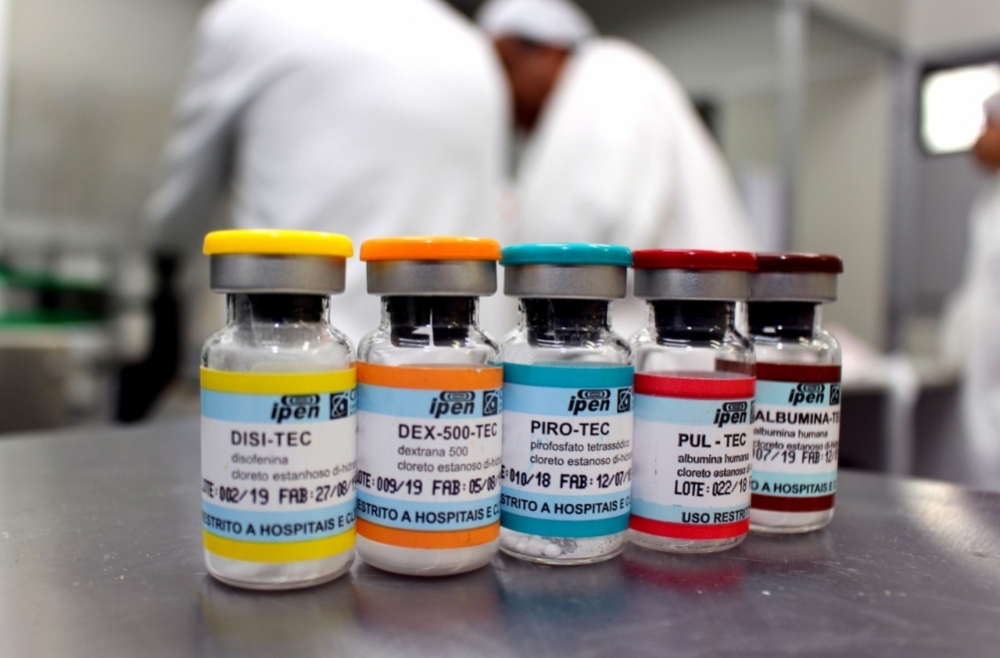

With FAPESP’s support, the Nuclear and Energy Research Institute is assembling a world-class laboratory that associates nanotechnology with radiopharmacy. The aim is to develop new products, mainly for cancer treatment.
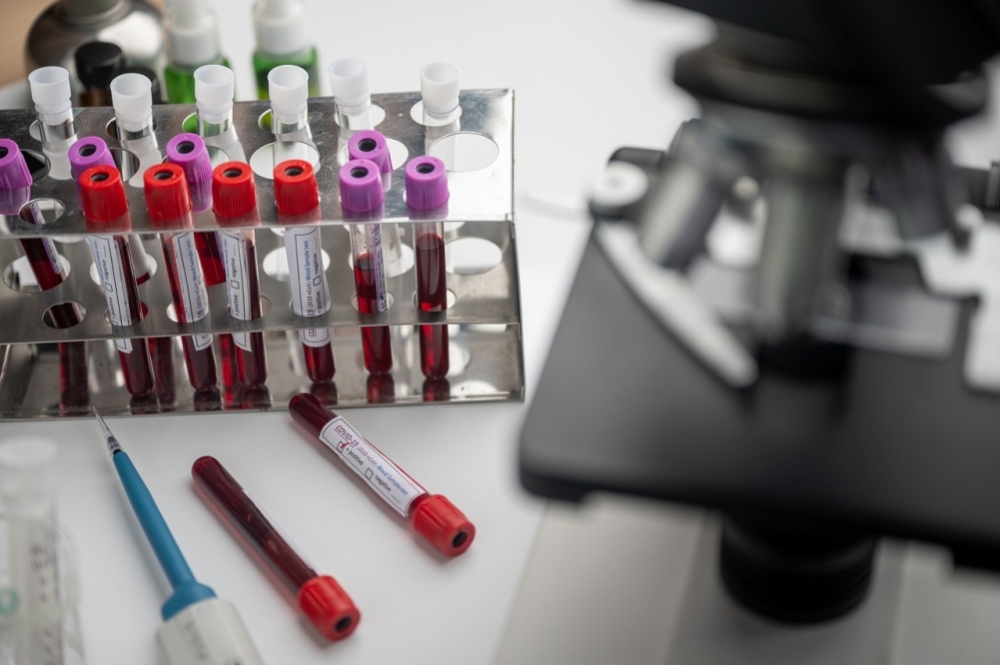
Researchers at the University of São Paulo identified proteins found at augmented levels in the blood plasma of high-risk patients using equipment present in Brazilian hospitals. The result of the test could help physicians make better-targeted decisions.
Analysis of DNA from 1,171 over-sixties living in São Paulo will enable scientists to identify genetic mutations responsible for diseases or important to healthy aging, according to the authors of the study.

In laboratory tests, the material eliminated 79.9% of SARS-CoV-2 particles in three minutes and 99.99% in up to 15 minutes.