


Designed and built by researchers at the Center for Development of Functional Materials, the device is much cheaper than the conventional technology.

Brazilian scientists have developed an innovation that can be used in sensors to monitor brain function with even greater sensitivity than existing devices.
One of the most promising fields is photovoltaics. Prototype perovskite solar cells have been shown to be more efficient than commercial silicon-based cells.

Technology developed by a startup with FAPESP’s support dispenses with manual inspection, diagnosing problems rapidly and accurately, facilitating preventive maintenance, and cutting costs.
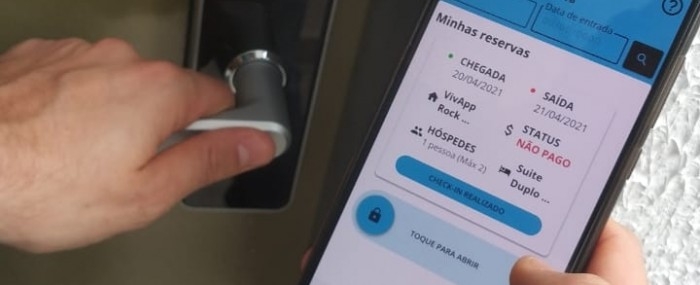
A system for identifying people and controlling access developed by a Brazilian startup lets guests check in remotely and open room doors using smartphones.

The Brazilian startup Crop Biotecnologia has developed a peptide that inhibits bad cholesterol receptors in the liver. The researchers who founded it took part in the 18th edition of the PIPE High Tech Entrepreneurial Training Program.
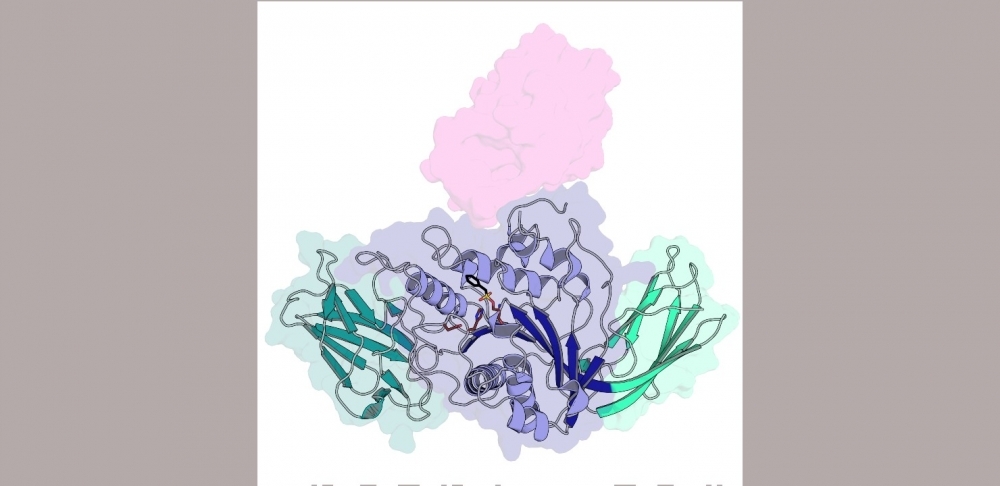
A study led by Brazilian scientists revealed the biological process used by Xanthomonas to weaken the defenses of plants and discovered a novel class of enzyme that can be used to obtain advanced sugars from agroindustrial waste.
The platform is used by several hospitals, has more than 2,500 users, and performs 800 care processes per month on average.
With FAPESP’s support, Cellco created a novel process to produce enzymes used in DNA manipulation in vitro, including cloning, sequencing and mutagenesis, among other techniques, with applications in medical diagnostics and forensic analysis based on genetic material.
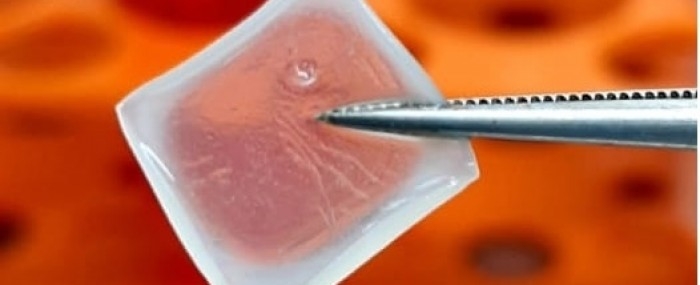
Developed by startup In Situ from stem cells and a hydrogel, the product is bioprinted and placed lightly on the skin.

Non-invasive method uses samples of saliva or other body fluids. The diagnosis can be obtained by means of computational techniques for visualizing data and machine learning.
The platform holds more than 50 million datasets from 800,000 patients in Brazil and has registered some 4,000 downloads by users in 36 countries.

Packaging paper and corrugated cardboard eliminate 99.99% of viral particles in up to 10 minutes of contact.

A solution developed by a startup based in São Paulo state combines fungicidal action and delayed ripening. The researchers who founded the startup took part in the 17th edition of the PIPE High-Tech Entrepreneurial Training Program.

Researchers have completed the first stage of a technical study on the creation of environments designed to foster the development of innovative solutions and creativity in the cities of São Paulo and Campinas.

The system, developed by a startup supported by FAPESP, in partnership with researchers at the University of Campinas, helps plantation managers choose the optimal time to harvest the crop.

Hybrid material made from magnetite nanoparticles sticks to contaminants and can be removed from water by a magnet. The technique can be adapted for use in removing synthetic dyes, drugs, hormones and pesticides.

With support from FAPESP via its program to fund innovative research, the startup has developed a rejuvenating serum based on bioactives obtained from sweet wormwood, a plant used in traditional Chinese medicine.

Inexpensive test is non-invasive and based on detection of bladder cancer biomarkers in urine.

Machines designed and prototyped by Setup Automação with PIPE-FAPESP’s support could come to market costing 25% less than currently available devices.
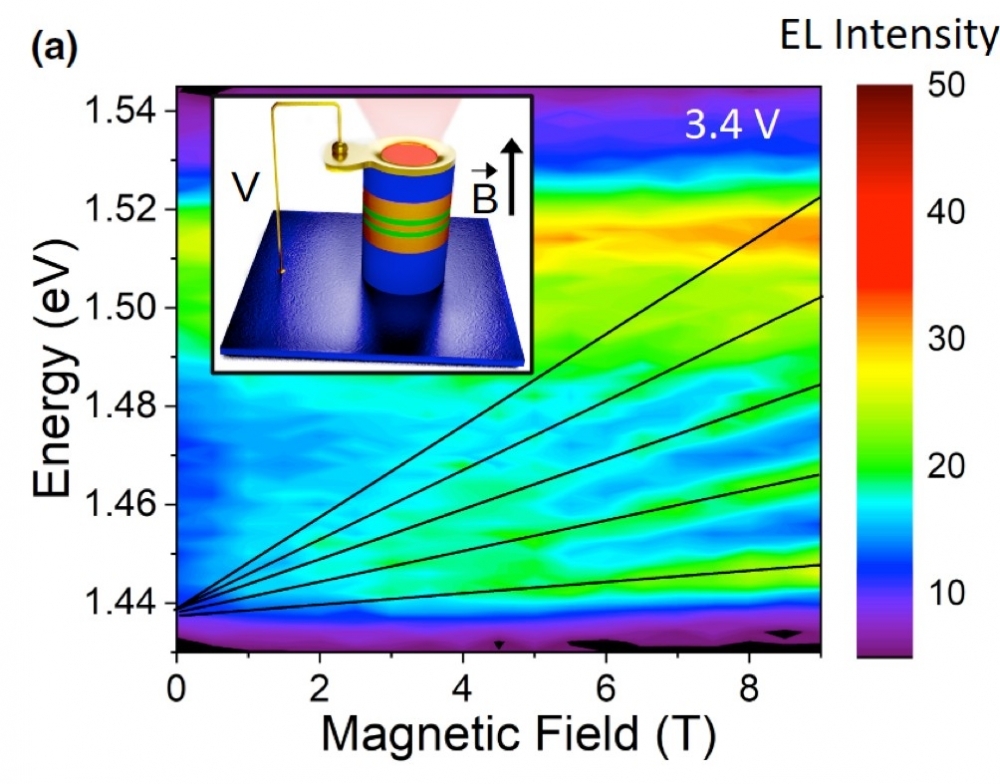
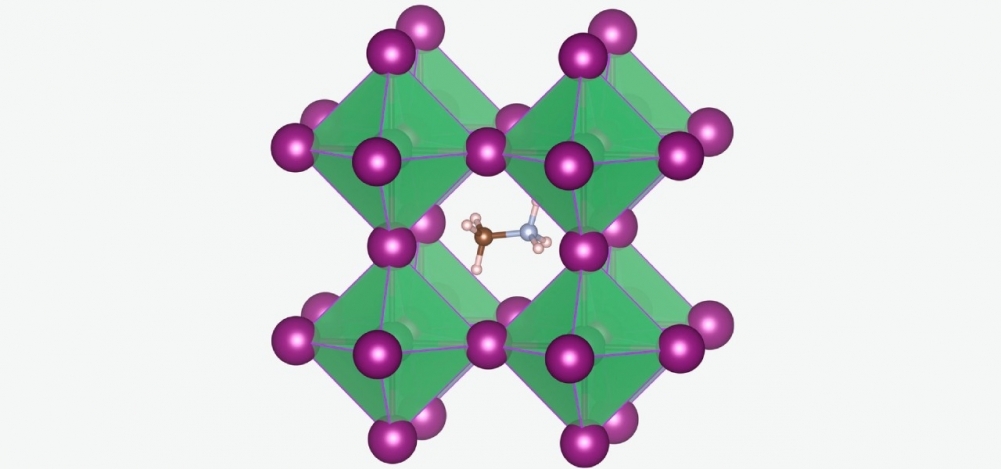
Resonant-tunneling diodes are used in high-frequency oscillators, wave emitters and detectors, logic gates, photodetectors, and optoelectronic circuits. The study was a collaboration between Brazilian and German researchers.

By means of specific biomarkers, a diagnostic test developed by the Brazilian startup Onkos shows whether a lump in the gland is benign or malignant, reducing the risk of unnecessary surgery.

The platform developed by researchers from Brazil and Chile lets users view geolocation of cases, deaths and vaccinations over time.
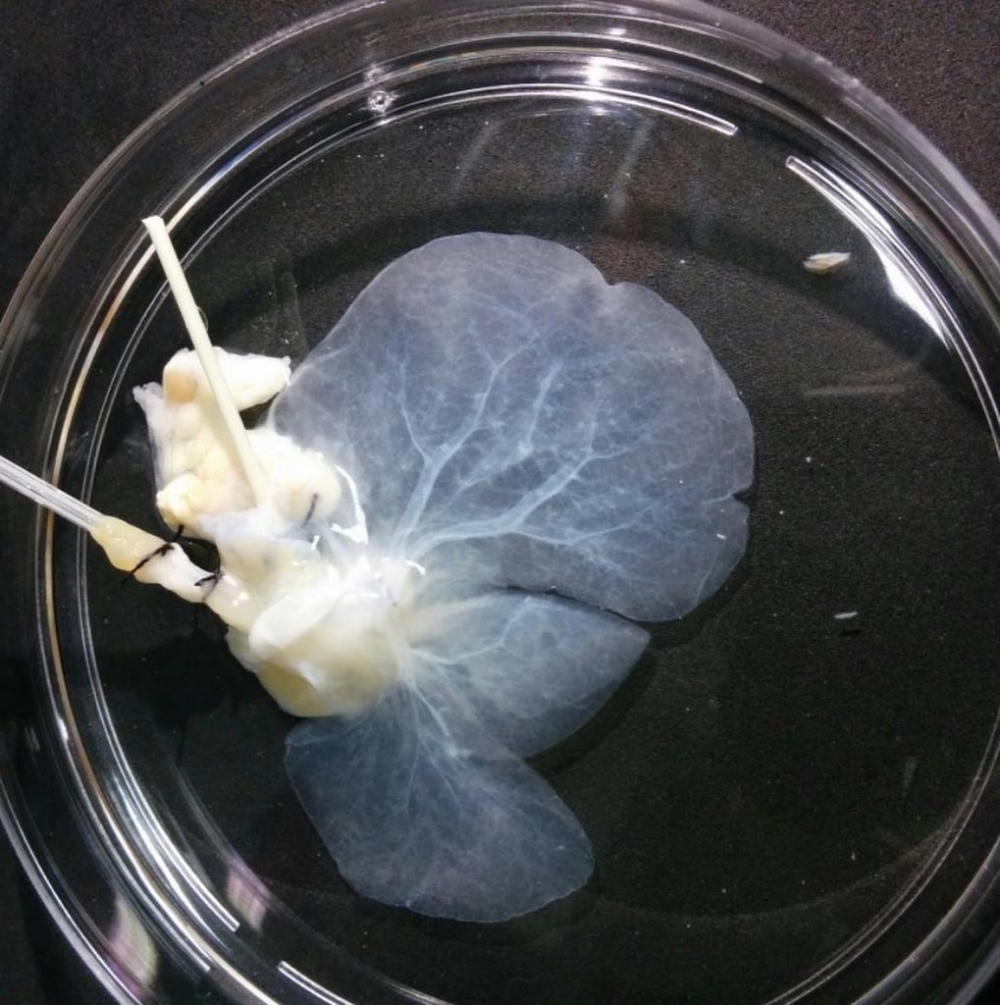
A method created in Brazil by the Human Genome and Stem Cell Research Center could be used for large-scale production of livers for transplantation.
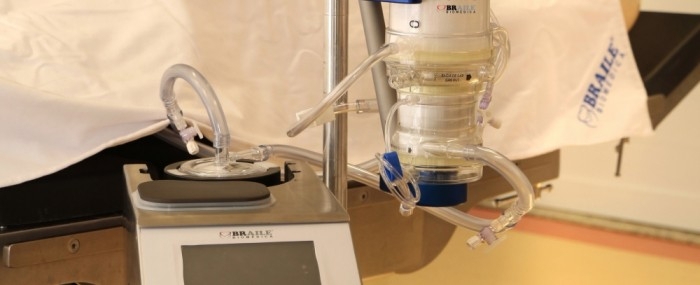
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) can keep patients alive until the disease recedes.