


Agricultural residues already produce 25% of the electricity used by households in the state. The proportion could jump to 70%, according to researchers who took part in an online seminar on the topic.

Operating in the São José dos Campos Technology Park, Autaza’s RIC has an optical system for automotive paint quality inspection using computer vision and artificial intelligence.
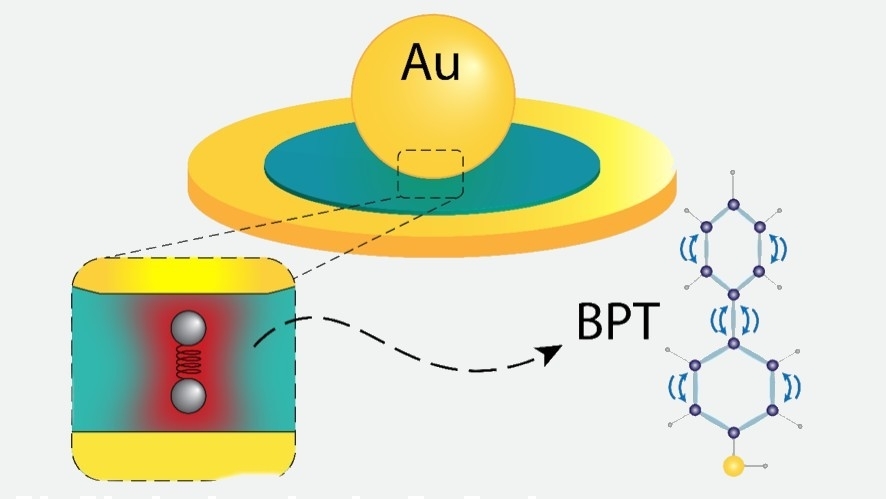
Study by researchers at the University of Campinas published in Physical Review Letters discusses both light dispersion by vibrations inside the device and light dissipation to the exterior, an aspect rarely studied hitherto.
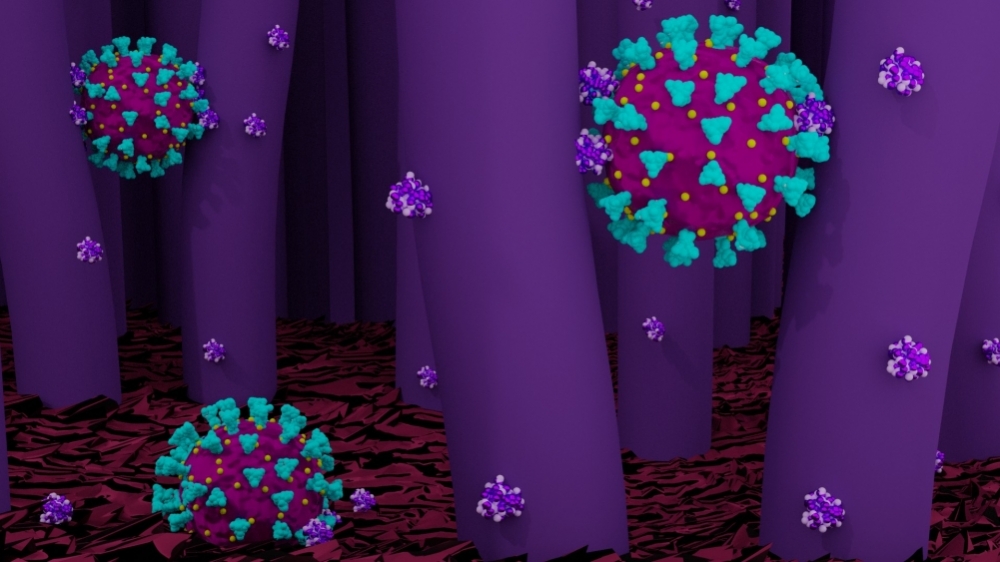

According to a paper by Brazilian researchers published in Nano Today, the spatial arrangement of proteins on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 assures highly efficient interaction with target receptors on human cells.
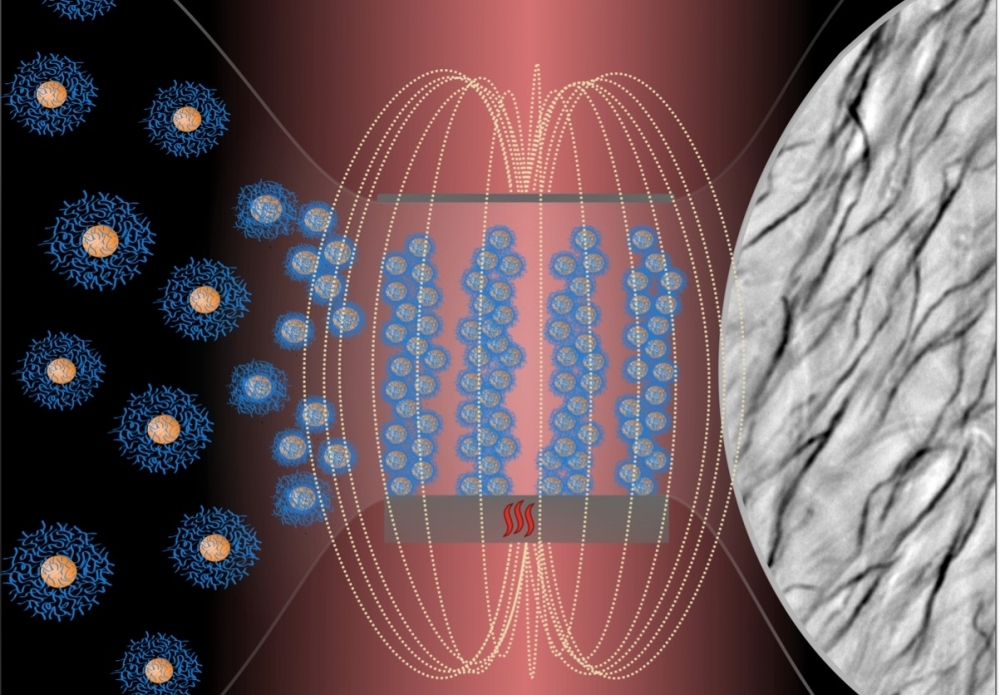
Filaments made of polymer-coated iron oxide nanoparticles are obtained by exposing the material to a magnetic field under controlled temperature. The applications are myriad and include transporting substances into cells or directing fluids.

With FAPESP’s support, Hytron has developed a containerized solution for hydrogen production via ethanol reforming that eliminates the need for shipping by tanker trucks. The equipment can supply the gas to factories and vehicle service stations.
Technology to manage hospital flows is being tested by health units in metropolitan São Paulo.
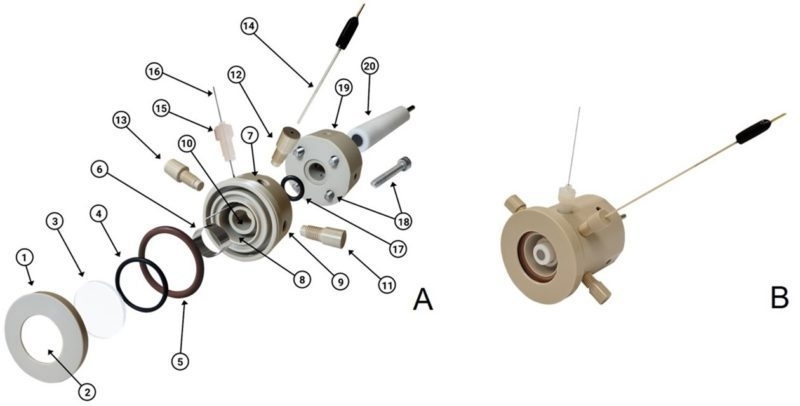
Developed at an Engineering Research Center supported by FAPESP, the novel spectroelectrochemical cell can be used to study the behavior of electrolytes and catalysts by means of X-rays and infrared or even visible light.

The study could help upgrade satellite communications equipment.
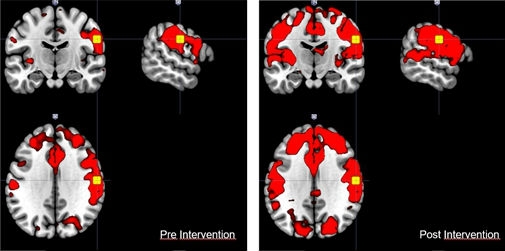
A study performed at one of the Research Centers supported by FAPESP resulted in development of a novel rehabilitation device. The article was recognized as outstanding by the 20th International Conference on Computational Science and its Applications.
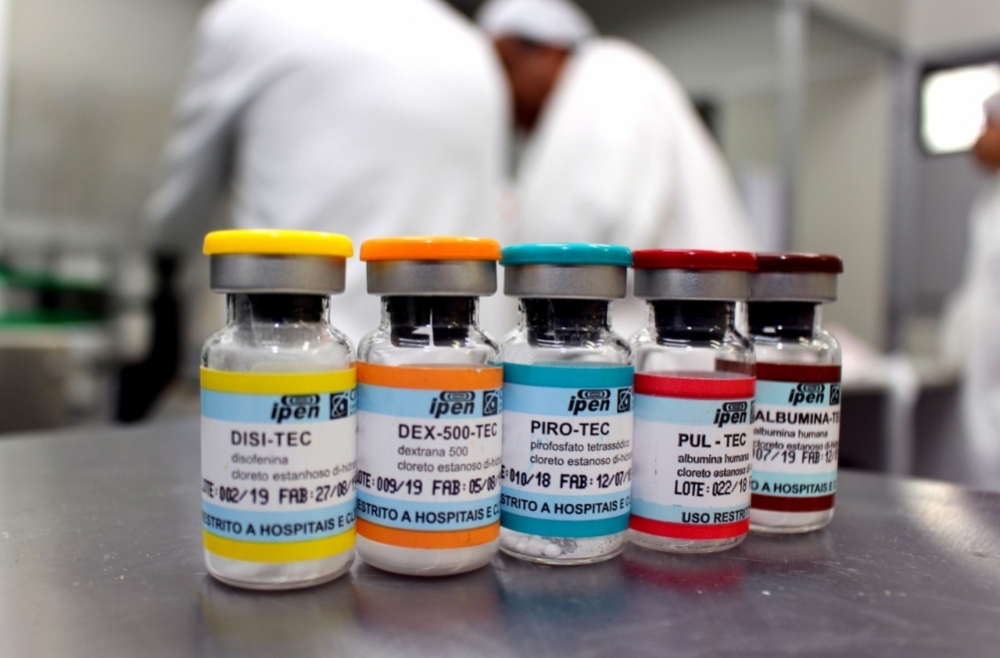

With FAPESP’s support, the Nuclear and Energy Research Institute is assembling a world-class laboratory that associates nanotechnology with radiopharmacy. The aim is to develop new products, mainly for cancer treatment.

Study by FAPESP-Shell Engineering Research Center hosted at University of Campinas set out to develop supercapacitors that store more energy and batteries that charge faster.

In laboratory tests, the material eliminated 79.9% of SARS-CoV-2 particles in three minutes and 99.99% in up to 15 minutes.

Model developed by startup supported by FAPESP enables scientists to assess efficacy and safety of sunscreens and anti-aging products under conditions closely resembling real life.
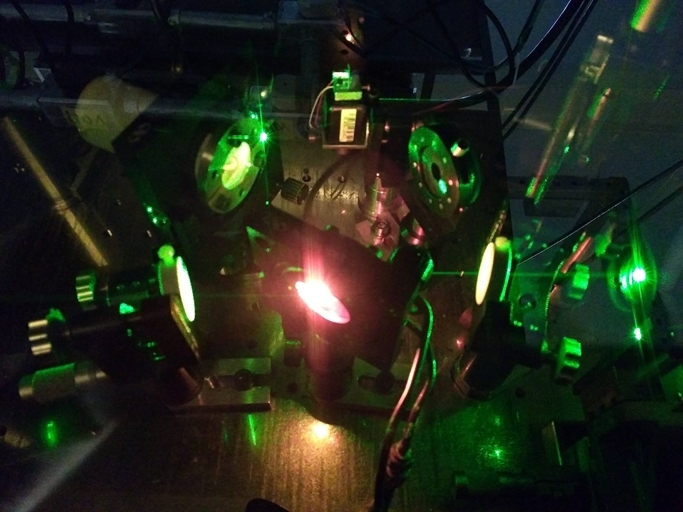

Potential applications of research conducted at the University of São Paulo include high-precision metrology and information encoding.
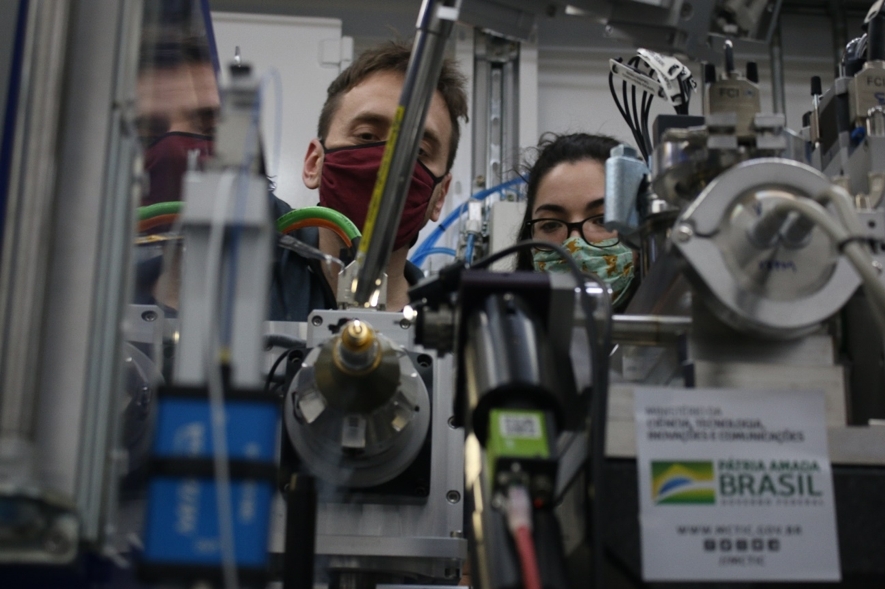

Sirius’s protein crystallography beamline analyzed more than 200 protein crystals from the novel coronavirus as they were exposed to tiny fragments of widely used drugs. If a compound fits perfectly into a target protein, its action can be blocked in the virus.

Devices developed by Brazilian startup BioLambda decontaminate face shields, surfaces, workspaces and air.

The newest Engineering Research Center will initially focus on challenges relating to health, the environment, food production chains, the future of work, and the development of natural language processing tools for Brazilian Portuguese.

Brazilian startup Agrobee signs agreement with Agroven, an investment club run by family farmers who want to promote technological development in the sector.

Laboratory tests showed film containing silver-silica nanoparticles to be capable of eliminating 99.84% of SARS-CoV-2 particles after exposure for two minutes.
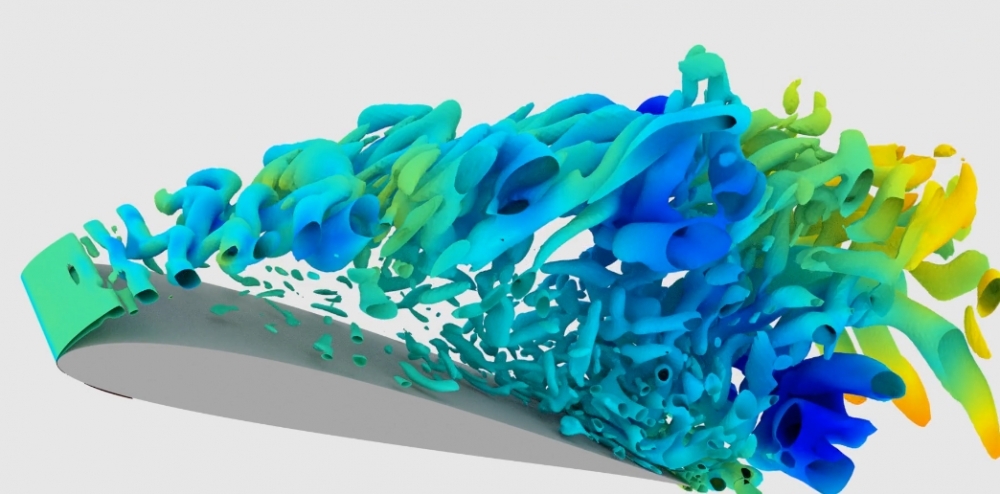
Brazilian researchers studied the morphology of owl wings in search of characteristics that enable these birds to fly silently.

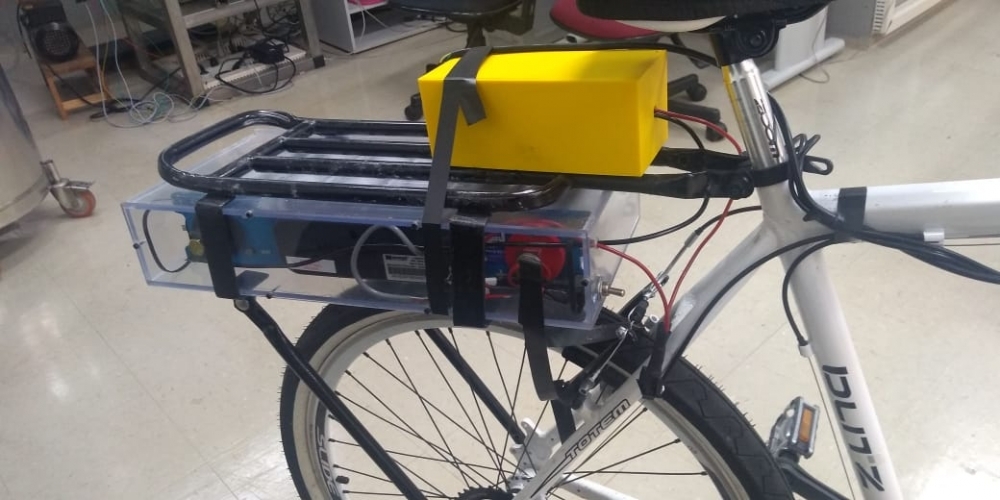
Portable nuclear magnetic resonance device designed with FAPESP’s support will inform consumers regarding value added to beef products.
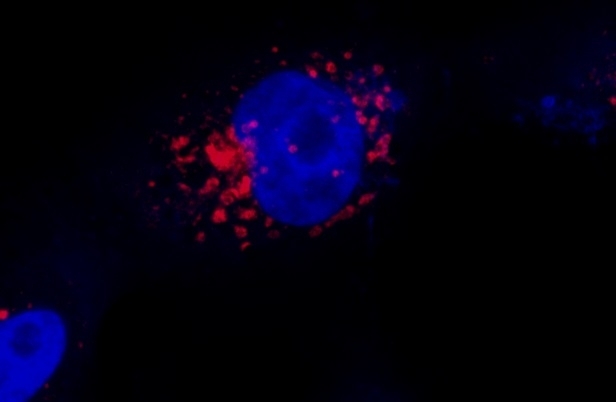
Protocol developed by Brazilian researchers shows SARS-CoV-2 replicating near cell nucleus. Methodology helps scientists understand coronavirus’s action mechanism and could also be used to study other viruses.
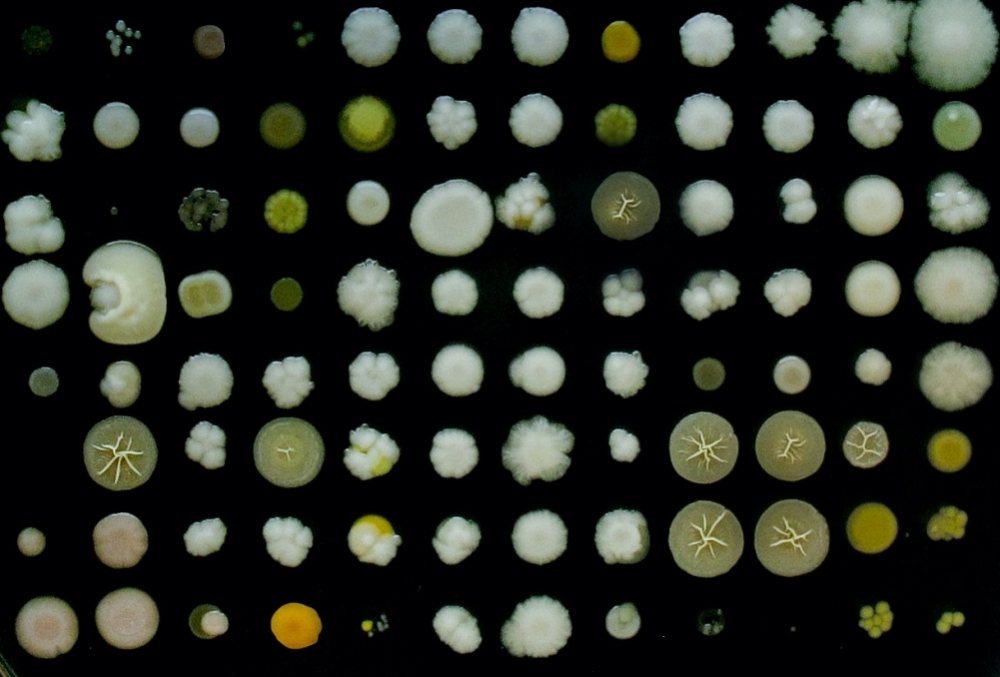

New research field promises to transform food production and treatment of diseases. A global panel of experts unified concepts to define research priorities and offer basis for legislation.

The startup’s founders were researchers at the University of São Paulo and adjusted their marketing strategy to focus on regenerative, veterinary and sports medicine thanks to training provided by PIPE, FAPESP’s program for Innovative Research in Small Business.